Contd…
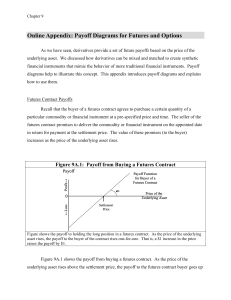
... you might hear somebody say they bought "oil futures", which means the same thing as "oil futures contract". If you want to get really specific, you could say that a futures contract refers only to the specific characteristics of the underlying asset, while "futures" is more general and can also ref ...
... you might hear somebody say they bought "oil futures", which means the same thing as "oil futures contract". If you want to get really specific, you could say that a futures contract refers only to the specific characteristics of the underlying asset, while "futures" is more general and can also ref ...
Answer to PP2001
... PED is the percentage change in the quantity demanded of a product (1) divided by the percentage change in its price (1) Or PED is the responsiveness of demand (1) to a change in price (1). Up to 2 marks for expansion: Its value can range from perfectly inelastic (1) to perfectly elastic (1) inelast ...
... PED is the percentage change in the quantity demanded of a product (1) divided by the percentage change in its price (1) Or PED is the responsiveness of demand (1) to a change in price (1). Up to 2 marks for expansion: Its value can range from perfectly inelastic (1) to perfectly elastic (1) inelast ...
testimony of christine a - North American Securities Administrators
... are exempt from registration or are properly registered. Digital Currency & Cybersecurity Risks: Digital currencies are emerging as trendy way to pay for goods and services. Bitcoin, perhaps the most popular digital currency, was priced at around $10 per unit in early 2013 but peaked at around $1,20 ...
... are exempt from registration or are properly registered. Digital Currency & Cybersecurity Risks: Digital currencies are emerging as trendy way to pay for goods and services. Bitcoin, perhaps the most popular digital currency, was priced at around $10 per unit in early 2013 but peaked at around $1,20 ...
Chapter 5
... Monopoly (ex: utility companies) • One company controls market and selling price • Government approves price changes ...
... Monopoly (ex: utility companies) • One company controls market and selling price • Government approves price changes ...
CLOSED FORM SOLUTION FOR HESTON PDE BY GEOMETRICAL
... volatility. One is going to focus here on relaxing the last assumption by allowing volatility to vary randomly, for the following reason: a well known discrepancy between the Black and Scholes predicted European option prices and market traded options prices, the smile curve, can be accounted for by ...
... volatility. One is going to focus here on relaxing the last assumption by allowing volatility to vary randomly, for the following reason: a well known discrepancy between the Black and Scholes predicted European option prices and market traded options prices, the smile curve, can be accounted for by ...
Absolute Dividends
... correlation, however the implied volatility depends on and therefore intuitively we need to strip off this ...
... correlation, however the implied volatility depends on and therefore intuitively we need to strip off this ...
2 Introduction to Option Management
... USD interest in the savings account and the difference between the 40 USD (initial principal in the savings account) and the stock price is yours to keep. Exercise 2.3. Consider a European call option on a stock with current spot price S0 = 20, dividend D = 2 USD, exercise price K = 18 and time to m ...
... USD interest in the savings account and the difference between the 40 USD (initial principal in the savings account) and the stock price is yours to keep. Exercise 2.3. Consider a European call option on a stock with current spot price S0 = 20, dividend D = 2 USD, exercise price K = 18 and time to m ...
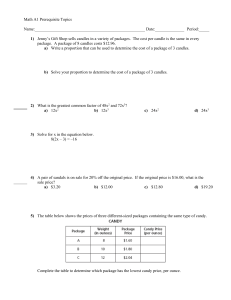
Math A1 Prerequisite Topics
... 8) Renee must solve the equation 4x + 12 = 6x. If she subtracts 4x from the left side of the equation, what should Renee write on the right side of the equation? a) 2 b) 2x c) 10 d) 10x ...
... 8) Renee must solve the equation 4x + 12 = 6x. If she subtracts 4x from the left side of the equation, what should Renee write on the right side of the equation? a) 2 b) 2x c) 10 d) 10x ...