Question Paper
... What is Empirical formula? Give an example for a compound whose Empirical formula and molecular formula are the same. ...
... What is Empirical formula? Give an example for a compound whose Empirical formula and molecular formula are the same. ...
Matter - tompkinsmath
... 1. Ionic- combinations of cations/anions metal/non-metal Ex. sodium chloride (NaCl) 2. Molecular – non-metal / non-metal combinations. Ex. sulfur dioxide - SO2(g) Water → H2O 3. Intermetallic – metal / metal combination ...
... 1. Ionic- combinations of cations/anions metal/non-metal Ex. sodium chloride (NaCl) 2. Molecular – non-metal / non-metal combinations. Ex. sulfur dioxide - SO2(g) Water → H2O 3. Intermetallic – metal / metal combination ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... 71) In an equilibrium reaction A) increasing the amount of one of the products will increase the amount of reactants available. B) decreasing the amount of one of the reactants will increase the amount of product formed. C) the rate of formation of products equals the rate of formation of reactants. ...
... 71) In an equilibrium reaction A) increasing the amount of one of the products will increase the amount of reactants available. B) decreasing the amount of one of the reactants will increase the amount of product formed. C) the rate of formation of products equals the rate of formation of reactants. ...
Strong and weak acids and bases
... groups, COOH): – methanoic acid (CHOOH) – ethanoic (acetic) acid • CH3COOH(l) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3COO-(aq) + H3O+ – carbonic acid: (CO2 in water) • CO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq) ...
... groups, COOH): – methanoic acid (CHOOH) – ethanoic (acetic) acid • CH3COOH(l) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3COO-(aq) + H3O+ – carbonic acid: (CO2 in water) • CO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq) ...
Document
... (B) decreases, decreases (C) increases, decreases (D) decreases, increases (E) More information is needed to answer this question 43. Which of the following is an acid-base neutralization reaction? (A) 2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g) (B) SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO3(g) (C) LiOH(aq) + HNO3(aq ...
... (B) decreases, decreases (C) increases, decreases (D) decreases, increases (E) More information is needed to answer this question 43. Which of the following is an acid-base neutralization reaction? (A) 2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g) (B) SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO3(g) (C) LiOH(aq) + HNO3(aq ...
A Classification of AP Chemistry Reactions
... Hydrogen gas, H2, is an effective reducing agent for some metal oxides. - Hydrogen gas is passed over hot copper (II) oxide. CuO + H2 Cu + H2O Electron Transfer Reactions The first general type of redox reactions are simple electron-transfer equations. These do not involve oxygen or oxyanions. The ...
... Hydrogen gas, H2, is an effective reducing agent for some metal oxides. - Hydrogen gas is passed over hot copper (II) oxide. CuO + H2 Cu + H2O Electron Transfer Reactions The first general type of redox reactions are simple electron-transfer equations. These do not involve oxygen or oxyanions. The ...
Effects of antioxidants for the degradation of flame
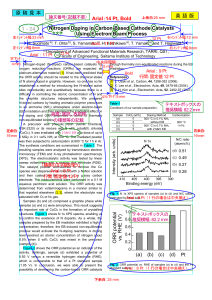
... 6 MGy in 0.1 vol% NH3 at 500 °C. The irradiated powder was then subjected to carbonization at 800 °C for 1 h in Ar. The synthesis conditions are summarized in Table 1. The resulting samples were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The electr ...
... 6 MGy in 0.1 vol% NH3 at 500 °C. The irradiated powder was then subjected to carbonization at 800 °C for 1 h in Ar. The synthesis conditions are summarized in Table 1. The resulting samples were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The electr ...
Document
... The self-ionization of water (also autoionization of water, and autodissociation of water) is an ionization reaction in pure water or an aqueous solution, in which a water molecule (H2O) loses the nucleus of one of its hydrogen atoms to become a hydroxide ion (OH−). The hydrogen nucleus H+, immediat ...
... The self-ionization of water (also autoionization of water, and autodissociation of water) is an ionization reaction in pure water or an aqueous solution, in which a water molecule (H2O) loses the nucleus of one of its hydrogen atoms to become a hydroxide ion (OH−). The hydrogen nucleus H+, immediat ...
2 - CronScience
... Reactants must be an element and a compound. Products will be a different element and a different compound. Na + KCl K + NaCl (Cations switched) (Anions switched) F2 + LiCl LiF + Cl2 ...
... Reactants must be an element and a compound. Products will be a different element and a different compound. Na + KCl K + NaCl (Cations switched) (Anions switched) F2 + LiCl LiF + Cl2 ...
Chapter 13: Properties of Solutions
... Be careful to distinguish the physical process of solution formation from chemical reactions that lead to a solution. For example, Ni(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → NiCl2(aq) + H2(g) ...
... Be careful to distinguish the physical process of solution formation from chemical reactions that lead to a solution. For example, Ni(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → NiCl2(aq) + H2(g) ...
solution is a solution that contains the maximum amount of solute
... Draw Lewis structures for each of the following chemical formulas. In each case, indicate the molecule’s (or ion’s) molecular geometry, and whether it is polar or non-polar [15 points/5 each] ...
... Draw Lewis structures for each of the following chemical formulas. In each case, indicate the molecule’s (or ion’s) molecular geometry, and whether it is polar or non-polar [15 points/5 each] ...
Regents Chemistry
... amount of solute at a given temp or how much solute will dissolve in a given amount of water o be able to predict the amount of solute that will crystallize (precipitate) from solution when it is chilled o use Table G to predict if a solution is saturated, unsaturated or supersaturated Determine whe ...
... amount of solute at a given temp or how much solute will dissolve in a given amount of water o be able to predict the amount of solute that will crystallize (precipitate) from solution when it is chilled o use Table G to predict if a solution is saturated, unsaturated or supersaturated Determine whe ...
Chemical Changes and Structure Homework Booklet
... 12Mg are two different kinds of magnesium atom. a. What word is used to describe these types of atoms? b. Explain why they can be regarded as atoms of the same element? c. The relative atomic mass of magnesium is 24.3. What does this tell you about the relative amounts of each atom? An atom has atom ...
... 12Mg are two different kinds of magnesium atom. a. What word is used to describe these types of atoms? b. Explain why they can be regarded as atoms of the same element? c. The relative atomic mass of magnesium is 24.3. What does this tell you about the relative amounts of each atom? An atom has atom ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.