Barnard Castle School Chemistry Department
... A solute dissolves in a solvent to form a solution. A solution is a mixture of a solute and a solvent, and is clear in appearance. An example of a common solution is sea water. The solute is salt (sodium chloride) and the solvent is water. A substance is soluble in a solvent if it dissolves in it, b ...
... A solute dissolves in a solvent to form a solution. A solution is a mixture of a solute and a solvent, and is clear in appearance. An example of a common solution is sea water. The solute is salt (sodium chloride) and the solvent is water. A substance is soluble in a solvent if it dissolves in it, b ...
Chemistry Review2
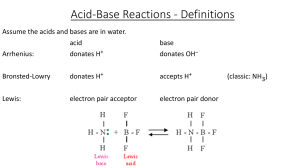
... will take the H+. Mixing acid and bases will create water and a salt. Sometimes acids and bases are reactants, conjugate bases and conjugate acids are products. HCO3-(aq) + H20(l) CO3 -2 (aq) + H3O+ (aq), Identify the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base. Acids and Bases are on a pH scale ...
... will take the H+. Mixing acid and bases will create water and a salt. Sometimes acids and bases are reactants, conjugate bases and conjugate acids are products. HCO3-(aq) + H20(l) CO3 -2 (aq) + H3O+ (aq), Identify the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base. Acids and Bases are on a pH scale ...
Role of Water as a Solvent
... 4 Ag(CN)2-(aq) + OH -(aq) Add 4 OH- to balance charge. Since there hydrogen is absent on the reactant side, add 2 H2O to balance the hydrogen and oxygen. 4 Ag(s) + 8 CN -(aq) + O2 (g) + 2 H2O(l) ...
... 4 Ag(CN)2-(aq) + OH -(aq) Add 4 OH- to balance charge. Since there hydrogen is absent on the reactant side, add 2 H2O to balance the hydrogen and oxygen. 4 Ag(s) + 8 CN -(aq) + O2 (g) + 2 H2O(l) ...
Honors Chemistry
... 10. Give the different waves of the magnetic spectrum. 11. Which wave has more energy: red or blue? Short or long? Microwave or x-ray? 12. What does Bohr’s Model say about the hydrogen atom? 13. What does it mean when an electron is excited? What happens when the excited electron returns to the grou ...
... 10. Give the different waves of the magnetic spectrum. 11. Which wave has more energy: red or blue? Short or long? Microwave or x-ray? 12. What does Bohr’s Model say about the hydrogen atom? 13. What does it mean when an electron is excited? What happens when the excited electron returns to the grou ...
Chemistry II Exams and Keys 2014 Season
... 11. A cylinder of unknown volume contains neon gas, Ne(g), at 4.0 atm and 400 K. The neon gas is then transferred to a 10.0 L gas cylinder containing Ar(g), at 6.0 atm and 400 K. If the final total pressure at 400 K is 9.0 atm, then what is the volume of the cylinder that initially contained the neo ...
... 11. A cylinder of unknown volume contains neon gas, Ne(g), at 4.0 atm and 400 K. The neon gas is then transferred to a 10.0 L gas cylinder containing Ar(g), at 6.0 atm and 400 K. If the final total pressure at 400 K is 9.0 atm, then what is the volume of the cylinder that initially contained the neo ...
6.5 Half-reactions and electrodes
... equilibrium can do electrical work as the reaction drives electrons through an external circuit • With a large potential difference, a given number of electrons travelling can do a larger amount of electrical work. • A cell in which the overall reaction is at equilibrium can do no work with zero p ...
... equilibrium can do electrical work as the reaction drives electrons through an external circuit • With a large potential difference, a given number of electrons travelling can do a larger amount of electrical work. • A cell in which the overall reaction is at equilibrium can do no work with zero p ...
Chapter 8
... Steps for Balancing Equations • Identify the names of reactants and products, and write a word equation. • Write a formula equation by substituting correct formulas for the names of the reactants and the products. • Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. • Count ...
... Steps for Balancing Equations • Identify the names of reactants and products, and write a word equation. • Write a formula equation by substituting correct formulas for the names of the reactants and the products. • Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. • Count ...
Chemical Equations Worksheet (Oct 2007)
... Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the word equations below. Include states. 1. Aqueous sodium chloride reacts with aqueous lead (II) nitrate to yield a lead (II) chloride precipitate and aqueous sodium nitrate ...
... Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the word equations below. Include states. 1. Aqueous sodium chloride reacts with aqueous lead (II) nitrate to yield a lead (II) chloride precipitate and aqueous sodium nitrate ...
GCE Chemistry Question Paper Unit 05 - Energetics, Redox
... The diagram shows a non-rechargeable cell that can be used to power electronic devices. The relevant half-equations for this cell are equations 2 and 4 in the table above. ...
... The diagram shows a non-rechargeable cell that can be used to power electronic devices. The relevant half-equations for this cell are equations 2 and 4 in the table above. ...
Lecture 4
... Solutions in which water is the dissolving medium are called aqueous solutions. There are three major types of chemical processes occurring in aqueous solutions: precipitation reactions acid-base reactions redox reactions ...
... Solutions in which water is the dissolving medium are called aqueous solutions. There are three major types of chemical processes occurring in aqueous solutions: precipitation reactions acid-base reactions redox reactions ...
Hydrogen peroxide solution about 30% w/v AnalaR
... Wear appropriate protective clothing. If local regulations permit, mop up with plenty of water and run to waste, diluting greatly with running water. Otherwise absorb on an inert absorbent, transfer to container and arrange removal by disposal company. Ventilate area to dispel residual vapour. For l ...
... Wear appropriate protective clothing. If local regulations permit, mop up with plenty of water and run to waste, diluting greatly with running water. Otherwise absorb on an inert absorbent, transfer to container and arrange removal by disposal company. Ventilate area to dispel residual vapour. For l ...
3(aq)
... with aqueous copper (II) chloride. 1. NaOH(aq) + CuCl2(aq) ? 2. Solubility rules show that NaCl is soluble, which means it will remain as ions in solution 3. Solubility rules show that Cu(OH)2 is insoluble, which means it will come “out” of solution and form a precipitate. 2NaOH(aq) + CuCl2(aq) ...
... with aqueous copper (II) chloride. 1. NaOH(aq) + CuCl2(aq) ? 2. Solubility rules show that NaCl is soluble, which means it will remain as ions in solution 3. Solubility rules show that Cu(OH)2 is insoluble, which means it will come “out” of solution and form a precipitate. 2NaOH(aq) + CuCl2(aq) ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context
... 57) Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize? A) ionic bonds B) both hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds C) polar covalent bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) both polar covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds 58) Temperature usually increases when water condenses. Which behavior of water is most directl ...
... 57) Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize? A) ionic bonds B) both hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds C) polar covalent bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) both polar covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds 58) Temperature usually increases when water condenses. Which behavior of water is most directl ...
A Review of High School Chemistry
... What is the big deal with acids and bases? Again, it is because we are working with water, which, as we will see, has its own chemistry that produces ions like H+ and OH-, and which as everyone knows, are what Arrhenius called acids and bases. Consequently, we will spend a lot of time looking at wha ...
... What is the big deal with acids and bases? Again, it is because we are working with water, which, as we will see, has its own chemistry that produces ions like H+ and OH-, and which as everyone knows, are what Arrhenius called acids and bases. Consequently, we will spend a lot of time looking at wha ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.