Review for Physical Science Test #2
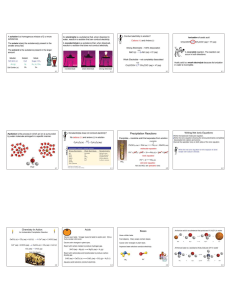
... To tell a strong acid from a weak acid To tell an acid from a neutral solution To tell a strong base from a weak base To create a temporary tattoo on your little sister’s face right before picture day. ...
... To tell a strong acid from a weak acid To tell an acid from a neutral solution To tell a strong base from a weak base To create a temporary tattoo on your little sister’s face right before picture day. ...
Non-Equilibrium Hysteresis and Wien Effect Water Dissociation at a
... surface group of an anion exchange membrane but the proton is soon released from the functional group, resulting in a net generation of both mobile hydroxyl and proton ions. Zabolotski et al.12 have recently observed that phosphoric acid group cation exchange membranes also intensely split water. If ...
... surface group of an anion exchange membrane but the proton is soon released from the functional group, resulting in a net generation of both mobile hydroxyl and proton ions. Zabolotski et al.12 have recently observed that phosphoric acid group cation exchange membranes also intensely split water. If ...
Final exam 2007
... Note: There are 18 questions in this exam. Fill in your answer in the blank space provided immediately following each question. 1/2 point will be subtracted every time you report a numerical result with an incorrect number of significant figures. A Data Sheet with useful information is at the end. ...
... Note: There are 18 questions in this exam. Fill in your answer in the blank space provided immediately following each question. 1/2 point will be subtracted every time you report a numerical result with an incorrect number of significant figures. A Data Sheet with useful information is at the end. ...
am 06 chemistry - University of Malta
... 6. Fill in the blanks in the following table using any of the following chemical substances. Each property may fit one or more substances in which case include all correct answers in the table. Each substance may be used once or more than once or not at all. NaNO3, C60, BaO2, CaCO3, BeO, AlCl3, SiCl ...
... 6. Fill in the blanks in the following table using any of the following chemical substances. Each property may fit one or more substances in which case include all correct answers in the table. Each substance may be used once or more than once or not at all. NaNO3, C60, BaO2, CaCO3, BeO, AlCl3, SiCl ...
Acids
... 5) Stomach produces HCl acid So, our pH is usually tending to _____ …a condition called ____________ ...
... 5) Stomach produces HCl acid So, our pH is usually tending to _____ …a condition called ____________ ...
Topic 3 Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Bonding and
... • This Idea was developed by Arrhenius by looking at the conductivity of solutions prepared by dissolving “ionic compounds” in water (not believed at first, but got the 1903 Nobel prize) ...
... • This Idea was developed by Arrhenius by looking at the conductivity of solutions prepared by dissolving “ionic compounds” in water (not believed at first, but got the 1903 Nobel prize) ...
3. Chemical changes and Structure Unit Questions
... o The ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms o You can have second and third ionisation energies, but note that if there is a full outer shell the atom will not want to lose another electron making the energy very high. o The general f ...
... o The ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms o You can have second and third ionisation energies, but note that if there is a full outer shell the atom will not want to lose another electron making the energy very high. o The general f ...
Fe(H2O)63+ + H2O → ← H3O+ + Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+
... An increase in temperature increases the solubility of a gas in a liquid. The change of solubility with temperature is the same for all substances. The solubility of a liquid in a liquid is independent of temperature. The solubility of most solids in water increases with increasing temperature. The ...
... An increase in temperature increases the solubility of a gas in a liquid. The change of solubility with temperature is the same for all substances. The solubility of a liquid in a liquid is independent of temperature. The solubility of most solids in water increases with increasing temperature. The ...
1.1 Safety in the Science Classroom
... Compounds come in two basic types: covalent and ionic. To determine whether a compound is covalent or ionic, the periodic table is required. ...
... Compounds come in two basic types: covalent and ionic. To determine whether a compound is covalent or ionic, the periodic table is required. ...
Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions
... The only way to be certain what the products of a chemical reaction are is to carry out the reaction in the laboratory There are millions of compounds that will produce endless chemical reactions, therefore not all chemical reactions can be carried out in the laboratory A system is used to cla ...
... The only way to be certain what the products of a chemical reaction are is to carry out the reaction in the laboratory There are millions of compounds that will produce endless chemical reactions, therefore not all chemical reactions can be carried out in the laboratory A system is used to cla ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 63. A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. ...
... 63. A 2.0g sample of SX6 (g) has a volume of 329.5 cm3 at 1.00 atm and 20oC. Identify the element ‘X’. Name the compound. ...
Rate and Equilibrium
... A dynamic equilibrium exists when two reversible or opposing is continually taking place on the molecular level but that are balanced. It can further divide into physical equilibria and chemical equilbria The most important types of physical equilibria are phase equilibria. The equilibria existing b ...
... A dynamic equilibrium exists when two reversible or opposing is continually taking place on the molecular level but that are balanced. It can further divide into physical equilibria and chemical equilbria The most important types of physical equilibria are phase equilibria. The equilibria existing b ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.