Modern Chemistry
... 2. Give an example of a chemical or physical process that illustrates the law of conservation of mass. ...
... 2. Give an example of a chemical or physical process that illustrates the law of conservation of mass. ...
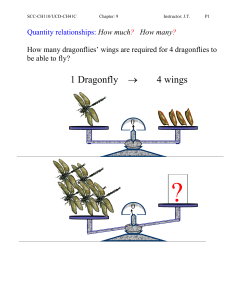
Quantity relationships: How much
... Percent Yield: The calculated amount of product if is based on the assumption that all of the reactant is converted into product is called the theoretical yield. In laboratory or in industrial production, the actual amount of product isolated from a reaction is usually less than the theoretical yiel ...
... Percent Yield: The calculated amount of product if is based on the assumption that all of the reactant is converted into product is called the theoretical yield. In laboratory or in industrial production, the actual amount of product isolated from a reaction is usually less than the theoretical yiel ...
Studies Regarding the Nickel Electrodeposition from
... have been reported, including the class of the so-called “ionic liquids”, defined as “ionic materials in liquid state for temperatures lower than 100oC” (Endres et al., 2008; Wasserscheid & Welton, 2007). The ionic liquids have some properties which make them adequate as metal electrodeposition elec ...
... have been reported, including the class of the so-called “ionic liquids”, defined as “ionic materials in liquid state for temperatures lower than 100oC” (Endres et al., 2008; Wasserscheid & Welton, 2007). The ionic liquids have some properties which make them adequate as metal electrodeposition elec ...
Kinetic Assay of Human Pepsin with Albumin
... one-to-one molar ratio. The value of k, the stability constant, was 3.72 x i0, which indicates that very little free dye or albumin is present when the two compounds are allowed to react in unimolar proportions. One of the curves is illustrated in Figure 1. Spectral properties of the complex. In Fig ...
... one-to-one molar ratio. The value of k, the stability constant, was 3.72 x i0, which indicates that very little free dye or albumin is present when the two compounds are allowed to react in unimolar proportions. One of the curves is illustrated in Figure 1. Spectral properties of the complex. In Fig ...
COMPETITION PTOBLEMS 1
... were often available in a brief form and necessary extent only, just for the needs of members of the International Jury. Some practical problems, in which experimental results and relatively simply calculations are required, have not been accompanied with their solutions. Recalculations of the solut ...
... were often available in a brief form and necessary extent only, just for the needs of members of the International Jury. Some practical problems, in which experimental results and relatively simply calculations are required, have not been accompanied with their solutions. Recalculations of the solut ...
Ternary nucleation of inorganic acids, ammonia, and water
... 共HCl兲–ammonia10 and water–sulfuric acid–methane sulfonic acid (CH3 SO3 H or MSA兲11 vapors has been done during the last decade. All these studies suffer from differences both in the thermodynamic modeling and the treatment of nucleation kinetics. Therefore, a reliable comparison between the above me ...
... 共HCl兲–ammonia10 and water–sulfuric acid–methane sulfonic acid (CH3 SO3 H or MSA兲11 vapors has been done during the last decade. All these studies suffer from differences both in the thermodynamic modeling and the treatment of nucleation kinetics. Therefore, a reliable comparison between the above me ...
Gas/particle partitioning of water-soluble organic aerosol in Atlanta
... for secondary organic gases and particles in Atlanta, but the relatively modest enhancement (∼20%) over pre-sunrise concentrations indicates a substantial regional WSOC background and a relatively long lifetime of both classes of material. This is consistent with the findings of Weber et al. (2007), ...
... for secondary organic gases and particles in Atlanta, but the relatively modest enhancement (∼20%) over pre-sunrise concentrations indicates a substantial regional WSOC background and a relatively long lifetime of both classes of material. This is consistent with the findings of Weber et al. (2007), ...
Chm 2
... b. same number of each kind of atom appears in the reactants and in the products. c. products and reactants are the same chemicals. d. subscripts of the reactants equal the subscripts of the products. 9. In the word equation, sodium oxide + water sodium hydroxide, the formula for sodium hydroxide ...
... b. same number of each kind of atom appears in the reactants and in the products. c. products and reactants are the same chemicals. d. subscripts of the reactants equal the subscripts of the products. 9. In the word equation, sodium oxide + water sodium hydroxide, the formula for sodium hydroxide ...
1999 U. S. NATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD
... 11. What is the coefficient for H +(aq) when the equation is balanced with whole number coefficients? 5. Which solid reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid at 25 ˚C to produce a gas that is more dense than air? (A) Zn ...
... 11. What is the coefficient for H +(aq) when the equation is balanced with whole number coefficients? 5. Which solid reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid at 25 ˚C to produce a gas that is more dense than air? (A) Zn ...
Date: 16 / 01 / 2014 - Qatar University QSpace
... Figure 4.2 Adsorption isotherm of Cu-ZSM5 catalyst ...................................................... 51 Figure 4.3 Illustration of how SEM works...................................................................... 52 Figure 4.4 SEM scan of Cu-ZSM5............................................... ...
... Figure 4.2 Adsorption isotherm of Cu-ZSM5 catalyst ...................................................... 51 Figure 4.3 Illustration of how SEM works...................................................................... 52 Figure 4.4 SEM scan of Cu-ZSM5............................................... ...
View
... The dihedral angles between the triazine (TZ) ring and the PQO groups, which mainly characterize the differences between the four energy minima are listed in Table 1. They show the same trend as the experimental values (vide supra), since there are always two rather close values which are largely sup ...
... The dihedral angles between the triazine (TZ) ring and the PQO groups, which mainly characterize the differences between the four energy minima are listed in Table 1. They show the same trend as the experimental values (vide supra), since there are always two rather close values which are largely sup ...
Stoichiometric Calculations
... A. How many moles of silver are needed to react with 40 moles of nitric acid? B. From the amount of nitric acid given in Part A, how many moles of silver nitrate will be produced? C. From the amount of nitric acid given in Part A, how many moles of water will be produced? D. From the amount o ...
... A. How many moles of silver are needed to react with 40 moles of nitric acid? B. From the amount of nitric acid given in Part A, how many moles of silver nitrate will be produced? C. From the amount of nitric acid given in Part A, how many moles of water will be produced? D. From the amount o ...
chemical equilibrium type 1
... Changing concentration or pressure upsets an equilibrium because the reaction quotient is shifted away from the equilibrium value. Changing the temperature of a system at equilibrium has a different effect: A change in temperature changes the value of the equilibrium constant. However, we can predic ...
... Changing concentration or pressure upsets an equilibrium because the reaction quotient is shifted away from the equilibrium value. Changing the temperature of a system at equilibrium has a different effect: A change in temperature changes the value of the equilibrium constant. However, we can predic ...
2 H 2
... of product is the limiting reactant. 3. The number of moles of product produced by the limiting reactant is ALL the product possible. There is no more limiting reactant left. ...
... of product is the limiting reactant. 3. The number of moles of product produced by the limiting reactant is ALL the product possible. There is no more limiting reactant left. ...
Stoichiometry Worksheet
... 7. Molten iron and carbon monoxide are produced in a blast furnace by the reaction of iron(III) oxide and coke (pure carbon). If 25.0 kilograms of pure Fe2O3 is used, how many kilograms of iron can be produced? The reaction is: Fe2O3 + 3 C 2 Fe + 3 CO ...
... 7. Molten iron and carbon monoxide are produced in a blast furnace by the reaction of iron(III) oxide and coke (pure carbon). If 25.0 kilograms of pure Fe2O3 is used, how many kilograms of iron can be produced? The reaction is: Fe2O3 + 3 C 2 Fe + 3 CO ...
Objectives - hartman
... • The limiting reactant is the reactant that limits the amount of the other reactant that can combine and the amount of product that can form in a chemical reaction. • The excess reactant is the substance that is not used up completely in a reaction. ...
... • The limiting reactant is the reactant that limits the amount of the other reactant that can combine and the amount of product that can form in a chemical reaction. • The excess reactant is the substance that is not used up completely in a reaction. ...
1 Solid State - Unique Solutions
... negative charges hence, the molecule arrange themselves in such a way that opposite charges of neighbouring molecules are brought together. (b) Non-polar molecular solids : Crystalline solids in which the constituent particles are either atoms like those of noble gases or non-polar molecules. e.g. s ...
... negative charges hence, the molecule arrange themselves in such a way that opposite charges of neighbouring molecules are brought together. (b) Non-polar molecular solids : Crystalline solids in which the constituent particles are either atoms like those of noble gases or non-polar molecules. e.g. s ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.