Chapter 6 - semo.edu
... if they are innocent victims. Derogating victims by dehumanizing them may lead to a continuation or escalation of violence against them. ...
... if they are innocent victims. Derogating victims by dehumanizing them may lead to a continuation or escalation of violence against them. ...
Discussion 1: Theory - UCI Social Sciences
... information that increases dissonance are likely to discount that information, either by ignoring it, misinterpreting it, or denying it. ...
... information that increases dissonance are likely to discount that information, either by ignoring it, misinterpreting it, or denying it. ...
Soc213(001) Social Deviance Bogart Test01A 02/15/00
... Cloward argued that Merton (in his anomie model) erred in failing to pay adequate attention to differential . income B. motivation, C. legitimate opportunities generally, D. illegitimate opportunities generally, E. marginality. ...
... Cloward argued that Merton (in his anomie model) erred in failing to pay adequate attention to differential . income B. motivation, C. legitimate opportunities generally, D. illegitimate opportunities generally, E. marginality. ...
The philosophical commitments and disputes which inform
... subject to, empirical testing. Hence either empirical verification, or more usually falsification, is the key to all scientific research. 2. Positivists believe that observation of the empirical world - through our senses - provides the only foundation for knowledge. This entails the claim that such ...
... subject to, empirical testing. Hence either empirical verification, or more usually falsification, is the key to all scientific research. 2. Positivists believe that observation of the empirical world - through our senses - provides the only foundation for knowledge. This entails the claim that such ...
Explain the formation of stereotypes and their effect on behavior.
... • Placing one’s own group at the center ...
... • Placing one’s own group at the center ...
Prejudice and discrimination - gleneaglespsych1-2
... who had never heard of Tony Abbott so you might conclude that all blondes are naïve and do not care about politics. You might not consider that she has been out of the country for 2 years and this is her first weekend back! ...
... who had never heard of Tony Abbott so you might conclude that all blondes are naïve and do not care about politics. You might not consider that she has been out of the country for 2 years and this is her first weekend back! ...
Chapter 5: Interaction, Groups, and Organizations: Connections that
... Role strain is tension between roles within one status Role conflict is conflict between the roles of two or more ...
... Role strain is tension between roles within one status Role conflict is conflict between the roles of two or more ...
implicit nationalism as system justification: the case
... power over other nations directly helps to ensure national sovereignty. In a series of studies, Carter and colleagues (2009) found an implicit link between America and the concept of power, demonstrating that the concept of power was both more accessible and more desirable after exposure to American ...
... power over other nations directly helps to ensure national sovereignty. In a series of studies, Carter and colleagues (2009) found an implicit link between America and the concept of power, demonstrating that the concept of power was both more accessible and more desirable after exposure to American ...
What is a group?
... • Norms define and prescribe how one should behave (using one’s perceptions, feelings, attitudes, and behaviours) as a member of a particular social group — they provide a frame of reference for our behaviour. • Norms have a powerful, long-term, internalized effect on our behaviour, influencing what ...
... • Norms define and prescribe how one should behave (using one’s perceptions, feelings, attitudes, and behaviours) as a member of a particular social group — they provide a frame of reference for our behaviour. • Norms have a powerful, long-term, internalized effect on our behaviour, influencing what ...
Test #1
... The extent to which team members are attracted to the team and motivated to remain in it. A close and unified group will behave differently, for better or worse, than one that is distant and fragmented The consequences of sticking together are an important issue for productivity, satisfaction and de ...
... The extent to which team members are attracted to the team and motivated to remain in it. A close and unified group will behave differently, for better or worse, than one that is distant and fragmented The consequences of sticking together are an important issue for productivity, satisfaction and de ...
Prejudice and Discrimination
... comprised of distinct negative emotions. B. Depending on what emotion underlies prejudice toward a particular group, the discriminatory action that might be expected could be different. 1) When people’s prejudice primarily reflects anger, they may attempt to harm the out-group directly. 2) Prejudice ...
... comprised of distinct negative emotions. B. Depending on what emotion underlies prejudice toward a particular group, the discriminatory action that might be expected could be different. 1) When people’s prejudice primarily reflects anger, they may attempt to harm the out-group directly. 2) Prejudice ...
foot-in-the-door phenomenon.
... Linda, a third grade teacher, has been observing that hostility is growing between some of the children in her class. The best way for her to decrease the conflict between the children would be to: A. have the children identify what they like most about each other. B. have the children cooperate to ...
... Linda, a third grade teacher, has been observing that hostility is growing between some of the children in her class. The best way for her to decrease the conflict between the children would be to: A. have the children identify what they like most about each other. B. have the children cooperate to ...
Self-justification • People are motivated to justify their actions
... Self-justification • People are motivated to justify their actions, beliefs and feelings • When they do something, they will try, if at all possible, to convince themselves (and others) that it was a logical, reasonable thing to do –I.e. Prasad and Sinha’s rumors in neighboring village p.145 ...
... Self-justification • People are motivated to justify their actions, beliefs and feelings • When they do something, they will try, if at all possible, to convince themselves (and others) that it was a logical, reasonable thing to do –I.e. Prasad and Sinha’s rumors in neighboring village p.145 ...
Social Identity - Yorkshire and the Humber Deanery
... perpetrator’s actions were incoherent, senseless, incomprehensible. Either that or he was an abnormal sadist, motivated only by a desire to see me suffer, though I was completely innocent. The harm he did is grievous and irreparable, with effects that will last forever. None of us should forget it. ...
... perpetrator’s actions were incoherent, senseless, incomprehensible. Either that or he was an abnormal sadist, motivated only by a desire to see me suffer, though I was completely innocent. The harm he did is grievous and irreparable, with effects that will last forever. None of us should forget it. ...
The Power of the Situation
... Group-Serving Bias – we are lenient with ingroup members and quick to condemn outgroups Just-World Phenomenon – false belief that the world is fair and people get what they deserve ...
... Group-Serving Bias – we are lenient with ingroup members and quick to condemn outgroups Just-World Phenomenon – false belief that the world is fair and people get what they deserve ...
One Hundred Years of Groups Research: Introduction to the Special
... campsite in the United States. Gaertner and his colleagues (2000) revisit this study, examining its findings in light of more recent theory and research. They find that many of the causes of intergroup conflict highlighted by contemporary models of intergroup conflict and prejudice were present at t ...
... campsite in the United States. Gaertner and his colleagues (2000) revisit this study, examining its findings in light of more recent theory and research. They find that many of the causes of intergroup conflict highlighted by contemporary models of intergroup conflict and prejudice were present at t ...
Social Status in America
... As classes are political groups cohered by common interests, the struggle between two classes is a political struggle. Within this approach, the society’s structure is represented by those who manage and those who are managed. The first ones are further divided into owners and non-owners or bureaucr ...
... As classes are political groups cohered by common interests, the struggle between two classes is a political struggle. Within this approach, the society’s structure is represented by those who manage and those who are managed. The first ones are further divided into owners and non-owners or bureaucr ...
Status-Relevant Cues and Conspicuous Consumption: the
... petitive and dominant behaviors in humans (Manning, 2002; Millet, 2009). Therefore, we expect that the effect of status-relevant experiences on status oriented behavior will be more pronounced in low DR individuals. In a first study, we randomly approached 51 individuals on their way to (N = 19), or ...
... petitive and dominant behaviors in humans (Manning, 2002; Millet, 2009). Therefore, we expect that the effect of status-relevant experiences on status oriented behavior will be more pronounced in low DR individuals. In a first study, we randomly approached 51 individuals on their way to (N = 19), or ...
Explain the formation of stereotypes and their effect on behavior.
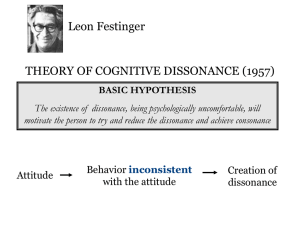
... – Uncomfortable clash between self-image, thoughts, beliefs, attitudes or perceptions and one’s behavior • Cognitions thoughts • Dissonance “clashing” ...
... – Uncomfortable clash between self-image, thoughts, beliefs, attitudes or perceptions and one’s behavior • Cognitions thoughts • Dissonance “clashing” ...
Slides
... (“I occasionally pick up other people’s garbage and take it to the trash can,” I occasionally carpool rather than drive separately,” “I frequently litter.” ...
... (“I occasionally pick up other people’s garbage and take it to the trash can,” I occasionally carpool rather than drive separately,” “I frequently litter.” ...