Unit 2 Assignments Answers
... Unlike gases, molecules in liquid phase have significantly less spaces between them. Hence, there is not enough room to compact these molecules to a smaller volume. Therefore, liquids are incompressible. Surface tension is the amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid ...
... Unlike gases, molecules in liquid phase have significantly less spaces between them. Hence, there is not enough room to compact these molecules to a smaller volume. Therefore, liquids are incompressible. Surface tension is the amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid ...
Exp7. Birefringence in Calcite Crystals
... As illustrated in the figure, when the beam of polarized light is incident on the surface of crystal, the refractive indices are different since the light has both parallel and perpendicular electric field component on the optical axis. Hence, every point on the wave-front propagates as elliptic wav ...
... As illustrated in the figure, when the beam of polarized light is incident on the surface of crystal, the refractive indices are different since the light has both parallel and perpendicular electric field component on the optical axis. Hence, every point on the wave-front propagates as elliptic wav ...
Numerical modelling of LCD electro
... The LCD is composed of plane parallel layers like glass substrates, LC layer, polarises etc. As long as the lateral extensions are much larger compared to the thickness of the individual layers and if sufficient homogeneity of the material and cell parameters along the surface can be assumed, a one- ...
... The LCD is composed of plane parallel layers like glass substrates, LC layer, polarises etc. As long as the lateral extensions are much larger compared to the thickness of the individual layers and if sufficient homogeneity of the material and cell parameters along the surface can be assumed, a one- ...
Linear Polarization 5.2.4 Polarization and Materials
... The basic ideas are easy to state. First, if there is an optical anisotropy, it can take two basic forms (and then mixtures of the two, of course): 1. The index of refraction depends on the crystal direction. The optical effects resulting from this are called "birefringence" or double refraction (La ...
... The basic ideas are easy to state. First, if there is an optical anisotropy, it can take two basic forms (and then mixtures of the two, of course): 1. The index of refraction depends on the crystal direction. The optical effects resulting from this are called "birefringence" or double refraction (La ...
Surface and colloidal chemistry
... • Surface tension of a liquid is highly depend on the solutes/ impurities dissolved in the liquid. • Therefore γ depends upon what substances (molecules) are at or near the surface of that liquid. • Since the "surface" is a boundary of a very thin thickness, surface tension is a sensitive function o ...
... • Surface tension of a liquid is highly depend on the solutes/ impurities dissolved in the liquid. • Therefore γ depends upon what substances (molecules) are at or near the surface of that liquid. • Since the "surface" is a boundary of a very thin thickness, surface tension is a sensitive function o ...
CONTENTS Optic Axis Principal Section of a Crystal Geometry of
... • Double refraction is an optical property in which a single ray of unpolarised light when passes through a uniaxial crystal gets split into two refracted rays, each propagating in a different direction. • These two rays are named as O-ray and E-ray. Therefore, the phenomenon of splitting of light i ...
... • Double refraction is an optical property in which a single ray of unpolarised light when passes through a uniaxial crystal gets split into two refracted rays, each propagating in a different direction. • These two rays are named as O-ray and E-ray. Therefore, the phenomenon of splitting of light i ...
Examples of Colligative properties are
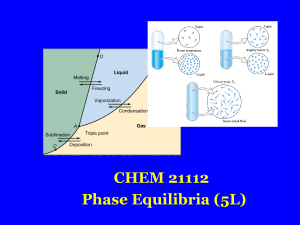
... To see this in graphical form, see the phase diagram for pure water, below. Three lines are present indicating the phase transition (read equilibrium) between solid, liquid and gas. Where all three lines meet is the triple point where all three phases are in equilibrium. We see that at an external p ...
... To see this in graphical form, see the phase diagram for pure water, below. Three lines are present indicating the phase transition (read equilibrium) between solid, liquid and gas. Where all three lines meet is the triple point where all three phases are in equilibrium. We see that at an external p ...
Foreign molecules and ions in beryl obtained by infrared and visible
... and spectrophotometry (VIS) was used for determination of foreign molecules and ions in the structure and the obtained data is shown in this paper. The infrared (IR) and visible spectra (VIS) of two natural beryl samples indicate the presence of two types of water molecule, Fe2+, Fe3+ ions and CO3 . ...
... and spectrophotometry (VIS) was used for determination of foreign molecules and ions in the structure and the obtained data is shown in this paper. The infrared (IR) and visible spectra (VIS) of two natural beryl samples indicate the presence of two types of water molecule, Fe2+, Fe3+ ions and CO3 . ...
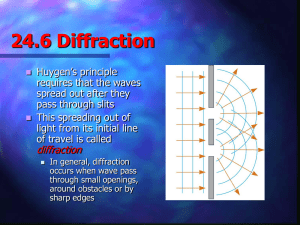
Single Slit Diffraction & Gratings
... vector simultaneously causes them to vibrate vertically Horizontally and vertically polarized waves are emitted ...
... vector simultaneously causes them to vibrate vertically Horizontally and vertically polarized waves are emitted ...
Regents Chemistry
... Determine how soluble a compound is at a given temperature using the solubility traces found in Table G o use solubility curves to predict how much water is required to dissolve a given amount of solute at a given temp or how much solute will dissolve in a given amount of water o be able to predict ...
... Determine how soluble a compound is at a given temperature using the solubility traces found in Table G o use solubility curves to predict how much water is required to dissolve a given amount of solute at a given temp or how much solute will dissolve in a given amount of water o be able to predict ...
11-16 States of Matter
... Very large amounts of energy (more than solids, liquids, or regular gases) Is a super-heated gas, with lots & lots of movement Examples: Stars, fire, and lightning Lightning Stars ...
... Very large amounts of energy (more than solids, liquids, or regular gases) Is a super-heated gas, with lots & lots of movement Examples: Stars, fire, and lightning Lightning Stars ...
Document
... time & the mean free path between collisions: If the molecules are not points, but rather rigid spheres of radius r, the number of molecules inside a cylinder of radius 2r is dN = (N/V) (p (2r)2 v dt) ...
... time & the mean free path between collisions: If the molecules are not points, but rather rigid spheres of radius r, the number of molecules inside a cylinder of radius 2r is dN = (N/V) (p (2r)2 v dt) ...
CHEMISTRY 313 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY I Additional Problems for
... II.5. At 20◦ C, the density of a 20% by mass ethanol/water solution is 968.7 kg/m3 . Given that the partial molar volume of ethanol in the solution is 52.2 mL/mol, calculate the partial molar volume of the water. II.6. The addition of 5.00 g of a compound to 250 g of naphthalene lowered the freezin ...
... II.5. At 20◦ C, the density of a 20% by mass ethanol/water solution is 968.7 kg/m3 . Given that the partial molar volume of ethanol in the solution is 52.2 mL/mol, calculate the partial molar volume of the water. II.6. The addition of 5.00 g of a compound to 250 g of naphthalene lowered the freezin ...
Temperature dependence of liquid Sn sputtering by - CPMI
... possible. Recent studies have found that bubble formation from He implantation in liquid Li is unclear or unlikely [25,26]. However, He bubbles are stable in liquid Sn due to its relatively high, almost 40% greater at their respective melting points [27], surface tension and could therefore be an ad ...
... possible. Recent studies have found that bubble formation from He implantation in liquid Li is unclear or unlikely [25,26]. However, He bubbles are stable in liquid Sn due to its relatively high, almost 40% greater at their respective melting points [27], surface tension and could therefore be an ad ...
Growth and characterization of Urea Lead nitrate
... complexes. It has shown interesting properties for nonlinear optical applications. Its optical and mechanical properties are comparable to those of semiorganic NLO crystals [1-4]. Lead (II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb(NO3)2. It commonly occurs as a colourless crysta ...
... complexes. It has shown interesting properties for nonlinear optical applications. Its optical and mechanical properties are comparable to those of semiorganic NLO crystals [1-4]. Lead (II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb(NO3)2. It commonly occurs as a colourless crysta ...
Chapter 12: Intermolecular Attractions and the Properties of Liquids
... positive ends of water dipoles surround an anion. The attractions can be quite strong because the ions have full charges. ...
... positive ends of water dipoles surround an anion. The attractions can be quite strong because the ions have full charges. ...
INERT GASES -
... the inert gases in such a way that molecules of the substance under study are trapped in the crystal lattice. Diatomic carbon frozen in a solid xenon lattice is particularly interesting because it is an experimental example of a quantum mechanical harmonic oscillator in a small box. The inert gases ...
... the inert gases in such a way that molecules of the substance under study are trapped in the crystal lattice. Diatomic carbon frozen in a solid xenon lattice is particularly interesting because it is an experimental example of a quantum mechanical harmonic oscillator in a small box. The inert gases ...
Document
... be changed independently without causing the appearance of a new phase or disappearance of an existing phase ...
... be changed independently without causing the appearance of a new phase or disappearance of an existing phase ...
Introduction
... gas phase is measured with the chromatograph (Model TCD 580, Gow-mac) with a Porapak N column (Model VDP-DVB, Alltech). The concentration in liquid phase is analyzed by back-titration and also measured with a ammonia electrode (Model 9512 BN, Orion®). Isothermal measurements are performed as follows ...
... gas phase is measured with the chromatograph (Model TCD 580, Gow-mac) with a Porapak N column (Model VDP-DVB, Alltech). The concentration in liquid phase is analyzed by back-titration and also measured with a ammonia electrode (Model 9512 BN, Orion®). Isothermal measurements are performed as follows ...
Book 2,Part 7 - GEOCITIES.ws
... The solid-liquid equilibrium line is vertical since the volume of solid and liquid He is the same for a fixed mass of He, i.e. pressure has no effect on mp. ...
... The solid-liquid equilibrium line is vertical since the volume of solid and liquid He is the same for a fixed mass of He, i.e. pressure has no effect on mp. ...
Document
... First order transition: first derivatives of the chemical potential with respect to temperature and pressure are discontinuous. Second order phase transition: first derivative of the chemical potential is continuous but the second derivative is discontinuous discontinuous. Though the symmetry change ...
... First order transition: first derivatives of the chemical potential with respect to temperature and pressure are discontinuous. Second order phase transition: first derivative of the chemical potential is continuous but the second derivative is discontinuous discontinuous. Though the symmetry change ...
Acids and bases
... 9.12 Ionic liquids (also called molten or fused salts ) A eutectic is a mixture of two substances and is characterized by a sharp melting point lower than that of either of the components; a eutectic behaves as though it were a single substance. For example, the melting point of NaCl is 1073 K, but ...
... 9.12 Ionic liquids (also called molten or fused salts ) A eutectic is a mixture of two substances and is characterized by a sharp melting point lower than that of either of the components; a eutectic behaves as though it were a single substance. For example, the melting point of NaCl is 1073 K, but ...
Mr Alasdair Ross at Southpointe Academy
... freezing point of -0.102 degrees celcius. The sorbitol contains 39.56% C, 7.75% H and 52.7% O by mass. What are the molar mass and molecular formula of sorbitol? ...
... freezing point of -0.102 degrees celcius. The sorbitol contains 39.56% C, 7.75% H and 52.7% O by mass. What are the molar mass and molecular formula of sorbitol? ...
Liquid crystal

Liquid crystals (LCs) are matter in a state that has properties between those of conventional liquid and those of solid crystal. For instance, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many different types of liquid-crystal phases, which can be distinguished by their different optical properties (such as birefringence). When viewed under a microscope using a polarized light source, different liquid crystal phases will appear to have distinct textures. The contrasting areas in the textures correspond to domains where the liquid-crystal molecules are oriented in different directions. Within a domain, however, the molecules are well ordered. LC materials may not always be in a liquid-crystal phase (just as water may turn into ice or steam).Liquid crystals can be divided into thermotropic, lyotropic and metallotropic phases. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist of organic molecules. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the liquid-crystal phase as temperature is changed. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of both temperature and concentration of the liquid-crystal molecules in a solvent (typically water). Metallotropic LCs are composed of both organic and inorganic molecules; their liquid-crystal transition depends not only on temperature and concentration, but also on the inorganic-organic composition ratio.Examples of liquid crystals can be found both in the natural world and in technological applications. Most contemporary electronic displays use liquid crystals. Lyotropic liquid-crystalline phases are abundant in living systems. For example, many proteins and cell membranes are liquid crystals. Other well-known examples of liquid crystals are solutions of soap and various related detergents, as well as the tobacco mosaic virus.