Teacher Resource Pack Unit Planning Resources
... toward a common center. Unlike the much larger outer planets, help, but it is essential that all which are mostly gas, the earth is mostly rock, with three-fourths students, sometimes working of its surface covered by a relatively thin layer of water and the together in small groups, make entire pla ...
... toward a common center. Unlike the much larger outer planets, help, but it is essential that all which are mostly gas, the earth is mostly rock, with three-fourths students, sometimes working of its surface covered by a relatively thin layer of water and the together in small groups, make entire pla ...
Our Planetary System 7.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) How does
... 5) Which of the following statements about the asteroid belt is not true? A) The combined mass of all the asteroids is roughly the same as the mass of Earth. B) It is located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. C) Asteroids in the asteroid belt orbit the Sun in the same direction that planets o ...
... 5) Which of the following statements about the asteroid belt is not true? A) The combined mass of all the asteroids is roughly the same as the mass of Earth. B) It is located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. C) Asteroids in the asteroid belt orbit the Sun in the same direction that planets o ...
ppt
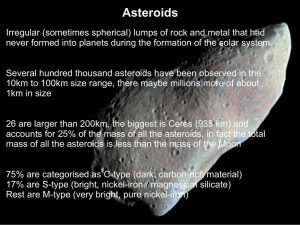
... Asteroids Irregular (sometimes spherical) lumps of rock and metal that had never formed into planets during the formation of the solar system Several hundred thousand asteroids have been observed in the 10km to 100km size range, there maybe millions more of about 1km in size 26 are larger than 200km ...
... Asteroids Irregular (sometimes spherical) lumps of rock and metal that had never formed into planets during the formation of the solar system Several hundred thousand asteroids have been observed in the 10km to 100km size range, there maybe millions more of about 1km in size 26 are larger than 200km ...
Midterm 1 Short Answer (+1-3pts) Record the answers to these
... Note: Many of you got this question partially correct by mentioning that it helped to block dangerous radiation from the Sun, but I was looking for specifically what type of radiation from the Sun is dangerous, ie ultravolet and also the fact that this was the key to having the first land species ev ...
... Note: Many of you got this question partially correct by mentioning that it helped to block dangerous radiation from the Sun, but I was looking for specifically what type of radiation from the Sun is dangerous, ie ultravolet and also the fact that this was the key to having the first land species ev ...
1 Exoplanets 2 Types of Exoplanets
... What good is learning about the habitable zone for each star if we don’t know where the planets are in relation to it? Therefore, using the information in Tables 3, and 4, you should be able to figure out how far each planet is from its host star. We have direct imaging data of the Terranova system ...
... What good is learning about the habitable zone for each star if we don’t know where the planets are in relation to it? Therefore, using the information in Tables 3, and 4, you should be able to figure out how far each planet is from its host star. We have direct imaging data of the Terranova system ...
userfiles/602xxh/files/2013%e5%b1%8a%e9%ab%98%e4%b8%89
... there’s our star, the sun. Orbiting the sun are eight planets, including Earth. But what about planets outside our solar system? About 15 years ago, scientists developed the tools to detect these “exoplanets”. Since then, they’ve spotted about 450. Most of the findings include one, two or three enor ...
... there’s our star, the sun. Orbiting the sun are eight planets, including Earth. But what about planets outside our solar system? About 15 years ago, scientists developed the tools to detect these “exoplanets”. Since then, they’ve spotted about 450. Most of the findings include one, two or three enor ...
INTERPLANET JANET Interplanet Janet: Rebecca Soloists
... Brody: Mercury was near the Sun so Janet stopped by, But the mercury on Mercury was much too high so Mohammad: Janet split for Venus but on Venus she found, she couldn't see a thing for all the clouds around. Jerad: Earth looked exciting, kind of green and inviting, So Janet thought she'd give it a ...
... Brody: Mercury was near the Sun so Janet stopped by, But the mercury on Mercury was much too high so Mohammad: Janet split for Venus but on Venus she found, she couldn't see a thing for all the clouds around. Jerad: Earth looked exciting, kind of green and inviting, So Janet thought she'd give it a ...
Final Study Guide Questions Earth Science Spring 2016 Mr. Traeger 1
... Which planets are only visible from earth either in the morning or the evening? ...
... Which planets are only visible from earth either in the morning or the evening? ...
Our Unique Planet - Ball State University
... combination for complex life to exist. There are two planetary attributes that this activity looks at which are necessary for life support: planetary distance from the sun and the size of the planet. One of the most basic needs for the support of life on a planet is liquid water on its surface. Wate ...
... combination for complex life to exist. There are two planetary attributes that this activity looks at which are necessary for life support: planetary distance from the sun and the size of the planet. One of the most basic needs for the support of life on a planet is liquid water on its surface. Wate ...
Print
... sun. It is a huge ball of superhot gas, made up mainly of hydrogen and helium. The sun is by far the largest object in our solar system. The Earth orbits around our sun, and so do all the other planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets in our solar system. The sun is really just an averag ...
... sun. It is a huge ball of superhot gas, made up mainly of hydrogen and helium. The sun is by far the largest object in our solar system. The Earth orbits around our sun, and so do all the other planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets in our solar system. The sun is really just an averag ...
Slide 1 - leslie09
... are a result of Earth's axis of rotation being tilted more than 23 degrees. ...
... are a result of Earth's axis of rotation being tilted more than 23 degrees. ...
CHAPTER 2 - THE RISE OF ASTRONOMY
... 7. This is an application of Kepler’s third law, P2 = a3, where a is in AU and P is in years. If P = 125 yrs, then a3 = 1252. Solving for a, we take the cube root of both sides to get a = (1252)1/3, where we have used the fact that the cube root of a number is the number to the 1/3 power. This can b ...
... 7. This is an application of Kepler’s third law, P2 = a3, where a is in AU and P is in years. If P = 125 yrs, then a3 = 1252. Solving for a, we take the cube root of both sides to get a = (1252)1/3, where we have used the fact that the cube root of a number is the number to the 1/3 power. This can b ...
Student Text, pp. 278-284
... Although Copernicus was at the forefront of the scientific revolution, his explanation of the orbits of the planets did not account for slight irregularities observed over long periods. The orbits were not exactly circles. More analysis was needed to find the true shapes of the orbits. The next infl ...
... Although Copernicus was at the forefront of the scientific revolution, his explanation of the orbits of the planets did not account for slight irregularities observed over long periods. The orbits were not exactly circles. More analysis was needed to find the true shapes of the orbits. The next infl ...
AST 207 Test 2 26 October 2011
... The sun will be a main-sequence star for 10 Byr, and then it becomes a giant, which engulfs Earth. Therefore the sun will stay small for another 5 Byr. b. (2 pts.) Why does the helium in the core of the sun not fuse at the present time? (1 pt.) When that helium does fuse eventually, what will the he ...
... The sun will be a main-sequence star for 10 Byr, and then it becomes a giant, which engulfs Earth. Therefore the sun will stay small for another 5 Byr. b. (2 pts.) Why does the helium in the core of the sun not fuse at the present time? (1 pt.) When that helium does fuse eventually, what will the he ...
On the migration of a system of protoplanets
... Cochran & Mayor 1999): the 51 Peg-type planets. They all have masses of the order of MJup, and orbit their central stars very closely, having orbital periods of only a few days. As massive planets, according to standard theory, have formed at distances of ...
... Cochran & Mayor 1999): the 51 Peg-type planets. They all have masses of the order of MJup, and orbit their central stars very closely, having orbital periods of only a few days. As massive planets, according to standard theory, have formed at distances of ...
On the migration of a system of protoplanets
... Cochran & Mayor 1999): the 51 Peg-type planets. They all have masses of the order of MJup, and orbit their central stars very closely, having orbital periods of only a few days. As massive planets, according to standard theory, have formed at distances of ...
... Cochran & Mayor 1999): the 51 Peg-type planets. They all have masses of the order of MJup, and orbit their central stars very closely, having orbital periods of only a few days. As massive planets, according to standard theory, have formed at distances of ...
ISP205L Visions of the Universe Laboratory
... SG-2: Motions of the Stars SG-3: Celestial Sphere SG-4: Motions of the Sun. SG-5: Ecliptic, Parts 1-3. No homework. Study for Quiz. SG-8: Precession and Proper Motion. ...
... SG-2: Motions of the Stars SG-3: Celestial Sphere SG-4: Motions of the Sun. SG-5: Ecliptic, Parts 1-3. No homework. Study for Quiz. SG-8: Precession and Proper Motion. ...
Lesson 120125 - WordPress.com
... How did the planets move (so as match the way we saw them moving)? Perhaps their orbits were elliptical not circular Why were there only 6 planets? Why not 4? Or 9? ...
... How did the planets move (so as match the way we saw them moving)? Perhaps their orbits were elliptical not circular Why were there only 6 planets? Why not 4? Or 9? ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... 1. Sketch: The distance unit used her is the astronomical unit (AU), equal to the average Earth-Sun distance. Place the planet on the i axis at r = –3.00i AU. Move the velocity vector so that v = -8.0j km/s (|v| = 8.00 km/s). The resulting vectors should look like the vectors in the image at right. ...
... 1. Sketch: The distance unit used her is the astronomical unit (AU), equal to the average Earth-Sun distance. Place the planet on the i axis at r = –3.00i AU. Move the velocity vector so that v = -8.0j km/s (|v| = 8.00 km/s). The resulting vectors should look like the vectors in the image at right. ...
Keplers Laws
... 1. Sketch: The distance unit used her is the astronomical unit (AU), equal to the average Earth-Sun distance. Place the planet on the i axis at r = –3.00i AU. Move the velocity vector so that v = -8.0j km/s (|v| = 8.00 km/s). The resulting vectors should look like the vectors in the image at right. ...
... 1. Sketch: The distance unit used her is the astronomical unit (AU), equal to the average Earth-Sun distance. Place the planet on the i axis at r = –3.00i AU. Move the velocity vector so that v = -8.0j km/s (|v| = 8.00 km/s). The resulting vectors should look like the vectors in the image at right. ...
Aug - Wadhurst Astronomical Society
... We began by looking at how we see the Moon by eye relative to the landscape of the Earth. We can probably make out the ‘seas’ but we certainly can’t see the craters without the use of a good pair of binoculars or a telescope. The mass of the Moon is just over 1% that of the Earth and reaches a tempe ...
... We began by looking at how we see the Moon by eye relative to the landscape of the Earth. We can probably make out the ‘seas’ but we certainly can’t see the craters without the use of a good pair of binoculars or a telescope. The mass of the Moon is just over 1% that of the Earth and reaches a tempe ...
PLANET RESEARCH PAPER
... Rotation on its Axis: How long does it take for your planet to rotate on its own axis? (This is one day on your planet.) Size: How big is your planet? How does it rate in terms of the other planets in terms of size (is it the biggest, the smallest)? What is your planet's mass? Gravity: What is the f ...
... Rotation on its Axis: How long does it take for your planet to rotate on its own axis? (This is one day on your planet.) Size: How big is your planet? How does it rate in terms of the other planets in terms of size (is it the biggest, the smallest)? What is your planet's mass? Gravity: What is the f ...
BIG Education Pack:
... Definition of a star: A self-luminous sphere of gas.* Definition of the Sun: The star about which the Earth and the other planets revolve.* The Sun is our star, the main source of heat and light in the Solar System. It is a fairly average star, only looking as big as it does due to its close proximi ...
... Definition of a star: A self-luminous sphere of gas.* Definition of the Sun: The star about which the Earth and the other planets revolve.* The Sun is our star, the main source of heat and light in the Solar System. It is a fairly average star, only looking as big as it does due to its close proximi ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.