Life cycle of Stars Notes
... Stage 1: Protostars • Protostars form in cold, dark nebulae. • Interstellar gas and dust are the raw materials from which stars form. ...
... Stage 1: Protostars • Protostars form in cold, dark nebulae. • Interstellar gas and dust are the raw materials from which stars form. ...
Eratosthenes (250 B.C) Ptolemy`s Geocentric Model
... and the Plague. •The Church began to seize power through various means… means… ...
... and the Plague. •The Church began to seize power through various means… means… ...
Targets and their Environments - Pathways Towards Habitable Planets
... Toward smaller HZ: less perturbation by Jupiters & companions and: low-mass stars have fewer Jupiters (Endl et al. 03, Butler et al. 07) ...
... Toward smaller HZ: less perturbation by Jupiters & companions and: low-mass stars have fewer Jupiters (Endl et al. 03, Butler et al. 07) ...
A low mass for Mars from Jupiter`s early gas
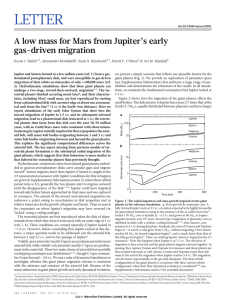
... Uranus–Neptune region it is 8–15. Thus, depending on which region dominated the implantation of C-type asteroids, we expect that (3{11)|10{2 M+ of C-type material entered the terrestrial planet region. This exceeds by a factor of 6–22 the minimal mass required to bring the current amount of water to ...
... Uranus–Neptune region it is 8–15. Thus, depending on which region dominated the implantation of C-type asteroids, we expect that (3{11)|10{2 M+ of C-type material entered the terrestrial planet region. This exceeds by a factor of 6–22 the minimal mass required to bring the current amount of water to ...
A low mass for Mars from Jupiter`s early gas-driven - ICE-CSIC
... Uranus–Neptune region it is 8–15. Thus, depending on which region dominated the implantation of C-type asteroids, we expect that (3{11)|10{2 M+ of C-type material entered the terrestrial planet region. This exceeds by a factor of 6–22 the minimal mass required to bring the current amount of water to ...
... Uranus–Neptune region it is 8–15. Thus, depending on which region dominated the implantation of C-type asteroids, we expect that (3{11)|10{2 M+ of C-type material entered the terrestrial planet region. This exceeds by a factor of 6–22 the minimal mass required to bring the current amount of water to ...
The Cosmic Perspective Our Planetary System
... a) The number of small rocky planets is equal to the number of large gas-rich planets. b) There are a large number of small rocky and icy objects in different regions of the solar system. c) The planets and moons generally orbit in the same plane. d) The Earth has an unusually large moon. e) Ur ...
... a) The number of small rocky planets is equal to the number of large gas-rich planets. b) There are a large number of small rocky and icy objects in different regions of the solar system. c) The planets and moons generally orbit in the same plane. d) The Earth has an unusually large moon. e) Ur ...
L11 Terrestrial planet formation and Impacts
... Water of Earth Inherent to the question of mixing during planetary formation is the question of the origin of water on the terrestrial planets. This question can be addressed by following the planetesimals originally located inside/outside the ice line and see in which planet they eventually get in ...
... Water of Earth Inherent to the question of mixing during planetary formation is the question of the origin of water on the terrestrial planets. This question can be addressed by following the planetesimals originally located inside/outside the ice line and see in which planet they eventually get in ...
AST 301 Test #3 Friday Nov. 12 Name: 1. a) The Sun is in
... 1. a) The Sun is in hydrostatic equilibrium. What does this mean? What is the definition of hydrostatic equilibrium as we apply it to the Sun? Pressure inside the star pushing it apart balances gravity pulling it together. So it doesn’t change its size. 1. a) The Sun is in thermal equilibrium. What ...
... 1. a) The Sun is in hydrostatic equilibrium. What does this mean? What is the definition of hydrostatic equilibrium as we apply it to the Sun? Pressure inside the star pushing it apart balances gravity pulling it together. So it doesn’t change its size. 1. a) The Sun is in thermal equilibrium. What ...
PHASES OF THE MOON
... Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto The Inner Planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars. They are called the Rocky planets. The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto. They are the Gas planets. The inner and outer planets are separated by the Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter. ...
... Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto The Inner Planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars. They are called the Rocky planets. The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto. They are the Gas planets. The inner and outer planets are separated by the Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter. ...
Earth, Sun, Moon System
... Rotation on its Axis: How long does it take for your planet to rotate on its own axis? (This is one day on your planet.) Size: How big is your planet? How does it rate in terms of the other planets in terms of size (is it the biggest, the smallest)? What is your planet's mass? Gravity: What is the f ...
... Rotation on its Axis: How long does it take for your planet to rotate on its own axis? (This is one day on your planet.) Size: How big is your planet? How does it rate in terms of the other planets in terms of size (is it the biggest, the smallest)? What is your planet's mass? Gravity: What is the f ...
Unit Two Worksheet – Astronomy
... Galaxy with no discernable shape and unevenly distributed stars within it States that galaxies are retreating away from the Milky Way Galaxy at a speed proportional to their distance Galaxy with a core of bright stars and flattened arms that swirl around the core Galaxy with a core of bright stars a ...
... Galaxy with no discernable shape and unevenly distributed stars within it States that galaxies are retreating away from the Milky Way Galaxy at a speed proportional to their distance Galaxy with a core of bright stars and flattened arms that swirl around the core Galaxy with a core of bright stars a ...
Owsley Brown II Portable Planetarium 9
... ● The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their distance from ...
... ● The sun is a star that appears larger and brighter than other stars because it is closer. Stars range greatly in their distance from ...
Physics 20 Concept 22 Orbits and Satellites
... At low speeds, a horizontal projectile will fall toward and hit the ground in a short time. As the speed of the horizontal projectile is increased, it will land further and further away from the starting point. For a flat Earth the projectile would always hit the ground; no matter how fast the proje ...
... At low speeds, a horizontal projectile will fall toward and hit the ground in a short time. As the speed of the horizontal projectile is increased, it will land further and further away from the starting point. For a flat Earth the projectile would always hit the ground; no matter how fast the proje ...
Stargazing Rules 01162013
... 17. The Moon rises an average of about 50 minutes later each day. The full Moon rises at about sunset and sets at about sunrise. The new Moon rises and sets approximately with the sun, which is why we cannot see it. The first quarter Moon, is straight overhead at sunset and sets at midnight. The thi ...
... 17. The Moon rises an average of about 50 minutes later each day. The full Moon rises at about sunset and sets at about sunrise. The new Moon rises and sets approximately with the sun, which is why we cannot see it. The first quarter Moon, is straight overhead at sunset and sets at midnight. The thi ...
AST 105 HW #1 Solution Week of August 24 , 2015
... 4. Why does the local sky look like a dome? Define horizon, zenith, and meridian. How do we describe the location of an object in the local sky? Answer: Since the view of the bottom half of the sky is blocked from us by the ground, the local sky look like a dome. Horizon is the line at which the Ear ...
... 4. Why does the local sky look like a dome? Define horizon, zenith, and meridian. How do we describe the location of an object in the local sky? Answer: Since the view of the bottom half of the sky is blocked from us by the ground, the local sky look like a dome. Horizon is the line at which the Ear ...
Additional Exercises for Chapter 7 In these exercises we will use
... information about the trajectories of the Voyager probes in the solar system. Suppose a space probe V has left the realm of the inner planets and is heading towards the farther reaches of the solar system. The probe V is far from the Sun and any planet. The fact that its mass is relatively small mea ...
... information about the trajectories of the Voyager probes in the solar system. Suppose a space probe V has left the realm of the inner planets and is heading towards the farther reaches of the solar system. The probe V is far from the Sun and any planet. The fact that its mass is relatively small mea ...
Atmospheres in the Solar System • The speed at which molecules
... • Maybe the atmosphere of Mars was “sandblasted” by the intense solar wind early in the history of the solar system (estimates that power in early solar wind 35X that at ...
... • Maybe the atmosphere of Mars was “sandblasted” by the intense solar wind early in the history of the solar system (estimates that power in early solar wind 35X that at ...
Revolutions of Earth
... To an observer, Earth appears to be the center of the universe. That is what the ancient Greeks believed. This view is called the geocentric model, or "Earth-centered" model, of the universe. In the geocentric model, the sky, or heavens, are a set of spheres layered on top of one another. Each objec ...
... To an observer, Earth appears to be the center of the universe. That is what the ancient Greeks believed. This view is called the geocentric model, or "Earth-centered" model, of the universe. In the geocentric model, the sky, or heavens, are a set of spheres layered on top of one another. Each objec ...
Astronomy Powerpoint
... releasing a tremendous amount of energy. • During nuclear fusion, energy is released because some matter is actually converted to energy. • It is thought that a star the size of the sun can exist in its present stable state for 10 billion years. As the sun is already 4.5 billion years old, it is “mi ...
... releasing a tremendous amount of energy. • During nuclear fusion, energy is released because some matter is actually converted to energy. • It is thought that a star the size of the sun can exist in its present stable state for 10 billion years. As the sun is already 4.5 billion years old, it is “mi ...
Our View of the SS - MMSD Planetarium
... Very few students, and adults for that matter, have a good concept of where the planets would be found in the Solar System beyond a simple, straight-line model. They wrongly assume that Venus and Mars are always the closest planets to the Earth. Their misconceptions become obvious by their questions ...
... Very few students, and adults for that matter, have a good concept of where the planets would be found in the Solar System beyond a simple, straight-line model. They wrongly assume that Venus and Mars are always the closest planets to the Earth. Their misconceptions become obvious by their questions ...
PDF only
... exist within our catalogue of confirmed and candidate exoplanets. The first exoplanets found in the mid-1990s were all gas giants similar in mass to Jupiter and orbiting far too close to their stars to harbor any life. Yet as planethunting techniques have improved over time, astronomers have begun f ...
... exist within our catalogue of confirmed and candidate exoplanets. The first exoplanets found in the mid-1990s were all gas giants similar in mass to Jupiter and orbiting far too close to their stars to harbor any life. Yet as planethunting techniques have improved over time, astronomers have begun f ...
Planet Travel Brochure
... Section 1: Name of your planet, your name and a drawing of your planet’s appearance Section 2: Position in the Solar System: Where is your planet located (for example, Earth is the third planet from the Sun)? How far from the Sun does it orbit? Orbit: How long does it take for your planet to orbit ...
... Section 1: Name of your planet, your name and a drawing of your planet’s appearance Section 2: Position in the Solar System: Where is your planet located (for example, Earth is the third planet from the Sun)? How far from the Sun does it orbit? Orbit: How long does it take for your planet to orbit ...
Armoring may be divided into natural or temporary muscular
... It has been shown that there is a simple functional relationship between the orientations of planetary rotation and the galactic plane, namely the axes of rotation of the sun and the planets tend to be close to the galactic plane. This finding is consistent with the simplest and most natural applica ...
... It has been shown that there is a simple functional relationship between the orientations of planetary rotation and the galactic plane, namely the axes of rotation of the sun and the planets tend to be close to the galactic plane. This finding is consistent with the simplest and most natural applica ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.