BIG Education Pack:
... Definition of a star: A self-luminous sphere of gas.* Definition of the Sun: The star about which the Earth and the other planets revolve.* The Sun is our star, the main source of heat and light in the Solar System. It is a fairly average star, only looking as big as it does due to its close proximi ...
... Definition of a star: A self-luminous sphere of gas.* Definition of the Sun: The star about which the Earth and the other planets revolve.* The Sun is our star, the main source of heat and light in the Solar System. It is a fairly average star, only looking as big as it does due to its close proximi ...
September 2015 - Hermanus Astronomy
... from their magnetic poles and sweep across space as the pulsar rotates. Since they are phenomenally dense and massive, yet comparatively small - a mere 20–25 km across some pulsars are able to maintain their rate of spin with a consistency that rivals the best atomic clocks on Earth. This makes puls ...
... from their magnetic poles and sweep across space as the pulsar rotates. Since they are phenomenally dense and massive, yet comparatively small - a mere 20–25 km across some pulsars are able to maintain their rate of spin with a consistency that rivals the best atomic clocks on Earth. This makes puls ...
Contributions To Science
... He proved that comets are not objects in the atmosphere. Made a extremely accurate star catalogue containing 1000 stars. Spent most of his life working on his astronomical tables (before the telescope ...
... He proved that comets are not objects in the atmosphere. Made a extremely accurate star catalogue containing 1000 stars. Spent most of his life working on his astronomical tables (before the telescope ...
New Worlds on the Horizon: Earth-Sized Planets Close to Other
... conditions that could support life as we understand it? Close-in planets around lowluminosity M dwarfs can orbit within the habitable zone (Fig. 3). However, charged particles in flares from the nearby host star or impacts at the high velocities of these orbits may remove such planets’ atmospheres, ...
... conditions that could support life as we understand it? Close-in planets around lowluminosity M dwarfs can orbit within the habitable zone (Fig. 3). However, charged particles in flares from the nearby host star or impacts at the high velocities of these orbits may remove such planets’ atmospheres, ...
Habitable Zone - Wando High School
... image to the right, how far away the habitable zone is depends on the size/strength of the sun. The bigger the sun, the further away the habitable zone is. Stars that are much larger than the Sun have much short lifetimes, which it is unlikely that there would be enough time for any kind of life, pa ...
... image to the right, how far away the habitable zone is depends on the size/strength of the sun. The bigger the sun, the further away the habitable zone is. Stars that are much larger than the Sun have much short lifetimes, which it is unlikely that there would be enough time for any kind of life, pa ...
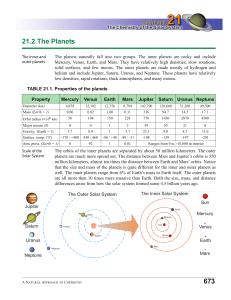
673 21.2 The Planets - District 196 e
... The outer planets have many moons and are more like miniature solar systems themselves. This is very different from the inner planets. Earth has 1 large moon, Mercury and Venus have none, and Mars has two tiny orbiting asteroids that hardly qualify as moons. By comparison, as of the writing of this ...
... The outer planets have many moons and are more like miniature solar systems themselves. This is very different from the inner planets. Earth has 1 large moon, Mercury and Venus have none, and Mars has two tiny orbiting asteroids that hardly qualify as moons. By comparison, as of the writing of this ...
Planetary Orbit Simulator – Student Guide
... Question 5: If a planet is twice as far from the sun at aphelion than at perihelion then the strength of the gravitational force at aphelion will be… a) will be half as much than it is at perihelion. b) twice as much than it is at perihelion. c) four times less than it is at perihelion. d) the same ...
... Question 5: If a planet is twice as far from the sun at aphelion than at perihelion then the strength of the gravitational force at aphelion will be… a) will be half as much than it is at perihelion. b) twice as much than it is at perihelion. c) four times less than it is at perihelion. d) the same ...
Unit XII Study Guide
... c. number of stars. b. sizes. d. brightness. ____ 24. When the absorption lines of a galaxy shift toward the blue end of the spectrum, it means that the galaxy is a. Moving away from Earth. c. moving closer to Earth. b. small and young. d. large and old. ____ 25. Hubble’s Law states that the speed a ...
... c. number of stars. b. sizes. d. brightness. ____ 24. When the absorption lines of a galaxy shift toward the blue end of the spectrum, it means that the galaxy is a. Moving away from Earth. c. moving closer to Earth. b. small and young. d. large and old. ____ 25. Hubble’s Law states that the speed a ...
Solar System: Small Bodies
... Astronomers once thought that the Main Belt was the debris ring left over from a destroyed__________. It’s much more likely that such a planet was, in fact, prevented from ever forming by Jupiter’s strong gravitational pull. In total, the mass of all the asteroids is less than that of Earth's moon. ...
... Astronomers once thought that the Main Belt was the debris ring left over from a destroyed__________. It’s much more likely that such a planet was, in fact, prevented from ever forming by Jupiter’s strong gravitational pull. In total, the mass of all the asteroids is less than that of Earth's moon. ...
The Dimensions of the Solar System
... the sizes, but we see this as an obstacle to students gaining a deeper insight into the scale of the solar system. The problem can be solved if we expand our model sufficiently, so that we can have realistic separations between the solar-system bodies and still have an Earth that is not microscopic. ...
... the sizes, but we see this as an obstacle to students gaining a deeper insight into the scale of the solar system. The problem can be solved if we expand our model sufficiently, so that we can have realistic separations between the solar-system bodies and still have an Earth that is not microscopic. ...
Sec 28.4 - Highland High School
... Possible answer: As a comet approaches the Sun, ices in the comet vaporize, or turn to gas. Dust is also released as the comet dissipates. Particles and radiation streaming away from the Sun then push the gas and dust away from the Sun. The gas often forms a blue tail that points directly away from ...
... Possible answer: As a comet approaches the Sun, ices in the comet vaporize, or turn to gas. Dust is also released as the comet dissipates. Particles and radiation streaming away from the Sun then push the gas and dust away from the Sun. The gas often forms a blue tail that points directly away from ...
New Worlds Ahead: The Discovery of Exoplanets
... gas giant planets like Jupiter (318 Earth masses, or M⊕ ) and Saturn (95 M⊕ ) are located further away (5 and 10 AU), and finally the icy giants Uranus and Neptune, located even further (20 and 30 AU), are much less massive (14 M⊕ and 17 M⊕ ). Pluto does not fit well in this picture, but in fact it ...
... gas giant planets like Jupiter (318 Earth masses, or M⊕ ) and Saturn (95 M⊕ ) are located further away (5 and 10 AU), and finally the icy giants Uranus and Neptune, located even further (20 and 30 AU), are much less massive (14 M⊕ and 17 M⊕ ). Pluto does not fit well in this picture, but in fact it ...
Physics 20 Lesson 23 Orbits and Satellites
... Physics 20 Lesson 23 Orbits and Satellites Refer to Pearson pages 269 to 286 for a discussion about orbits of planets and artificial satellites. ...
... Physics 20 Lesson 23 Orbits and Satellites Refer to Pearson pages 269 to 286 for a discussion about orbits of planets and artificial satellites. ...
Chapter 3
... 1. The point in the sky directly overhead. 2. The circle dividing the sky into eastern and western halves. 3. Locate the North Celestial Pole precisely in the Bryan sky. 4. Over what point on Earth is the North Celestial Pole? 5. The Celestial Equator is a circle on the sky that crosses the horizon ...
... 1. The point in the sky directly overhead. 2. The circle dividing the sky into eastern and western halves. 3. Locate the North Celestial Pole precisely in the Bryan sky. 4. Over what point on Earth is the North Celestial Pole? 5. The Celestial Equator is a circle on the sky that crosses the horizon ...
december 2010 - Holt Planetarium
... Season’s greetings to one and all. There are a couple of interesting astronomical events this month. On December 21 there is a total eclipse of the Moon. The total phase of this eclipse lasts for just over 72 minutes, with the partial umbral eclipse spanning almost 3.5 hours. All stages of the total ...
... Season’s greetings to one and all. There are a couple of interesting astronomical events this month. On December 21 there is a total eclipse of the Moon. The total phase of this eclipse lasts for just over 72 minutes, with the partial umbral eclipse spanning almost 3.5 hours. All stages of the total ...
december 2010 - Holt Planetarium
... Season’s greetings to one and all. There are a couple of interesting astronomical events this month. On December 21 there is a total eclipse of the Moon. The total phase of this eclipse lasts for just over 72 minutes, with the partial umbral eclipse spanning almost 3.5 hours. All stages of the total ...
... Season’s greetings to one and all. There are a couple of interesting astronomical events this month. On December 21 there is a total eclipse of the Moon. The total phase of this eclipse lasts for just over 72 minutes, with the partial umbral eclipse spanning almost 3.5 hours. All stages of the total ...
Spectral fingerprinting student project
... scientists may soon be hot on its trail. In 1995, the first planet around another sun-like star was discovered by astronomers using Doppler detection—a method that scientists have used to reveal Saturn-sized (or larger) planets close to their parent suns. Today, astronomers know of more than 100 can ...
... scientists may soon be hot on its trail. In 1995, the first planet around another sun-like star was discovered by astronomers using Doppler detection—a method that scientists have used to reveal Saturn-sized (or larger) planets close to their parent suns. Today, astronomers know of more than 100 can ...
Unit 2 Section 1
... wander slowly among the stars. The Greeks called these objects planets, from the Greek word meaning “wanderers.” The Greeks made careful observations of the motions of the planets that they could see. You know these planets by the names the ancient Romans later gave them: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupit ...
... wander slowly among the stars. The Greeks called these objects planets, from the Greek word meaning “wanderers.” The Greeks made careful observations of the motions of the planets that they could see. You know these planets by the names the ancient Romans later gave them: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupit ...
Jovian Planet Systems
... • A storm twice as wide as Earth • But unlike typical storms on Earth, it is a high-pressure storm • You can tell this by considering the “Coriolis effect” ...
... • A storm twice as wide as Earth • But unlike typical storms on Earth, it is a high-pressure storm • You can tell this by considering the “Coriolis effect” ...
Lecture 12-13: Planetary atmospheres
... o For Earth, gives a “hot” side to the planet, with an average temperature of >330 K. o The “cold” side of a tidally locked planet would have extremely low temperatures. Strong winds would act to redistribute heat between hemispheres. o There would also be a latitudinal variation of heating. The ...
... o For Earth, gives a “hot” side to the planet, with an average temperature of >330 K. o The “cold” side of a tidally locked planet would have extremely low temperatures. Strong winds would act to redistribute heat between hemispheres. o There would also be a latitudinal variation of heating. The ...
Section 1
... wander slowly among the stars. The Greeks called these objects planets, from the Greek word meaning “wanderers.” The Greeks made careful observations of the motions of the planets that they could see. You know these planets by the names the ancient Romans later gave them: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupit ...
... wander slowly among the stars. The Greeks called these objects planets, from the Greek word meaning “wanderers.” The Greeks made careful observations of the motions of the planets that they could see. You know these planets by the names the ancient Romans later gave them: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupit ...
Origin of the solar system
... •Earth had already differentiated into core & mantle structure by this time ...
... •Earth had already differentiated into core & mantle structure by this time ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.