The Sun and Stars The Sun is a typical star with a mass of about 2
... the star is a ball of neutrons with a few kilometers diameter and a tremendous density It is a solar mass compressed to a few kilometers diameter. One cc would have a mass of some 6 × 1011 kg, or about 6 × 108 tons. ...
... the star is a ball of neutrons with a few kilometers diameter and a tremendous density It is a solar mass compressed to a few kilometers diameter. One cc would have a mass of some 6 × 1011 kg, or about 6 × 108 tons. ...
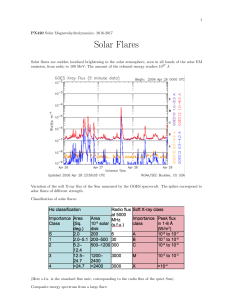
Solar Flares
... 6. “Post-flare loops” (sometimes having a cusp-like shape) are formed over the neutral line; they gradually cool down by radiation. 7. More field lines are involved in reconnection; the reconnection site is going up, forming new postflare loops situated above the previously created ones. 8. A multi- ...
... 6. “Post-flare loops” (sometimes having a cusp-like shape) are formed over the neutral line; they gradually cool down by radiation. 7. More field lines are involved in reconnection; the reconnection site is going up, forming new postflare loops situated above the previously created ones. 8. A multi- ...
Pre-Main Sequence Evolution
... • Prior to hydrogen ignition, the star simply evolves via contraction, on a thermal timescale ...
... • Prior to hydrogen ignition, the star simply evolves via contraction, on a thermal timescale ...
The Stellar Graveyard
... this cone of emitted radiation emerging from the magnetic polar axis. This radiation can be in the form of radio, optical or x-rays and usually all three sources can come from a single pulsar. The Crab nebula, the core remnant of a supernova that occurred in 1054 AD and was visible in the daytime sk ...
... this cone of emitted radiation emerging from the magnetic polar axis. This radiation can be in the form of radio, optical or x-rays and usually all three sources can come from a single pulsar. The Crab nebula, the core remnant of a supernova that occurred in 1054 AD and was visible in the daytime sk ...
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM (H
... marked “solar radii” (radii is plural for radius) on the righthand side. These lines are used to represent the physical size of stars on the diagram. Using the diagonal solar radii lines, give the solar radius (size) of the sun. ___________ ...
... marked “solar radii” (radii is plural for radius) on the righthand side. These lines are used to represent the physical size of stars on the diagram. Using the diagonal solar radii lines, give the solar radius (size) of the sun. ___________ ...
HST reveals upheaval in Jupiter`s clouds
... times the mass of the Sun, some 20 000 light-years from Earth. Such jets are normally associated with black holes, so this discovery should clarify which features of superdense stars are required to form jets. “Gravity appears to be the key to creating these jets, not some trick of the event horizon ...
... times the mass of the Sun, some 20 000 light-years from Earth. Such jets are normally associated with black holes, so this discovery should clarify which features of superdense stars are required to form jets. “Gravity appears to be the key to creating these jets, not some trick of the event horizon ...
Black Holes
... by the probe would become yellow, and then red as the probe nears the black hole. • From the probe’s perspective, the light would stay green. • As the probe got closer to the event horizon, the radiation from its light source would no longer be visible light. • The radiation reaching the orbiting sp ...
... by the probe would become yellow, and then red as the probe nears the black hole. • From the probe’s perspective, the light would stay green. • As the probe got closer to the event horizon, the radiation from its light source would no longer be visible light. • The radiation reaching the orbiting sp ...
The REAL OCCULT: - Montgomery College
... Near Black Holes An astronaut descending down towards the event horizon of the black hole will be stretched vertically (tidal effects) and squeezed laterally unless the black hole is very large like thousands of solar masses, so the multi-million solar mass black hole in the center of the galaxy is ...
... Near Black Holes An astronaut descending down towards the event horizon of the black hole will be stretched vertically (tidal effects) and squeezed laterally unless the black hole is very large like thousands of solar masses, so the multi-million solar mass black hole in the center of the galaxy is ...
Astrophysics
... If galaxies are moving away from us, they must have been closer together millions of years ago. If Hubble’s graph is used, the origin of this movement = approx. 10 000 million years old ...
... If galaxies are moving away from us, they must have been closer together millions of years ago. If Hubble’s graph is used, the origin of this movement = approx. 10 000 million years old ...
What is a Star? - Lisle CUSD 202
... can also form when binary stars (two stars revolving around each other) get too close and one sucks mass from the other until BOOM! ...
... can also form when binary stars (two stars revolving around each other) get too close and one sucks mass from the other until BOOM! ...
Summer 2001 Day 07: Intro to Solar System
... E) Ratio problems: Suppose star A is 81 times dimmer than Star B, but we believe that they are the same luminosity. i) Which star is farther away? ii) How much farther? 5) Absolute Magnitude, M i) A numerical representation of luminosity ii) the apparent brightness at a standard distance of 10 parse ...
... E) Ratio problems: Suppose star A is 81 times dimmer than Star B, but we believe that they are the same luminosity. i) Which star is farther away? ii) How much farther? 5) Absolute Magnitude, M i) A numerical representation of luminosity ii) the apparent brightness at a standard distance of 10 parse ...
Forging the elements
... If the Sun becomes a white dwarf, r ~6400km, P = 3 min (typical white dwarf rotation from 33 sec upwards) If the Sun became a neutron star, r~10km, P = 0.5 ms (typical neutron star rotation from 1ms upwards) ...
... If the Sun becomes a white dwarf, r ~6400km, P = 3 min (typical white dwarf rotation from 33 sec upwards) If the Sun became a neutron star, r~10km, P = 0.5 ms (typical neutron star rotation from 1ms upwards) ...
The Family of Stars
... => Rapidly pulsed (optical and radio) emission from some objects interpreted as spin period of neutron stars ...
... => Rapidly pulsed (optical and radio) emission from some objects interpreted as spin period of neutron stars ...
Document
... Estimate the intensity of the radiation emitted per unit area from a star if it’s effective surface Temp is 6000K Estimate the energy emitted from a star if its peak wavelength is 600nm. Total power radiated Power output = E x surface area of star Surface area of a star = 4 R 2 Where R is the rad ...
... Estimate the intensity of the radiation emitted per unit area from a star if it’s effective surface Temp is 6000K Estimate the energy emitted from a star if its peak wavelength is 600nm. Total power radiated Power output = E x surface area of star Surface area of a star = 4 R 2 Where R is the rad ...
Stellar Evolution Diagram Answer Key:
... supernova after an explosion which causes it to contract into a very small but incredibly dense ball of neutrons. A spoonful of matter from a neutron star would weight 100 million tons on earth. Black Hole: The lifetime of black holes is not known. A black hole is when the core of an extremely large ...
... supernova after an explosion which causes it to contract into a very small but incredibly dense ball of neutrons. A spoonful of matter from a neutron star would weight 100 million tons on earth. Black Hole: The lifetime of black holes is not known. A black hole is when the core of an extremely large ...
The Life Cycles of Stars MEDIUM STARS MASSIVE STARS
... Neutron stars spin rapidly giving off radio waves. If the radio waves are emitted in pulses (due to the star's spin), these neutron stars are called pulsars. The core of a massive star that has 8 or more times the mass of our Sun remains massive after the supernova. No nuclear fusion is taking place ...
... Neutron stars spin rapidly giving off radio waves. If the radio waves are emitted in pulses (due to the star's spin), these neutron stars are called pulsars. The core of a massive star that has 8 or more times the mass of our Sun remains massive after the supernova. No nuclear fusion is taking place ...
SALT Science – UW Madison
... (obs Jan 2012, spectra: Brown et al. SALT/RSS; photometry: Kowalski et al. WHT/La Palma) ...
... (obs Jan 2012, spectra: Brown et al. SALT/RSS; photometry: Kowalski et al. WHT/La Palma) ...
Variability of Be stars
... ~200 Be stars are currently known among 1660 B-type stars brighter than V=6.5 mag ...
... ~200 Be stars are currently known among 1660 B-type stars brighter than V=6.5 mag ...
Star Jeopardy "Review #1
... 1.4 to 3 solar masses becomes a neutron star from a Type II supernova explosion. Above 3 solar masses becomes a black hole ...
... 1.4 to 3 solar masses becomes a neutron star from a Type II supernova explosion. Above 3 solar masses becomes a black hole ...
Stellar Masses and the Main Sequence
... heat with it) or sink back to where it started? In other words, at location r + δr, is it denser or less dense than its new environment? Therefore, for convection to occur ...
... heat with it) or sink back to where it started? In other words, at location r + δr, is it denser or less dense than its new environment? Therefore, for convection to occur ...
Teaching ideas for Option E, Astrophysics
... The magnitude scale is confusing to students when they first meet it, so it is important to give many examples to make sure students understand that the smaller the magnitude the brighter the star appears to be. Students will always ask where the letters OBAFGKM for spectral classes come from. There ...
... The magnitude scale is confusing to students when they first meet it, so it is important to give many examples to make sure students understand that the smaller the magnitude the brighter the star appears to be. Students will always ask where the letters OBAFGKM for spectral classes come from. There ...
What`s Brewing in the Teapot - Indiana University Astronomy
... - causing some very unusual visual distortions. • In the distorted frame, every star in the normal frame has at least two bright images - one on each side of the black hole. •Near the blackhole, you can see the whole sky - light from every direction is bent around and comes back to you. Approaching ...
... - causing some very unusual visual distortions. • In the distorted frame, every star in the normal frame has at least two bright images - one on each side of the black hole. •Near the blackhole, you can see the whole sky - light from every direction is bent around and comes back to you. Approaching ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Younger stars and star forming regions near the center, older stars above and below ...
... Younger stars and star forming regions near the center, older stars above and below ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.