HEIC0410: FOR RELEASE 15:00 (CEST)/9:00 AM EDT 15 June
... Both components of the binary system belong to the L spectral class that includes the lowest mass stars and the highest mass brown dwarfs in our solar neighbourhood. This spectral class was discovered in 1997 and was added to the spectral classification that had remained unchanged for half a century ...
... Both components of the binary system belong to the L spectral class that includes the lowest mass stars and the highest mass brown dwarfs in our solar neighbourhood. This spectral class was discovered in 1997 and was added to the spectral classification that had remained unchanged for half a century ...
Supernovae - Michigan State University
... If a stellar core grows beyond its Chandrasekhar mass limit, it will collapse. Typically this will result in a Supernova explosion at least the outer part of a star is blown off into space ...
... If a stellar core grows beyond its Chandrasekhar mass limit, it will collapse. Typically this will result in a Supernova explosion at least the outer part of a star is blown off into space ...
Chapter 18 Notes - Valdosta State University
... these galaxies had been apparently changed due to the expansion of space towards the red end of the spectrum. He concluded that the universe must be expanding. Hubble's Law states the recessional velocity of a galaxy depends directly on the distance from us to the galaxy. The equation is: ...
... these galaxies had been apparently changed due to the expansion of space towards the red end of the spectrum. He concluded that the universe must be expanding. Hubble's Law states the recessional velocity of a galaxy depends directly on the distance from us to the galaxy. The equation is: ...
Part 1—Stages of Human Life
... life for this high mass star. 2. Shuffle the images and place them in order from youngest to oldest, but do NOT glue them down yet. 3. List the logic and the reasons for why you placed the images in the order you did. (“Because it was a guess” is not an acceptable reason.) ...
... life for this high mass star. 2. Shuffle the images and place them in order from youngest to oldest, but do NOT glue them down yet. 3. List the logic and the reasons for why you placed the images in the order you did. (“Because it was a guess” is not an acceptable reason.) ...
B - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... C. *They are burning helium into carbon and oxygen in their cores D. They are burning helium into carbon and oxygen in a shell around their cores 4. In the process of helium shell fusion in low-mass stars near the end of their lives, the stars moves upward and to the right on the asymptotic giant b ...
... C. *They are burning helium into carbon and oxygen in their cores D. They are burning helium into carbon and oxygen in a shell around their cores 4. In the process of helium shell fusion in low-mass stars near the end of their lives, the stars moves upward and to the right on the asymptotic giant b ...
Announcements
... How do we know it’s a Black Hole? • Only Neutron Stars and Black Holes have strong enough gravity to make infalling gas hot enough to emit x-rays. • If can determine mass of suspect (in a binary system) & Mass > 3 Msun Must be Black Hole ...
... How do we know it’s a Black Hole? • Only Neutron Stars and Black Holes have strong enough gravity to make infalling gas hot enough to emit x-rays. • If can determine mass of suspect (in a binary system) & Mass > 3 Msun Must be Black Hole ...
The Life Cycles of Stars, Part I
... ball of neutrons. It is possible that this core will remain intact after the supernova, and be called a neutron star. However, if the original star was very massive (say 15 or more times the mass of our Sun), even the neutrons will not be able to survive the core collapse and a black hole will form! ...
... ball of neutrons. It is possible that this core will remain intact after the supernova, and be called a neutron star. However, if the original star was very massive (say 15 or more times the mass of our Sun), even the neutrons will not be able to survive the core collapse and a black hole will form! ...
Слайд 1 - University of Wrocław
... 2. The neutron star matter is so dense that P is almost independen t of the temperatu re T and is determined by the mass density and the compositio n of the matter; one usually w rites P P ( ). 3. The mass density is defined as E / c 2 , where E [erg/cc] is the total energy density (includ ...
... 2. The neutron star matter is so dense that P is almost independen t of the temperatu re T and is determined by the mass density and the compositio n of the matter; one usually w rites P P ( ). 3. The mass density is defined as E / c 2 , where E [erg/cc] is the total energy density (includ ...
01.05.10 Centuries-Old Star Mystery Coming to a Close For almost
... Now, new observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope -- in combination with archived ultraviolet, visible and other infrared data -- point to one of two competing theories, and a likely solution to this age-old puzzle. One theory holds that the bright star is a massive supergiant, periodically ...
... Now, new observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope -- in combination with archived ultraviolet, visible and other infrared data -- point to one of two competing theories, and a likely solution to this age-old puzzle. One theory holds that the bright star is a massive supergiant, periodically ...
Estimate the Kelvin-Helmholtz timescale for a 5 solar mass star on
... figure 13.7, and accommodate a drop in radius by a factor of 100 as the temperature rises from about 107 K to about 108 K between hydrogen exhaustion and helium core ignition, using a blackbody approximation for constant core luminosity). If these values are substituted into the above calculation, t ...
... figure 13.7, and accommodate a drop in radius by a factor of 100 as the temperature rises from about 107 K to about 108 K between hydrogen exhaustion and helium core ignition, using a blackbody approximation for constant core luminosity). If these values are substituted into the above calculation, t ...
11 Stellar Remnants - Journigan-wiki
... dwarfs different from ordinary stars, although they are at hydrostatic equilibrium. External pressure is supplied by an interaction between its electrons that limit how many can occupy a given volume. This gives the remnant a peculiar property, added mass will make the white ...
... dwarfs different from ordinary stars, although they are at hydrostatic equilibrium. External pressure is supplied by an interaction between its electrons that limit how many can occupy a given volume. This gives the remnant a peculiar property, added mass will make the white ...
Sun, Stars, HR Diagram
... C) become hotter and expand into a blue supergiant D) to become a black hole 17. By using a spectroscope an astronomer can A) B) C) D) ...
... C) become hotter and expand into a blue supergiant D) to become a black hole 17. By using a spectroscope an astronomer can A) B) C) D) ...
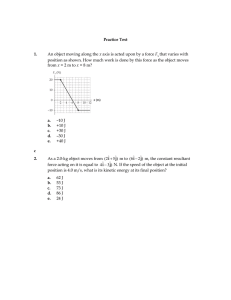
Practice Test 1. An object moving along the x axis is acted upon by a
... P should be directed upwards, not down. P should be perpendicular to the wall, not parallel to it. N should be down into the floor for f s to have the given direction. P is correct, but there should also be a force perpendicular to the wall. ...
... P should be directed upwards, not down. P should be perpendicular to the wall, not parallel to it. N should be down into the floor for f s to have the given direction. P is correct, but there should also be a force perpendicular to the wall. ...
Slide 1
... looking at data from a radio telescope and found, much to her surprise, that one radio source was emitting a pulse of radiation every 1.33 seconds. For a while, astronomers thought this might be a signal from intelligent extraterrestrials: “little green men.” Soon, however, many more of these source ...
... looking at data from a radio telescope and found, much to her surprise, that one radio source was emitting a pulse of radiation every 1.33 seconds. For a while, astronomers thought this might be a signal from intelligent extraterrestrials: “little green men.” Soon, however, many more of these source ...
Galactic Neighborhood and (Chandra-enabled) X-ray Astrophysics Q. Daniel Wang
... enough background sources, which causes the cosmic variance. • To check physical properties of hot plasma near outer boundaries if they are present. Mkn 231, 0.5 Ms ACIS 0.5-8 keV Veilleux et al. 2014 ...
... enough background sources, which causes the cosmic variance. • To check physical properties of hot plasma near outer boundaries if they are present. Mkn 231, 0.5 Ms ACIS 0.5-8 keV Veilleux et al. 2014 ...
HR Diagram - Geneva 304
... Stars Star Color and Temperature 1. Stars give off _____ wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. 2. What is the peak wavelength of a star? 3. A star that is _____ in color is hotter than a yellow star. This means that stars with _____ have a hotter temperature. 4. Stars are referred to as _____ be ...
... Stars Star Color and Temperature 1. Stars give off _____ wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. 2. What is the peak wavelength of a star? 3. A star that is _____ in color is hotter than a yellow star. This means that stars with _____ have a hotter temperature. 4. Stars are referred to as _____ be ...
BlackBubbles2014
... Near Black Holes An astronaut descending down towards the event horizon of the black hole will be stretched vertically (tidal effects) and squeezed laterally unless the black hole is very large like thousands of solar masses, so the multi-million solar mass black hole in the center of the galaxy is ...
... Near Black Holes An astronaut descending down towards the event horizon of the black hole will be stretched vertically (tidal effects) and squeezed laterally unless the black hole is very large like thousands of solar masses, so the multi-million solar mass black hole in the center of the galaxy is ...
Astronomical terms and constants
... mbol = Mbol + 5 log (d/10pc) = apparent bolometric magnitude of a star at a distance d . V = MV + 5 log (d/10pc) = apparent “visual” magnitude of a star as seen in the sky. B = MB + 5 log (d/10pc) = apparent “blue” magnitude of a star as seen in the sky. B − V = MB − MV = a difference between “visua ...
... mbol = Mbol + 5 log (d/10pc) = apparent bolometric magnitude of a star at a distance d . V = MV + 5 log (d/10pc) = apparent “visual” magnitude of a star as seen in the sky. B = MB + 5 log (d/10pc) = apparent “blue” magnitude of a star as seen in the sky. B − V = MB − MV = a difference between “visua ...
The Life and Death of Stars
... White dwarf created by stars after Red Giant phase Stars which have 1/10 to 8 solar masses Small – about the size of the earth Similar mass to our Sun Therefore very dense – A teaspoon of white dwarf matter weighs 5 tons (5000 kg) ...
... White dwarf created by stars after Red Giant phase Stars which have 1/10 to 8 solar masses Small – about the size of the earth Similar mass to our Sun Therefore very dense – A teaspoon of white dwarf matter weighs 5 tons (5000 kg) ...
Observations of Water and other molecules in Protoplanetary Disk
... Small scales at large distances make resolution of planet-forming regions difficult. The bulk of the disk mass is H2, which is difficult to detect. ...
... Small scales at large distances make resolution of planet-forming regions difficult. The bulk of the disk mass is H2, which is difficult to detect. ...
Stellar Evolution
... need to consider two more areas before we begin to put this all together and see if we can see some kind of “stellar life cycle” (also called stellar evolution). Those last two areas are interstellar material: atoms, dust, and nebula; and variable stars. ...
... need to consider two more areas before we begin to put this all together and see if we can see some kind of “stellar life cycle” (also called stellar evolution). Those last two areas are interstellar material: atoms, dust, and nebula; and variable stars. ...
Star Life Cycle Powerpoin
... BLACK DWARFS • As the white dwarf cools, the light it gives off will fade through the visible light spectrum, blue to red to back (no light). ...
... BLACK DWARFS • As the white dwarf cools, the light it gives off will fade through the visible light spectrum, blue to red to back (no light). ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... 2nd Item Specification: Recognize the life-cycles of mid-size and massive stars and their stellar remnants. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 8. When fusion of hydrogen ceases in our Sun’s core, the Sun will A. explode as a supernova. B. collapse into white dwarf star. C. contract into a black hole. D. exp ...
... 2nd Item Specification: Recognize the life-cycles of mid-size and massive stars and their stellar remnants. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 8. When fusion of hydrogen ceases in our Sun’s core, the Sun will A. explode as a supernova. B. collapse into white dwarf star. C. contract into a black hole. D. exp ...
Lect22
... hole and a normal star, the material from the normal star can be pulled into the black hole This material forms an accretion disk around the black hole Friction among the particles in the disk transforms mechanical energy into internal energy The orbital height of the material above the event horizo ...
... hole and a normal star, the material from the normal star can be pulled into the black hole This material forms an accretion disk around the black hole Friction among the particles in the disk transforms mechanical energy into internal energy The orbital height of the material above the event horizo ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.