The Milky Way Galaxy
... Younger stars and star forming regions near the center, older stars above and below ...
... Younger stars and star forming regions near the center, older stars above and below ...
slides
... The central core (which, in the most massive stars, is made of iron) undergoes a sudden gravitational collapse, reducing in size until all the electrons in the atoms are smashed down into the nulcei. ...
... The central core (which, in the most massive stars, is made of iron) undergoes a sudden gravitational collapse, reducing in size until all the electrons in the atoms are smashed down into the nulcei. ...
formation2
... • This pocket of over density is much bigger than a single star. • This over dense region is not uniform, but has within it other, smaller regions of high density. • As the over density begins to be drawn together by gravity, it fragments into smaller pockets of gas which go on to form individual st ...
... • This pocket of over density is much bigger than a single star. • This over dense region is not uniform, but has within it other, smaller regions of high density. • As the over density begins to be drawn together by gravity, it fragments into smaller pockets of gas which go on to form individual st ...
Gravitational Waves Homework 5 Questions? Uncharged black
... h = 0.01. Depends on source, distance. (h is called the “dimensionless strain”) ...
... h = 0.01. Depends on source, distance. (h is called the “dimensionless strain”) ...
Lecture 15
... opacity over all wavelengths • Weight by the rate at which Intensity distribution (blackbody radiation) varies with temperature. • Determine dependence of other parameters such as temperature ...
... opacity over all wavelengths • Weight by the rate at which Intensity distribution (blackbody radiation) varies with temperature. • Determine dependence of other parameters such as temperature ...
Lecture 10a Neutron Star and Black Holes (Test 2 overview)
... • Black holes can keep accumulating mass…including “colliding” Black holes. Very massive (million times mass Sun) at center of many galaxies ...
... • Black holes can keep accumulating mass…including “colliding” Black holes. Very massive (million times mass Sun) at center of many galaxies ...
Birth and Life of a Star
... fusing Hydrogen into Helium and then Helium into Lithium . Our sun has insufficient mass to fuse heavier elements than Carbon. Heavier elements like gold, lead and iron are created in much larger stars. The Expansion Phase: The Hydrogen in the core of the star has all been used and the star starts t ...
... fusing Hydrogen into Helium and then Helium into Lithium . Our sun has insufficient mass to fuse heavier elements than Carbon. Heavier elements like gold, lead and iron are created in much larger stars. The Expansion Phase: The Hydrogen in the core of the star has all been used and the star starts t ...
Birth and Life of a Star
... fusing Hydrogen into Helium and then Helium into Lithium . Our sun has insufficient mass to fuse heavier elements than Carbon. Heavier elements like gold, lead and iron are created in much larger stars. The Expansion Phase: The Hydrogen in the core of the star has all been used and the star starts t ...
... fusing Hydrogen into Helium and then Helium into Lithium . Our sun has insufficient mass to fuse heavier elements than Carbon. Heavier elements like gold, lead and iron are created in much larger stars. The Expansion Phase: The Hydrogen in the core of the star has all been used and the star starts t ...
A not so massive cluster hosting a very massive star
... spectroscopically observed the cluster main-sequence stellar population and a very-massive star candidate: WR62-2. CMFGEN modelling to our near-infrared spectra indicates that WR62-2 is a very luminous (106.4±0.2 L ) and massive (∼ 80M ) star. The current census of Wolf-Rayet (WR) in the Milky Way ...
... spectroscopically observed the cluster main-sequence stellar population and a very-massive star candidate: WR62-2. CMFGEN modelling to our near-infrared spectra indicates that WR62-2 is a very luminous (106.4±0.2 L ) and massive (∼ 80M ) star. The current census of Wolf-Rayet (WR) in the Milky Way ...
Teacher`s Guide The Solar Empire: A Star is Born
... Context: The temperature shoots up another two million degrees above the already scorching surface in the sun’s corona. cosmic rays Definition: Extremely high-energy, short wavelength particles such as protons, neutrons, and atomic nuclei which originate outside the solar system. Context: Harmful co ...
... Context: The temperature shoots up another two million degrees above the already scorching surface in the sun’s corona. cosmic rays Definition: Extremely high-energy, short wavelength particles such as protons, neutrons, and atomic nuclei which originate outside the solar system. Context: Harmful co ...
CBradleyLoutl
... . Looking at what wavelengths of light are present on emission/absorption spectra will tell exact constituents. Examples: ...
... . Looking at what wavelengths of light are present on emission/absorption spectra will tell exact constituents. Examples: ...
Stars Part Two
... in England was studying the scintillation of radio sources due to the solar wind. 2. A graduate student named Jocelyn Bell Burnell discovered a strong night time source of “twinkling”. 3. Its location was fixed with respect to the stars. From Jay Pasachoff’s “Contemporary Astronomy” ...
... in England was studying the scintillation of radio sources due to the solar wind. 2. A graduate student named Jocelyn Bell Burnell discovered a strong night time source of “twinkling”. 3. Its location was fixed with respect to the stars. From Jay Pasachoff’s “Contemporary Astronomy” ...
bYTEBoss lesson 3 life of star
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
QSOs . Continuum Radiation Energy Source
... Velocities of stars in very center 4 million M black hole at position of Sagittarius A* ...
... Velocities of stars in very center 4 million M black hole at position of Sagittarius A* ...
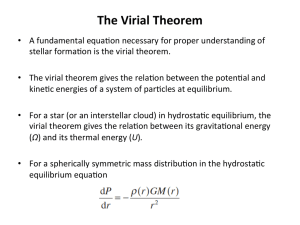
The Virial Theorem
... • the average kine-c energy of the par-cles in a gas at temperature T is equal to 3kT/2. • If N is the total number of par-cles in a given volume V small enough inside the star so tha ...
... • the average kine-c energy of the par-cles in a gas at temperature T is equal to 3kT/2. • If N is the total number of par-cles in a given volume V small enough inside the star so tha ...
Stellar Evolution Lab
... Stage 1- Stars are born in clouds of gas and dust called Nebulas. Stage 2- The gas and dust spiral together and contract under their own gravity. The gas and dust will begin to heat up and start to glow forming Protostars. Stage 3- If a protostar contains enough matter, the central temperature will ...
... Stage 1- Stars are born in clouds of gas and dust called Nebulas. Stage 2- The gas and dust spiral together and contract under their own gravity. The gas and dust will begin to heat up and start to glow forming Protostars. Stage 3- If a protostar contains enough matter, the central temperature will ...
Life and Death of a Star
... • Compare and Contrast the Life of a Star to the Life of a Human. Mention the Growth, Stages of Development, Life Expectancy, and Death of Each. • Compare and Contrast the Formation, Life, Destruction and Recycling of Veterans Stadium to a Solar System • Compare and Contrast the Big Bang to a Bag of ...
... • Compare and Contrast the Life of a Star to the Life of a Human. Mention the Growth, Stages of Development, Life Expectancy, and Death of Each. • Compare and Contrast the Formation, Life, Destruction and Recycling of Veterans Stadium to a Solar System • Compare and Contrast the Big Bang to a Bag of ...
Document
... 1. An x-ray source was discovered in the constellation Cygnus in 1972 (Cygnus X-1). X-ray sources are candidates for black holes because matter streaming into black holes will be ionized and greatly accelerated, producing x-rays. 2. A blue supergiant star, about 15 times the mass of the sun, was fou ...
... 1. An x-ray source was discovered in the constellation Cygnus in 1972 (Cygnus X-1). X-ray sources are candidates for black holes because matter streaming into black holes will be ionized and greatly accelerated, producing x-rays. 2. A blue supergiant star, about 15 times the mass of the sun, was fou ...
White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
... • By accumulating mass (hydrogen), periodic bursts of fusion can occur on the surface called a nova • If too much mass is accumulated, the explosion may take place within the star blowing it apart in a supernova • Supernovae can also happen if two white dwarfs collide ...
... • By accumulating mass (hydrogen), periodic bursts of fusion can occur on the surface called a nova • If too much mass is accumulated, the explosion may take place within the star blowing it apart in a supernova • Supernovae can also happen if two white dwarfs collide ...
Birth of Stars
... 5: Stars are a part of the universe, mankind needs them. Stars like Supernovas, (Supernova: A rare explosion of most of the material in a star, causing an extremely bright, short-lived object that emits large amounts of energy) are needed because the oxygen you breathe, carbon in your bones, and hyd ...
... 5: Stars are a part of the universe, mankind needs them. Stars like Supernovas, (Supernova: A rare explosion of most of the material in a star, causing an extremely bright, short-lived object that emits large amounts of energy) are needed because the oxygen you breathe, carbon in your bones, and hyd ...
Problem Set 04
... a 2.0 m hill and collides with 20,000 kg boxcar initially at rest. The two cars couple in the collision and roll into a large spring (with spring constant 4.0×106 N/m). The spring sends the coupled cars back left towards the hill. Given this information please determine the following (being sure to ...
... a 2.0 m hill and collides with 20,000 kg boxcar initially at rest. The two cars couple in the collision and roll into a large spring (with spring constant 4.0×106 N/m). The spring sends the coupled cars back left towards the hill. Given this information please determine the following (being sure to ...
The Life Cycles of Stars, Part II
... supernova. Neutron stars spin rapidly giving off radio waves. If the radio waves are emitted in pulses (due to the star’s spin), these neutron stars are called pulsars. The core of a massive star that has 8 or more times the mass of our Sun remains massive after the supernova. No nuclear fusion is t ...
... supernova. Neutron stars spin rapidly giving off radio waves. If the radio waves are emitted in pulses (due to the star’s spin), these neutron stars are called pulsars. The core of a massive star that has 8 or more times the mass of our Sun remains massive after the supernova. No nuclear fusion is t ...
The Life Cycles of Stars
... supernova. Neutron stars spin rapidly giving off radio waves. If the radio waves are emitted in pulses (due to the star’s spin), these neutron stars are called pulsars. The core of a massive star that has 8 or more times the mass of our Sun remains massive after the supernova. No nuclear fusion is t ...
... supernova. Neutron stars spin rapidly giving off radio waves. If the radio waves are emitted in pulses (due to the star’s spin), these neutron stars are called pulsars. The core of a massive star that has 8 or more times the mass of our Sun remains massive after the supernova. No nuclear fusion is t ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.