WHO/CDS/CSR/EDC/99.1 Influenza Pandemic Plan. The Role of WHO and Guidelines
... from the preceding epidemic. The viruses are spreading among people with varying levels of immunity from infections earlier in life. Such circulation, over a period of usually 2-3 years, promotes the selection of new strains which have changed enough to again cause an epidemic among the general popu ...
... from the preceding epidemic. The viruses are spreading among people with varying levels of immunity from infections earlier in life. Such circulation, over a period of usually 2-3 years, promotes the selection of new strains which have changed enough to again cause an epidemic among the general popu ...
Report for week ending January 25, 2014
... Sporadic: Small numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported. Local: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported in a single region of New York State; sporadic in rest of state. Regional: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of infl ...
... Sporadic: Small numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported. Local: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported in a single region of New York State; sporadic in rest of state. Regional: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of infl ...
Future Global Shocks: Pandemics
... real-time about pandemic risk inventories, hazards or threatened segments of the built or natural infrastructure, 2) there is a dramatic lack of forward thinking and planning for the creation and distribution of medical countermeasures—including drugs, vaccines and surge capacity, which, in part, ar ...
... real-time about pandemic risk inventories, hazards or threatened segments of the built or natural infrastructure, 2) there is a dramatic lack of forward thinking and planning for the creation and distribution of medical countermeasures—including drugs, vaccines and surge capacity, which, in part, ar ...
Report for week ending May 17, 2014
... Sporadic: Small numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported. Local: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported in a single region of New York State; sporadic in rest of state. Regional: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of infl ...
... Sporadic: Small numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported. Local: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported in a single region of New York State; sporadic in rest of state. Regional: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of infl ...
Report for week ending April 26, 2014
... Sporadic: Small numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported. Local: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported in a single region of New York State; sporadic in rest of state. Regional: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of infl ...
... Sporadic: Small numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported. Local: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of influenza reported in a single region of New York State; sporadic in rest of state. Regional: Increased or sustained numbers of lab‐confirmed cases of infl ...
Swine influenza
... WHO: having cared for, lived with, or had direct contact with respiratory secretions or body fluids of a probable or confirmed case of swine influenza A (H1N1). WHO未訂距離 ...
... WHO: having cared for, lived with, or had direct contact with respiratory secretions or body fluids of a probable or confirmed case of swine influenza A (H1N1). WHO未訂距離 ...
Avian influenza in humans
... typically from the day before17 (and up to a maximum of 5 days before)18 symptoms begin until usually 7 days after19 (and up to a maximum of 14 days after)20 symptoms begin. For practical public health purposes, adults and children older than 12 years of age should be considered infectious from 1 da ...
... typically from the day before17 (and up to a maximum of 5 days before)18 symptoms begin until usually 7 days after19 (and up to a maximum of 14 days after)20 symptoms begin. For practical public health purposes, adults and children older than 12 years of age should be considered infectious from 1 da ...
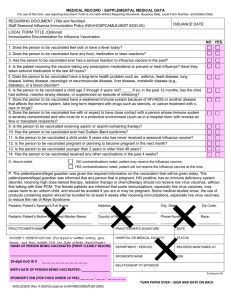
Flu Questionnaire
... P. The patient/parent/legal guardian was given the required information on the vaccination that will be given today. The patient/parent/legal guardian was informed that any person that is pregnant, HIV positive, has an immune deficiency system disorder, receiving high dose steroid therapy, radiation ...
... P. The patient/parent/legal guardian was given the required information on the vaccination that will be given today. The patient/parent/legal guardian was informed that any person that is pregnant, HIV positive, has an immune deficiency system disorder, receiving high dose steroid therapy, radiation ...
Strategy Plan for Execution of Influenza Pandemic Response
... Kazakhstan, Nigeria, Iraq, and Turkey and into Europe can be traced back to the same source with the avian flu virus that infected wild birds in Qinghai Lake in northwestern China in spring 2005.[1,2] Besides, a survey around Poyang Lake in China showed that as much as 3.1% of wild duck excretion wa ...
... Kazakhstan, Nigeria, Iraq, and Turkey and into Europe can be traced back to the same source with the avian flu virus that infected wild birds in Qinghai Lake in northwestern China in spring 2005.[1,2] Besides, a survey around Poyang Lake in China showed that as much as 3.1% of wild duck excretion wa ...
The Spanish Flu – Part II: the second and third wave
... enza“. He also pointed out the possibility of the disease being caused by a virus 17. It was in this year that the influenza virus was isolated from swine, and two years later, so was the human virus. A clinical picture of the Spanish Flu was well depicted by Dr. Dimitrije Antiü on a poster printed ...
... enza“. He also pointed out the possibility of the disease being caused by a virus 17. It was in this year that the influenza virus was isolated from swine, and two years later, so was the human virus. A clinical picture of the Spanish Flu was well depicted by Dr. Dimitrije Antiü on a poster printed ...
Phase 0, Level 3: Pandemic Alert
... flu virus emerges to which few people, if any, have immunity. Any vaccine or therapeutic drugs are likely to be delayed and in short supply. Because of these features, pandemic flu is likely to last several months and affect a large percentage of the national and world population, causing major soci ...
... flu virus emerges to which few people, if any, have immunity. Any vaccine or therapeutic drugs are likely to be delayed and in short supply. Because of these features, pandemic flu is likely to last several months and affect a large percentage of the national and world population, causing major soci ...
Abstract
... active against the novel H1N1v 2009 pandemic influenza A strain. The recommended adult dose for oseltamivir, considered the first-line therapy for H1N1 influenza infection, is 75 mg orally twice a day for a total of 5 days [44]. Dose adjustment may be required in the presence of reduced creatinine c ...
... active against the novel H1N1v 2009 pandemic influenza A strain. The recommended adult dose for oseltamivir, considered the first-line therapy for H1N1 influenza infection, is 75 mg orally twice a day for a total of 5 days [44]. Dose adjustment may be required in the presence of reduced creatinine c ...
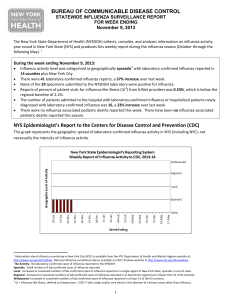
Report for week ending November 9, 2013
... There were 41 laboratory‐confirmed influenza reports, a 37% increase over last week. None of the 29 specimens submitted to the NYSDOH laboratory were positive for influenza. Reports of percent of patient visits for influenza‐like illness (ILI3) from ILINet providers was 0.53%, which is below the ...
... There were 41 laboratory‐confirmed influenza reports, a 37% increase over last week. None of the 29 specimens submitted to the NYSDOH laboratory were positive for influenza. Reports of percent of patient visits for influenza‐like illness (ILI3) from ILINet providers was 0.53%, which is below the ...
Contingency Plan for Management of Human Cases of Avian Influenza
... epidemics (“pandemics”) with high morbidity and mortality. The present outbreak of H5N1 Avian Influenza in the south-east asian countries merits attention because of increasing evidence to suggest that the avian strains are getting more virulent, capable of causing severe disease. As of now, it has ...
... epidemics (“pandemics”) with high morbidity and mortality. The present outbreak of H5N1 Avian Influenza in the south-east asian countries merits attention because of increasing evidence to suggest that the avian strains are getting more virulent, capable of causing severe disease. As of now, it has ...
Influenza Vaccination
... known whether or not a transplant patient can be severely infected with the weakened LAIV influenza virus. No serious illness was observed in children (with normal immune systems) who inadvertently became infected with the weakened LAIV influenza virus (please see CDC statement in appendix for furth ...
... known whether or not a transplant patient can be severely infected with the weakened LAIV influenza virus. No serious illness was observed in children (with normal immune systems) who inadvertently became infected with the weakened LAIV influenza virus (please see CDC statement in appendix for furth ...
Influenza A (H1N1) - AIDS Education and Training Centers
... antibody evidence of influenza A(H1N1) flu infection but no serious illnesses were detected Severity from mild to severe. Severe disease ...
... antibody evidence of influenza A(H1N1) flu infection but no serious illnesses were detected Severity from mild to severe. Severe disease ...
National Influenza Pandemic Preparedness Plan
... Development of influenza viruses with pandemic potential Many animal influenza viruses naturally infect and circulate among avian and mammalian species. Most of these animal influenza viruses do not normally infect humans. However, on occasion, certain animal viruses ...
... Development of influenza viruses with pandemic potential Many animal influenza viruses naturally infect and circulate among avian and mammalian species. Most of these animal influenza viruses do not normally infect humans. However, on occasion, certain animal viruses ...
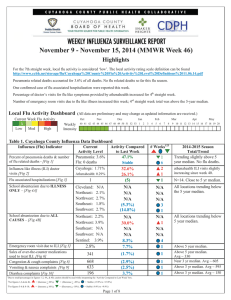
Table 1. Cuyahoga County Influenza Data Dashboard
... http://www.ccbh.net/storage/flu/Cuyahoga%20County%20Flu%20Activity%20Level%20Definitions%2011.06.14.pdf Pneumonia related deaths accounted for 3.6% of all deaths. No flu related deaths so far this flu season. One confirmed case of flu associated hospitalization were reported this week. Percentage of ...
... http://www.ccbh.net/storage/flu/Cuyahoga%20County%20Flu%20Activity%20Level%20Definitions%2011.06.14.pdf Pneumonia related deaths accounted for 3.6% of all deaths. No flu related deaths so far this flu season. One confirmed case of flu associated hospitalization were reported this week. Percentage of ...
2009 – 2010 Flu Season – Key Messages
... H1N1 influenza is affecting a somewhat different set of the population, including children and young adults. If H1N1 flu is severe, it could change daily life for a time, including limitations on travel and public gatherings. ...
... H1N1 influenza is affecting a somewhat different set of the population, including children and young adults. If H1N1 flu is severe, it could change daily life for a time, including limitations on travel and public gatherings. ...
Buncombe County Government
... H1N1 influenza is affecting a somewhat different set of the population, including children and young adults. If H1N1 flu is severe, it could change daily life for a time, including limitations on travel and public gatherings. ...
... H1N1 influenza is affecting a somewhat different set of the population, including children and young adults. If H1N1 flu is severe, it could change daily life for a time, including limitations on travel and public gatherings. ...
Massachusetts Department of Public Health (MDPH)
... ILI is defined as fever > 100o F with cough and/or sore throat, in the absence of a known cause. 1. MDPH epidemiologists can facilitate testing and provide control recommendations in the event of an outbreak. To prevent the transmission of all respiratory infections, including flu, implement the inf ...
... ILI is defined as fever > 100o F with cough and/or sore throat, in the absence of a known cause. 1. MDPH epidemiologists can facilitate testing and provide control recommendations in the event of an outbreak. To prevent the transmission of all respiratory infections, including flu, implement the inf ...
blank slide with blue background and CDC logo
... Those who participate in the COCA Conference Calls and who wish to receive continuing education and will complete the online evaluation by August 14, 2009 will use the course code EC1265. Those who wish to receive continuing education and will complete the online evaluation between August 15, 2009 a ...
... Those who participate in the COCA Conference Calls and who wish to receive continuing education and will complete the online evaluation by August 14, 2009 will use the course code EC1265. Those who wish to receive continuing education and will complete the online evaluation between August 15, 2009 a ...