CV- RambaccussingOct2010 (5)
... A Real time Trading Rule This paper tests the profitability of a trading strategy which consists in identifying whether equity indices are under or overvalued in real-time. The model rests on the assumptions that the equity index is dynamically efficient and that mean reversion to the fundamental pr ...
... A Real time Trading Rule This paper tests the profitability of a trading strategy which consists in identifying whether equity indices are under or overvalued in real-time. The model rests on the assumptions that the equity index is dynamically efficient and that mean reversion to the fundamental pr ...
For Whom the Bell Tolls: The Demise of Exchange
... exchanges have raised regulatory concerns. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) have been struggling with that issue for nearly a decade. The SEC‘s burdensome regulations are driving capital away from public markets such as the NYSE and Nas ...
... exchanges have raised regulatory concerns. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) have been struggling with that issue for nearly a decade. The SEC‘s burdensome regulations are driving capital away from public markets such as the NYSE and Nas ...
Equilibrium Pricing and Trading Volume under Preference
... which firms’ willingness and ability to hold assets is reduced, due, e.g., to losses (Berndt et al., 2005), increased risk, asset downgrades or index changes (Greenwood, 2005), or margin calls and fund outflows (Coval and Stafford, 2007). As mentioned above, it is in such times of stress that prefe ...
... which firms’ willingness and ability to hold assets is reduced, due, e.g., to losses (Berndt et al., 2005), increased risk, asset downgrades or index changes (Greenwood, 2005), or margin calls and fund outflows (Coval and Stafford, 2007). As mentioned above, it is in such times of stress that prefe ...
Large Cap Value Select UMA Hancock Horizon
... Past performance is no guarantee of future results. Actual individual account results may differ from the performance shown in this profile. There is no guarantee that this investment strategy will work under all market conditions. Do not use this profile as the sole basis for your investment decisi ...
... Past performance is no guarantee of future results. Actual individual account results may differ from the performance shown in this profile. There is no guarantee that this investment strategy will work under all market conditions. Do not use this profile as the sole basis for your investment decisi ...
testing of risk anomalies in indian equity market by using
... sampling method adopted in our study. Fourth section explains research methodology which is followed by analysis. Sixth section briefly explains research findings while making recommendations and the last section concludes our research. LITERATURE REVIEW Throughout the world there have been many exa ...
... sampling method adopted in our study. Fourth section explains research methodology which is followed by analysis. Sixth section briefly explains research findings while making recommendations and the last section concludes our research. LITERATURE REVIEW Throughout the world there have been many exa ...
The Futures Market
... How do futures market prices change? 3. The relationship between supply and demand come together to create a price. a. Supply increases if people are willing and able to supply more of a product or service at every price. For example, supply would increase if farmers were willing to produce 8,000 po ...
... How do futures market prices change? 3. The relationship between supply and demand come together to create a price. a. Supply increases if people are willing and able to supply more of a product or service at every price. For example, supply would increase if farmers were willing to produce 8,000 po ...
Short- Sale Constraints and Dispersion of Opinion: Evidence from
... Options are traded in the National Stock Exchange and the Bombay Stock Exchange, whereas Futures are traded in the National Stock Exchange, the Bombay Stock Exchange and the Singapore Stock exchange. Both NSE and BSE have moved to an electronic platform, eliminating arbitrage opportunities from pric ...
... Options are traded in the National Stock Exchange and the Bombay Stock Exchange, whereas Futures are traded in the National Stock Exchange, the Bombay Stock Exchange and the Singapore Stock exchange. Both NSE and BSE have moved to an electronic platform, eliminating arbitrage opportunities from pric ...
What Price for a Dark Pool?
... similar. Essentially, buyers and sellers submit orders into the Pool. The main conditions that buyers and sellers attach to their orders are a limit price, minimum execution size (both these are generally optional) and importantly, whether they wish their order to remain on the Dark Pool as a restin ...
... similar. Essentially, buyers and sellers submit orders into the Pool. The main conditions that buyers and sellers attach to their orders are a limit price, minimum execution size (both these are generally optional) and importantly, whether they wish their order to remain on the Dark Pool as a restin ...
Information Aggregation and Allocative Efficiency in Smooth Markets
... cannot take opposing positions in the market and both expect to be better off. However, with risk aversion, trading can occur even if all traders are rational: traders may trade purely on the motive of hedging, if the initial allocation of risk is not ex-ante Pareto efficient. More generally, even i ...
... cannot take opposing positions in the market and both expect to be better off. However, with risk aversion, trading can occur even if all traders are rational: traders may trade purely on the motive of hedging, if the initial allocation of risk is not ex-ante Pareto efficient. More generally, even i ...
Exam MFE - Society of Actuaries
... Your company has just written one million units of a one-year European asset-or-nothing put option on an equity index fund. The equity index fund is currently trading at 1000. It pays dividends continuously at a rate proportional to its price; the dividend yield is 2%. It has a volatility of 20%. Th ...
... Your company has just written one million units of a one-year European asset-or-nothing put option on an equity index fund. The equity index fund is currently trading at 1000. It pays dividends continuously at a rate proportional to its price; the dividend yield is 2%. It has a volatility of 20%. Th ...
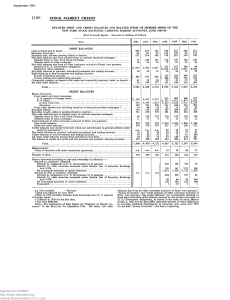
Detailed Debit and Credit Balances and Related Items of Member
... i Before 1958 probably includes some borrowing from U.S. agencies of foreign banks. NOTE.—End of month figures. Data not collected for June 1957. For explanation of these figures see "Statistics on Margin Accounts," Sept. 1936 BULL. The items "net debit balances due from all other customers exclusiv ...
... i Before 1958 probably includes some borrowing from U.S. agencies of foreign banks. NOTE.—End of month figures. Data not collected for June 1957. For explanation of these figures see "Statistics on Margin Accounts," Sept. 1936 BULL. The items "net debit balances due from all other customers exclusiv ...
Locals, foreigners, and multi-market trading of equities: Intraday
... The record of orders and trades supplied by the SET covers 58 of the more active issues listed on the SET, and 45 of these show activity on both the Main Board and the Alien Board. We restrict our sample to the 25 most active of these stocks, to ensure that we have sufficient data for analysis and, i ...
... The record of orders and trades supplied by the SET covers 58 of the more active issues listed on the SET, and 45 of these show activity on both the Main Board and the Alien Board. We restrict our sample to the 25 most active of these stocks, to ensure that we have sufficient data for analysis and, i ...
Price Impact and the Recovery of the Limit Order Book
... some impact of the trade on the price. In contrast to price discovery, price recovery is assigned by inventory control costs in the market maker literature. However this analogy can be applied in limit order markets, the theory often connects the recovery process to the limit order submitting proced ...
... some impact of the trade on the price. In contrast to price discovery, price recovery is assigned by inventory control costs in the market maker literature. However this analogy can be applied in limit order markets, the theory often connects the recovery process to the limit order submitting proced ...
Market-Wide Impact of the Disposition Effect: Evidence from IPO
... investments are ‘in the black’. This effect should be strongest for IPOs that have previously not traded above the offer price, i.e. on the day that an issue with negative initial return crosses the offer price from below for the first time. The timing of the increased volume also depends on the fre ...
... investments are ‘in the black’. This effect should be strongest for IPOs that have previously not traded above the offer price, i.e. on the day that an issue with negative initial return crosses the offer price from below for the first time. The timing of the increased volume also depends on the fre ...
The impact of dark trading and visible fragmentation on market quality
... computer programs to manage and execute trades in electronic limit order books. Algorithmic trading has strongly increased over time, and has drastically affected the trading environment (Hendershott and Riordan, 2009). In particular, it affects the level of market fragmentation analyzed in our samp ...
... computer programs to manage and execute trades in electronic limit order books. Algorithmic trading has strongly increased over time, and has drastically affected the trading environment (Hendershott and Riordan, 2009). In particular, it affects the level of market fragmentation analyzed in our samp ...
How are stock prices a!ected by the location of trade?
... The classical "nance paradigm predicts that an asset's price is una!ected by its location of trade. If international "nancial markets are perfectly integrated, then a given set of risky cash #ows has the same value and risk characteristics when its trade is redistributed across markets and investors ...
... The classical "nance paradigm predicts that an asset's price is una!ected by its location of trade. If international "nancial markets are perfectly integrated, then a given set of risky cash #ows has the same value and risk characteristics when its trade is redistributed across markets and investors ...
Liquidity Risk and Asset Pricing
... (5) the returns on hedge funds, (6) the valuation of closed-end funds, and (7) the low price of certain hard-to-trade securities relative to more liquid counterparts with identical cash flows, such as restricted stocks or illiquid derivatives. ...
... (5) the returns on hedge funds, (6) the valuation of closed-end funds, and (7) the low price of certain hard-to-trade securities relative to more liquid counterparts with identical cash flows, such as restricted stocks or illiquid derivatives. ...
Market Risk Management
... In a Markov process, the past cannot be used to predict the future. Stock prices are usually assumed to follow a Markov process. This means all the past data have been discounted by the current stock price. Let us elaborate this through a simple example provided by Paul Wilmott in his book “Quantita ...
... In a Markov process, the past cannot be used to predict the future. Stock prices are usually assumed to follow a Markov process. This means all the past data have been discounted by the current stock price. Let us elaborate this through a simple example provided by Paul Wilmott in his book “Quantita ...
Information Asymmetry Surrounding Earnings and
... When we use bid-ask spread as the dependent variable, firm size is significant. This implies that the bigger the size of the firm, the higher the reduction of bid-ask spread, contrary to our predictions. (+-) is significantly positive for all the regressions, suggesting that firms with a positive ea ...
... When we use bid-ask spread as the dependent variable, firm size is significant. This implies that the bigger the size of the firm, the higher the reduction of bid-ask spread, contrary to our predictions. (+-) is significantly positive for all the regressions, suggesting that firms with a positive ea ...
Modeling Price Differentials between A Shares and H Shares on the
... The shares initially listed on the SSE and SZE were called ‘A shares’ and could only be traded by Chinese investors, while ‘B shares’ were introduced exclusively for foreign investors since early 1992. The class A shares are domestic ordinary shares denominated and traded in Chinese Yuan by Chinese ...
... The shares initially listed on the SSE and SZE were called ‘A shares’ and could only be traded by Chinese investors, while ‘B shares’ were introduced exclusively for foreign investors since early 1992. The class A shares are domestic ordinary shares denominated and traded in Chinese Yuan by Chinese ...
PDF
... To correct for the non-constant error variance in this final regression, maximum likelihood estimates of sigma from the appropriate monthly regressions were scaled to sum to the number of observations and used in a weighted least squares procedure. The scaling has the effect of leaving the overall e ...
... To correct for the non-constant error variance in this final regression, maximum likelihood estimates of sigma from the appropriate monthly regressions were scaled to sum to the number of observations and used in a weighted least squares procedure. The scaling has the effect of leaving the overall e ...
Broker-Dealer Trading Activities
... the extent to which this order flow would be afforded better terms if executed in a market or with a market maker offering price improvement opportunities. In conducting the requisite evaluation of its internal order handling procedures, a broker-dealer must regularly and rigorously examine executio ...
... the extent to which this order flow would be afforded better terms if executed in a market or with a market maker offering price improvement opportunities. In conducting the requisite evaluation of its internal order handling procedures, a broker-dealer must regularly and rigorously examine executio ...