Mechanics, Sound, Heat and Thermodynamics
... Sunlight warms the earth’s surface during day time and earth’s surface radiates heat back to the space. Certain gases in the atmosphere absorb this radiant energy and re-emit the heat back to the space. Those gases which are capable of absorbing and re-emitting the heat radiation are called green ho ...
... Sunlight warms the earth’s surface during day time and earth’s surface radiates heat back to the space. Certain gases in the atmosphere absorb this radiant energy and re-emit the heat back to the space. Those gases which are capable of absorbing and re-emitting the heat radiation are called green ho ...
Full answers
... The ratio of neutrons to protons (N/Z) is approximately 1 for low atomic numbers (Z 20), but it slowly rises to about 1.5 as Z increases. All elements with Z > 83 are unstable. Atoms with even numbers of N and Z tend to be more stable than those with odd numbers. There are some particularly stable ...
... The ratio of neutrons to protons (N/Z) is approximately 1 for low atomic numbers (Z 20), but it slowly rises to about 1.5 as Z increases. All elements with Z > 83 are unstable. Atoms with even numbers of N and Z tend to be more stable than those with odd numbers. There are some particularly stable ...
Physical and Chemical equilibrium
... (ii)At equilibrium, concentration of all reactants and products becomes constant (iii)Equilibrium is dynamic in nature i.e. reaction seems to be static because no change in concentration of reactants or product, but actually reaction takes place in both the directions with same speed (iv)Catalyst do ...
... (ii)At equilibrium, concentration of all reactants and products becomes constant (iii)Equilibrium is dynamic in nature i.e. reaction seems to be static because no change in concentration of reactants or product, but actually reaction takes place in both the directions with same speed (iv)Catalyst do ...
A new, intrinsic, thermal parameter for enzymes reveals true
... less active) form. Thus, at temperatures above its optimum, the decrease in enzyme activity arising from the temperature-dependent shift in this equilibrium is up to two orders of magnitude greater than occurs through thermal denaturation. This parameter has important implications for our understand ...
... less active) form. Thus, at temperatures above its optimum, the decrease in enzyme activity arising from the temperature-dependent shift in this equilibrium is up to two orders of magnitude greater than occurs through thermal denaturation. This parameter has important implications for our understand ...
Noninteracting Particle Systems - Particle Solids Interactions group
... canonical ensemble. However, because the particles are not localized, they cannot be distinguished from each other as were the harmonic oscillators considered in Example 4.4 and the spins in Chapter 5. Hence, we cannot simply focus our attention on one particular particle. For this reason we will la ...
... canonical ensemble. However, because the particles are not localized, they cannot be distinguished from each other as were the harmonic oscillators considered in Example 4.4 and the spins in Chapter 5. Hence, we cannot simply focus our attention on one particular particle. For this reason we will la ...
13 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM W MODULE - 5
... reaction, it is believed that all the reactants would be converted into products with the release or absorption of energy. This is not true in all cases. Many chemical reactions proceed only to a certain extent and stop. When analysed, the resulting mixture contains both the reactants and products. ...
... reaction, it is believed that all the reactants would be converted into products with the release or absorption of energy. This is not true in all cases. Many chemical reactions proceed only to a certain extent and stop. When analysed, the resulting mixture contains both the reactants and products. ...
Physical Chemistry II
... As you make your way through this learning activity you will come across problems to test your conceptual understanding of the subject matter Rapid quizzes are provided to check your understanding Practical experiments will be given to evaluate your understanding of theory-practice relations Simulat ...
... As you make your way through this learning activity you will come across problems to test your conceptual understanding of the subject matter Rapid quizzes are provided to check your understanding Practical experiments will be given to evaluate your understanding of theory-practice relations Simulat ...
unit-4-notes-1_enthalpy-and-entropy
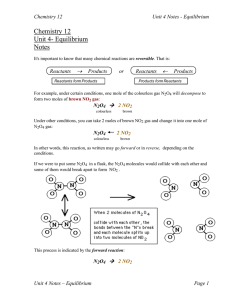
... and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at the start, but the reverse reaction rate eventually "caught up", the rates became equal and equilibrium was established. Can you guess what would happen if we had started with pure NO2 instead (no N2O4 )? The reverse rate would start out high and the ...
... and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at the start, but the reverse reaction rate eventually "caught up", the rates became equal and equilibrium was established. Can you guess what would happen if we had started with pure NO2 instead (no N2O4 )? The reverse rate would start out high and the ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. All chemical changes involve a transfer of energy, be it into the reaction or out of the reaction. Transformed energy in a chemical reaction comes from or forms chemical bonds and is exchanged with the surroundings as heat and/or work. W ...
... Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. All chemical changes involve a transfer of energy, be it into the reaction or out of the reaction. Transformed energy in a chemical reaction comes from or forms chemical bonds and is exchanged with the surroundings as heat and/or work. W ...
Quantum Mechanics_chemical potential
... concentrations in the mixture remaining constant, and at constant temperature. When pressure is constant, chemical potential is the partial molar Gibbs free energy. At chemical equilibrium or in phase equilibriumthe total sum of chemical potentials is zero, as the free energy is at a minimum.[1][2][ ...
... concentrations in the mixture remaining constant, and at constant temperature. When pressure is constant, chemical potential is the partial molar Gibbs free energy. At chemical equilibrium or in phase equilibriumthe total sum of chemical potentials is zero, as the free energy is at a minimum.[1][2][ ...