comparison of candidate materials for seasonal storage of solar heat
... in the simulation model the heat transport is due to some temperature difference and does not contradict the law of thermodynamics. The seasonal heat store in Figure 4 is modelled as a so-called "configurable subsystem". This means that it contains several heat store models ("members"), from which o ...
... in the simulation model the heat transport is due to some temperature difference and does not contradict the law of thermodynamics. The seasonal heat store in Figure 4 is modelled as a so-called "configurable subsystem". This means that it contains several heat store models ("members"), from which o ...
Department of Chemistry Second Year Syllabus
... The second year of the degree in Chemistry aims to provide the students with an expanded and deeper understanding of the fundamental concepts required to rationalise and predict chemical reactivity. To achieve this goal the students study the behaviour of a wide range of chemicals (both organic and ...
... The second year of the degree in Chemistry aims to provide the students with an expanded and deeper understanding of the fundamental concepts required to rationalise and predict chemical reactivity. To achieve this goal the students study the behaviour of a wide range of chemicals (both organic and ...
T - UCSD Physics
... (1) To measure the heat capacity of an object, all you usually have to do is put it in thermal contact with another object whose heat capacity is known. Suppose that a 100 g chunk of metal is immersed in boiling water (100◦ C). After a time, the metal is removed and quickly transferred to a Styrofoa ...
... (1) To measure the heat capacity of an object, all you usually have to do is put it in thermal contact with another object whose heat capacity is known. Suppose that a 100 g chunk of metal is immersed in boiling water (100◦ C). After a time, the metal is removed and quickly transferred to a Styrofoa ...
Document
... Vaporization requires more energy to change phase from liquid to gas phase. Gas molecules have high kinetic energy and distance between gas molecules is very high, requiring more energy to overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction.) Changes in the states of matter are often shown on phase dia ...
... Vaporization requires more energy to change phase from liquid to gas phase. Gas molecules have high kinetic energy and distance between gas molecules is very high, requiring more energy to overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction.) Changes in the states of matter are often shown on phase dia ...
20. Chemical Equilibrium
... In most of the chemical reactions we have studied so far, it appears as though all of the reactants are converted to products before a reaction stops. In truth, however, experiments show that the conversion of reactants into products is often incomplete in chemical reactions. This is the case no mat ...
... In most of the chemical reactions we have studied so far, it appears as though all of the reactants are converted to products before a reaction stops. In truth, however, experiments show that the conversion of reactants into products is often incomplete in chemical reactions. This is the case no mat ...
Chemistry - Plymouth Public Schools
... Properties of Matter Central Concept: Physical and chemical properties reflect the nature of the interactions between molecules or atoms, and can be used to classify and describe matter. MA CHM 1.1 Identify and explain physical properties (e.g., density, melting point, boiling point, conductivity, m ...
... Properties of Matter Central Concept: Physical and chemical properties reflect the nature of the interactions between molecules or atoms, and can be used to classify and describe matter. MA CHM 1.1 Identify and explain physical properties (e.g., density, melting point, boiling point, conductivity, m ...
Unit 1
... For Chemistry 3202, the rate-determining step will always be the hump that has the highest energy from its reaction intermediate to the peak, and, will also be the highest peak in the diagram. – given a reaction mechanism with the RDS identified, ...
... For Chemistry 3202, the rate-determining step will always be the hump that has the highest energy from its reaction intermediate to the peak, and, will also be the highest peak in the diagram. – given a reaction mechanism with the RDS identified, ...
Chemical Energy
... Mg(s) + 1/2O2(g) - MgO(s) Ho = -602 kJ/mol 2 P(s) + 3 Cl2(g) - 2 PCl3(s) Ho = -640 kJ/mol 2 P(s) + 5 Cl2(g) - 2 PCl5(s) Ho = -880 kJ/mol C(graphite) + 2 O(g) - CO2(g) Ho = -643 kJ/mol C(graphite) + O2(g) - CO2(g) Ho = -394 kJ/mol C(graphite) + 2 H2(g) - CH4(g) Ho = -75 kJ/mol 2 Al(s) + Fe2O3(s ...
... Mg(s) + 1/2O2(g) - MgO(s) Ho = -602 kJ/mol 2 P(s) + 3 Cl2(g) - 2 PCl3(s) Ho = -640 kJ/mol 2 P(s) + 5 Cl2(g) - 2 PCl5(s) Ho = -880 kJ/mol C(graphite) + 2 O(g) - CO2(g) Ho = -643 kJ/mol C(graphite) + O2(g) - CO2(g) Ho = -394 kJ/mol C(graphite) + 2 H2(g) - CH4(g) Ho = -75 kJ/mol 2 Al(s) + Fe2O3(s ...
Curriculum Map: AP Physics II MASH Science
... Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Big Idea 2: Fields existing in space can be used to explain interactions. Big Idea 3: The interactions of an object with other objects can be described by forces. Big Idea 4: Interactions be ...
... Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Big Idea 2: Fields existing in space can be used to explain interactions. Big Idea 3: The interactions of an object with other objects can be described by forces. Big Idea 4: Interactions be ...
Document
... A metal pellet with a mass of 100.0 g, originally at 88.4°C, is dropped into 125 g of water originally at 25.1°C. The final temperature of both pellet and the water is 31.3°C. Calculate the heat capacity C (in J/°C) of the pellet. Strategy Water constitutes the surroundings; the pellet is the system ...
... A metal pellet with a mass of 100.0 g, originally at 88.4°C, is dropped into 125 g of water originally at 25.1°C. The final temperature of both pellet and the water is 31.3°C. Calculate the heat capacity C (in J/°C) of the pellet. Strategy Water constitutes the surroundings; the pellet is the system ...
VALIDITY OF HENRY`S LAW IN DILUTE SOLUTIONS (l)
... ideally with respect to the solvent. This view is further supported by the fact that Raoult's Law empirically found for describing the behaviour of the solvent in dilute solutions can be deduced thermodynamically via the assumption of ideal behaviour of the solvent. As is commonly known on the basis ...
... ideally with respect to the solvent. This view is further supported by the fact that Raoult's Law empirically found for describing the behaviour of the solvent in dilute solutions can be deduced thermodynamically via the assumption of ideal behaviour of the solvent. As is commonly known on the basis ...
Sample Exercise 15.1 Writing Equilibrium
... Plan For equilibrium to be achieved, it must be possible for both the forward process and the reverse process to occur. For the forward process to occur, there must be some calcium carbonate present. For the reverse process to occur, there must be both calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. In both cases ...
... Plan For equilibrium to be achieved, it must be possible for both the forward process and the reverse process to occur. For the forward process to occur, there must be some calcium carbonate present. For the reverse process to occur, there must be both calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. In both cases ...
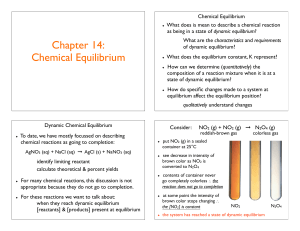
Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium
... as being in a state of dynamic equilibrium? What are the characteristics and requirements of dynamic equilibrium? ...
... as being in a state of dynamic equilibrium? What are the characteristics and requirements of dynamic equilibrium? ...
K eq
... No - The paper wads keep flying in both directions even after equilibrium is achieved ...
... No - The paper wads keep flying in both directions even after equilibrium is achieved ...
Chemical Reactivities: Fundamental and Nuclear Reactions
... The whole reaction in the graphic is balanced, i.e., there are the same numbers of sodium atoms on both sides of the reaction and there are the same numbers of chlorine atoms on both sides of the reaction. The balanced reaction is consistent with the Law of Conservation of Matter: atoms are neither ...
... The whole reaction in the graphic is balanced, i.e., there are the same numbers of sodium atoms on both sides of the reaction and there are the same numbers of chlorine atoms on both sides of the reaction. The balanced reaction is consistent with the Law of Conservation of Matter: atoms are neither ...




![Keq = [A] [B] [C] [D]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014463360_1-50a2de0db1e8b9a361c4b31c6e85c28d-300x300.png)