Epistasis is not dominance.
... The heterozygote expresses both traits at the same time. In this example, the heterozygous chickens are speckled. They express both feather colors at the same time. ...
... The heterozygote expresses both traits at the same time. In this example, the heterozygous chickens are speckled. They express both feather colors at the same time. ...
Biology Chapter 11- Gene Expression Miss Ventrone
... Discovered in the early 1960’s by Francois __________ and Jacques _____________ They were studying how __________ ______________ the _______________ of sugar lactose (found in milk) in _________________ Absence of Lactose ...
... Discovered in the early 1960’s by Francois __________ and Jacques _____________ They were studying how __________ ______________ the _______________ of sugar lactose (found in milk) in _________________ Absence of Lactose ...
HT180_Presentation
... For most (non-imprinted) genes, the maternal copy is functionally equivalent to the paternal copy Imprinted genes, however, are expressed differently from maternal and paternal alleles In most cases, imprinting selectively inactivates either the maternal or the paternal allele of a particular gene ...
... For most (non-imprinted) genes, the maternal copy is functionally equivalent to the paternal copy Imprinted genes, however, are expressed differently from maternal and paternal alleles In most cases, imprinting selectively inactivates either the maternal or the paternal allele of a particular gene ...
Angelman Syndrome (AS) and UBE3A (E6-AP)
... Monoallelic expression of an isoform found in mouse brain tissue depression of expression is also evident in the hippocampus of a paternal UPD mouse Evidence for decrease of expression in human brain Clinical description of AS indicates a developmental brain disorder and so differential expression o ...
... Monoallelic expression of an isoform found in mouse brain tissue depression of expression is also evident in the hippocampus of a paternal UPD mouse Evidence for decrease of expression in human brain Clinical description of AS indicates a developmental brain disorder and so differential expression o ...
Statistical Methods for Network-Based Analysis of Genomic Data
... are involved in diseases or perturbed during a biological process. Many methods have been developed for identifying genes in regression frameworks. The genes identified are often linked to known biological pathways through gene set enrichment analysis in order to identify the pathways involved. Howe ...
... are involved in diseases or perturbed during a biological process. Many methods have been developed for identifying genes in regression frameworks. The genes identified are often linked to known biological pathways through gene set enrichment analysis in order to identify the pathways involved. Howe ...
Lecture Slides
... ASD are in large parte genetic conditions but many ASD-genes are not identified yet Whole exome and whole genome analysis accelerated discoveries ...
... ASD are in large parte genetic conditions but many ASD-genes are not identified yet Whole exome and whole genome analysis accelerated discoveries ...
- PWSA UK
... example, are very different - thus leading to the development of a specialist organ able to carry out specific functions. This is an example of 'epigenesis' - the modifying of gene expression by some mechanism other than by altering the underlying DNA code. The expression of the gene or genes (as ye ...
... example, are very different - thus leading to the development of a specialist organ able to carry out specific functions. This is an example of 'epigenesis' - the modifying of gene expression by some mechanism other than by altering the underlying DNA code. The expression of the gene or genes (as ye ...
240.1 Caren
... their respective promoter regions. Methylation of CpG islands is a common mechanism for the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes and has been found in a wide range of tumor types. The most common way to analyze methylation status is based on bisulfite modification of DNA. In the current study, exp ...
... their respective promoter regions. Methylation of CpG islands is a common mechanism for the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes and has been found in a wide range of tumor types. The most common way to analyze methylation status is based on bisulfite modification of DNA. In the current study, exp ...
People Pieces
... mutations, that cause certain diseases or medical problems. One goal of the Human Genome Project is to learn the correct sequence for each gene, which mutations cause which problems, and how to correct the mutations in order to solve the problems. The genomes of other organisms are also being studie ...
... mutations, that cause certain diseases or medical problems. One goal of the Human Genome Project is to learn the correct sequence for each gene, which mutations cause which problems, and how to correct the mutations in order to solve the problems. The genomes of other organisms are also being studie ...
7th grade Ch. 5 section 2 and 3 Notes
... every gene in the human genome. • Humans contain at least 30,000 genes. • Average gene has about 3,000 bases. ...
... every gene in the human genome. • Humans contain at least 30,000 genes. • Average gene has about 3,000 bases. ...
Chapter 14 Review pages 316
... 4. The source of random variation on which natural selection operates are changes in: b) genes 5. An example of analogous structures are a: b) bird’s wing and a butterfly’s wing 6. Which of the following ideas proposed by Lamarck was later found to be incorrect: a) acquired characteristics can be in ...
... 4. The source of random variation on which natural selection operates are changes in: b) genes 5. An example of analogous structures are a: b) bird’s wing and a butterfly’s wing 6. Which of the following ideas proposed by Lamarck was later found to be incorrect: a) acquired characteristics can be in ...
C-13 Part II Non-Mendelian inheritance
... Continuous variation • When multiple genes act together to produce a physical (phenotypic) character, a gradation or range of differences occur. • Examples: height, weight in humans • Referred to as polygenic traits ...
... Continuous variation • When multiple genes act together to produce a physical (phenotypic) character, a gradation or range of differences occur. • Examples: height, weight in humans • Referred to as polygenic traits ...
Human Genome Project - College Heights Secondary School
... Goals of HGP • Create map of the 22 human chromosomes, X / Y) • Identify the entire set of genes & map them all to their chromosomes • Determine the nucleotide sequences of the estimated 3 billion base pairs • Analyze genetic variation among humans ...
... Goals of HGP • Create map of the 22 human chromosomes, X / Y) • Identify the entire set of genes & map them all to their chromosomes • Determine the nucleotide sequences of the estimated 3 billion base pairs • Analyze genetic variation among humans ...
Click Here For Worksheet
... A. How to function. B. What traits to express. C. Both A and B 5. How many chromosomes does a human typically have in their cells?____________________________________ ...
... A. How to function. B. What traits to express. C. Both A and B 5. How many chromosomes does a human typically have in their cells?____________________________________ ...
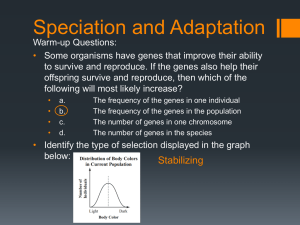
Adaptation and Speciation
... recombined to produce new combinations of alleles. This recombination process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflects differences in the DNA sequences of different organisms. ...
... recombined to produce new combinations of alleles. This recombination process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflects differences in the DNA sequences of different organisms. ...
COMPLEX PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE
... In most species of plants, the egg cell provides most of the zygote’s cytoplasm, while the much smaller male gamete often provides little more than a nucleus ...
... In most species of plants, the egg cell provides most of the zygote’s cytoplasm, while the much smaller male gamete often provides little more than a nucleus ...
Crossbreeding terminology
... gene at a particular location on a chromosome. For example, blue and brown eyes are determined by different alleles of the gene for eye colour. Chromosomes rod-like structures that are found in the nucleus of all cells. These structures contain genetic information and occur in pairs. Co-dominant two ...
... gene at a particular location on a chromosome. For example, blue and brown eyes are determined by different alleles of the gene for eye colour. Chromosomes rod-like structures that are found in the nucleus of all cells. These structures contain genetic information and occur in pairs. Co-dominant two ...
An Excel Macro to Visualise Patterns for Chosen Genes
... Can adapt for different combinations of chips to give different profiles Eg a range of organs. Similar in function to GenevestigATor ….but email me if you want to have a go. [email protected] ...
... Can adapt for different combinations of chips to give different profiles Eg a range of organs. Similar in function to GenevestigATor ….but email me if you want to have a go. [email protected] ...
2 Sex chromosomes
... a. Genes located on sex-chromosomes called sex-linked genes b. Many species have specialized sex chromosomes 1). In mammals and some other animals, individuals with XX are female and XY are male 2). X chromosome much larger than Y ...
... a. Genes located on sex-chromosomes called sex-linked genes b. Many species have specialized sex chromosomes 1). In mammals and some other animals, individuals with XX are female and XY are male 2). X chromosome much larger than Y ...
Genetics after Mendel
... Multifactorial – genes found at many loci Ex Height We have a range Humans and higher organisms ...
... Multifactorial – genes found at many loci Ex Height We have a range Humans and higher organisms ...
Further Clarification of GENE LINKAGE When you did Gamete
... gametes formed during meiosis. These two possibilities are equally likely to form. ...
... gametes formed during meiosis. These two possibilities are equally likely to form. ...