投影片 1
... chemical (NMR, IR, CHN) characterizations are typically the most representative, but have limited information potential 2. molecular (biomarker) characterizations carry a wealth of information (including isotopic), but can often be unrepresentative of bulk organic mixtures which contain many organic ...
... chemical (NMR, IR, CHN) characterizations are typically the most representative, but have limited information potential 2. molecular (biomarker) characterizations carry a wealth of information (including isotopic), but can often be unrepresentative of bulk organic mixtures which contain many organic ...
LIPIDS
... animal systems do not have enzymes that can insert a double bond distal to n-9 carbon in a fatty acid. the three polyunsaturated fatty acids usually thought of as EFAs – linoleate (18:2), linolenate (18:3) and arachidonate (20:4) – the highest biopotency for growth is seen with arachidonate. Arachid ...
... animal systems do not have enzymes that can insert a double bond distal to n-9 carbon in a fatty acid. the three polyunsaturated fatty acids usually thought of as EFAs – linoleate (18:2), linolenate (18:3) and arachidonate (20:4) – the highest biopotency for growth is seen with arachidonate. Arachid ...
B4 Lipids
... B.4.3 Describe the difference in structure between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. (2) B.4.4 Compare the structures of the two essential fatty acids linoleic (omega–6 fatty acid) and linolenic (omega–3 fatty acid) and state their importance. (3) B.4.5 Define the term iodine number and calcula ...
... B.4.3 Describe the difference in structure between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. (2) B.4.4 Compare the structures of the two essential fatty acids linoleic (omega–6 fatty acid) and linolenic (omega–3 fatty acid) and state their importance. (3) B.4.5 Define the term iodine number and calcula ...
I The THREE types of LIPIDS
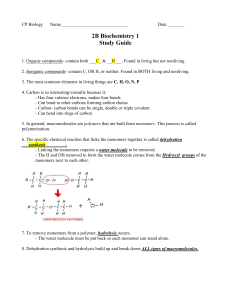
... 3. After enzymatic digestion of the carbohydrates and lipids in whole milk, what is absorbed (after enzymatic digestion) into the cells lining SI? The carbohydrate in the milk is ______________ & it is enzymatically digested down to ________________ and ________________. The lipid in the whole milk ...
... 3. After enzymatic digestion of the carbohydrates and lipids in whole milk, what is absorbed (after enzymatic digestion) into the cells lining SI? The carbohydrate in the milk is ______________ & it is enzymatically digested down to ________________ and ________________. The lipid in the whole milk ...
Extraction and Characterization of Fish Oil from Monopterus albus
... properties. Among the common sources of these PUFAs are fish oils. The PUFA composition in fish oils are affected by several factors, such as geographical location, temperature and water salinity [1,2]. The oils extracted from the northern hemisphere coldwater fishes are rich in n-3 PUFA, especially ...
... properties. Among the common sources of these PUFAs are fish oils. The PUFA composition in fish oils are affected by several factors, such as geographical location, temperature and water salinity [1,2]. The oils extracted from the northern hemisphere coldwater fishes are rich in n-3 PUFA, especially ...
I The THREE types of LIPIDS
... c. Sterols and d. one more type of lipid to be the emulsifier. What is this type of lipid called that is an emulsifier? The name of the package of protein and the 3 types of lipids (with the main one being TGs from food) is a E. What happens once triglycerides have been delivered to the cells? ...
... c. Sterols and d. one more type of lipid to be the emulsifier. What is this type of lipid called that is an emulsifier? The name of the package of protein and the 3 types of lipids (with the main one being TGs from food) is a E. What happens once triglycerides have been delivered to the cells? ...
CP Biology
... E. Phospholipids- create the cell membrane 21. Triglycerides: made of a glycerol and 3 fatty acid molecules 22. Fatty acids may be: Saturated ...
... E. Phospholipids- create the cell membrane 21. Triglycerides: made of a glycerol and 3 fatty acid molecules 22. Fatty acids may be: Saturated ...
Slide 1
... octadecenoic acid is the fatty acid derived from octadecene (18:1) Fatty acids containing more than one double bond are given the suffixes -dienoic, -trienoic, etc. octadecadienoic acid has 18 carbons and 2 double bonds (18:2) octadecatrienoic acid has 18 carbons and 3 double bonds (18:3) ...
... octadecenoic acid is the fatty acid derived from octadecene (18:1) Fatty acids containing more than one double bond are given the suffixes -dienoic, -trienoic, etc. octadecadienoic acid has 18 carbons and 2 double bonds (18:2) octadecatrienoic acid has 18 carbons and 3 double bonds (18:3) ...
Glycerol + Fatty acids
... either side of the double bond are either both “up” or both “down,” such that both are on the same side of the molecule ● In trans bonds, the two pieces of the molecule are on opposite sides of the double bond, that is, one “up” and one “down” across from each other ● Naturally-occurring unsaturated ...
... either side of the double bond are either both “up” or both “down,” such that both are on the same side of the molecule ● In trans bonds, the two pieces of the molecule are on opposite sides of the double bond, that is, one “up” and one “down” across from each other ● Naturally-occurring unsaturated ...
Biochemistry, Digestion, and Energy Transfer
... Cis fatty acids react with cholesterol and tie it up; trans fatty acids do not and allow the cholesterol to roam the ...
... Cis fatty acids react with cholesterol and tie it up; trans fatty acids do not and allow the cholesterol to roam the ...
Lipids • Triglycerides –Fats and oils • Phospholipids
... –5% - 10% of energy intake • Linolenic acid AI –0.6 - 1.2% of energy intake ...
... –5% - 10% of energy intake • Linolenic acid AI –0.6 - 1.2% of energy intake ...
Fatty Acids And Triglycerides - The Center for Cholesterol
... beta oxidation of FA or the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid (an acid containing oxygen). The acyl group is usually derived from a carboxylic acid of the form RC RC--O-OH. OH It therefore has the formula RC(=O)RC(=O)- , with a double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms (i. ...
... beta oxidation of FA or the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid (an acid containing oxygen). The acyl group is usually derived from a carboxylic acid of the form RC RC--O-OH. OH It therefore has the formula RC(=O)RC(=O)- , with a double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms (i. ...
OILS
... • have long nonpolar tails responsible for fatty/oily characteristics. • The carboxyl group is very hydrophilic under conditions of physiological pH (exists as –COO-). ...
... • have long nonpolar tails responsible for fatty/oily characteristics. • The carboxyl group is very hydrophilic under conditions of physiological pH (exists as –COO-). ...
Chapter 18_CHEM 131
... • have long nonpolar tails responsible for fatty/oily characteristics. • The carboxyl group is very hydrophilic under conditions of physiological pH (exists as –COO-). ...
... • have long nonpolar tails responsible for fatty/oily characteristics. • The carboxyl group is very hydrophilic under conditions of physiological pH (exists as –COO-). ...
( 1 x24 =24 Mark).
... B) two fatty acid and one phosphoric acid molecules. C) three phosphoric acid molecules. D) one fatty acid, one phosphoric acid and one amino alcohol molecule. 12. The “steroid nucleus” common to all steroid structures involves a fused-ring system involving A) four six-membered rings. B) four five- ...
... B) two fatty acid and one phosphoric acid molecules. C) three phosphoric acid molecules. D) one fatty acid, one phosphoric acid and one amino alcohol molecule. 12. The “steroid nucleus” common to all steroid structures involves a fused-ring system involving A) four six-membered rings. B) four five- ...
LIPIDS
... – Mono unsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) (1 double bond) – • Oleic acid (18C) – Poly unsaturated fatty acid (FUFA) (2 and more double bond) • Linoleic acid (2 double bond) (18C) • Linolenic acid (3 double bond) (18 C) • Aracidonic acid (5 double bond) (20C) • Called as essential fatty acid ...
... – Mono unsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) (1 double bond) – • Oleic acid (18C) – Poly unsaturated fatty acid (FUFA) (2 and more double bond) • Linoleic acid (2 double bond) (18C) • Linolenic acid (3 double bond) (18 C) • Aracidonic acid (5 double bond) (20C) • Called as essential fatty acid ...
Omega-3 again linked to lower colorectal cancer risk 2/23/2007
... by a whopping 66 per cent, but only in men not taking aspirin, suggests new research. Omega-3 has been identified as one of the super-nutrients taking the food and supplements industry by storm. Much of its healthy reputation that is seeping into consumer consciousness is based largely on evidence t ...
... by a whopping 66 per cent, but only in men not taking aspirin, suggests new research. Omega-3 has been identified as one of the super-nutrients taking the food and supplements industry by storm. Much of its healthy reputation that is seeping into consumer consciousness is based largely on evidence t ...
Chemistry of Lipids
... Contain more than one double bond bond. Eg: Linoleic acid, linolenic acid and arachidonic acid. acid These are not synthesised in human body due to lack of the desaturase enzyme enzyme, which introduces double bonds beyond 9th and 10th carbon atoms. Glycerol It is a trihydric alcohol [three hy ...
... Contain more than one double bond bond. Eg: Linoleic acid, linolenic acid and arachidonic acid. acid These are not synthesised in human body due to lack of the desaturase enzyme enzyme, which introduces double bonds beyond 9th and 10th carbon atoms. Glycerol It is a trihydric alcohol [three hy ...
The Critical Requirement for Linolenic Acid Is Pollen
... ω-3 desaturases differentially alters tolerance to various abiotic stresses in transgenic tobacco cells and plants. The Plant Journal 44, 361-371 ...
... ω-3 desaturases differentially alters tolerance to various abiotic stresses in transgenic tobacco cells and plants. The Plant Journal 44, 361-371 ...
Fatty Acids
... • It is important constituent of cell membranes. • It is converted into bile acids and bile salts in the liver. • It is the precursor of all steroid hormones. • It can be oxidized in the liver into 7-dehydro cholesterol which can be converted under the skin into vitamin D3 by ultra violet ...
... • It is important constituent of cell membranes. • It is converted into bile acids and bile salts in the liver. • It is the precursor of all steroid hormones. • It can be oxidized in the liver into 7-dehydro cholesterol which can be converted under the skin into vitamin D3 by ultra violet ...
fatty acids. - WordPress.com
... 2. Platelet-activating factor has a long ether-linked alkyl chain at C1. Acetic acid is ester-linked at C2, which makes it more water soluble than most glycerophospholipids. The head-group alcohol is choline. ...
... 2. Platelet-activating factor has a long ether-linked alkyl chain at C1. Acetic acid is ester-linked at C2, which makes it more water soluble than most glycerophospholipids. The head-group alcohol is choline. ...
Sandalwood Seed Oil
... Sandalwood Seed Oil is a reliable source of Ximenynic Acid which is an established anti-inflammatory lipid. This rare active oil can be formulated and delivered in a similar manner to normal carrier oils. Having excellent stability and favourable physicochemical characteristics, Sandalwood Seed Oil ...
... Sandalwood Seed Oil is a reliable source of Ximenynic Acid which is an established anti-inflammatory lipid. This rare active oil can be formulated and delivered in a similar manner to normal carrier oils. Having excellent stability and favourable physicochemical characteristics, Sandalwood Seed Oil ...
Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... the Carbon atoms. Start at the top of a chain & to the right of a ring. ...
... the Carbon atoms. Start at the top of a chain & to the right of a ring. ...
Eicosanoid
In biochemistry, eicosanoids (preferred IUPAC name icosanoids) are signaling molecules made by oxidation of 20-carbon fatty acids.They exert complex control over many bodily systems; mainly in growth during and after physical activity, inflammation or immunity after the intake of toxic compounds and pathogens, and as messengers in the central nervous system.The networks of controls that depend upon eicosanoids are among the most complex in the human body.Eicosanoids are derived from either omega-3 (ω-3) or omega-6 (ω-6) fatty acids.In general, the ω-6 eicosanoids are pro-inflammatory; ω-3s are much less so.The amounts and balance of these fats in a person's diet will affect the body's eicosanoid-controlled functions, with effects on cardiovascular disease, triglycerides, blood pressure, and arthritis. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and other NSAIDs act by downregulating eicosanoid synthesis.There are multiple subfamilies of eicosanoids, including the prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes, as well as the lipoxins and eoxins, and others. For each, there are two or three separate series, derived from either an ω-3 or an ω-6 EFA. These series' different activities largely explain the health effects of ω-3 and ω-6 fats.