03. Lipids. Classification, structure and biological role
... • The most important role of lipids is as а fuel. Thus fat is the most concentrated form in which potential energy can be stored. • Since fat is а bad conductor of heat, it provides excellent insulation. • Fat may also provide padding to protect the internal organs. • Some compounds derived from lip ...
... • The most important role of lipids is as а fuel. Thus fat is the most concentrated form in which potential energy can be stored. • Since fat is а bad conductor of heat, it provides excellent insulation. • Fat may also provide padding to protect the internal organs. • Some compounds derived from lip ...
palm butter - In
... in the lipidic phase of an emulsion or of a lipogel acting both as a vegetal triglycerids and as consistency factor (it can substitute the whole oil phase of an emulsion), moreover it makes the skin soft and acts as an antioxidant active in that it is rich of tocopherols and tocotrienols delivered t ...
... in the lipidic phase of an emulsion or of a lipogel acting both as a vegetal triglycerids and as consistency factor (it can substitute the whole oil phase of an emulsion), moreover it makes the skin soft and acts as an antioxidant active in that it is rich of tocopherols and tocotrienols delivered t ...
Molecular Modeling Activity Lipids (Saturated and Unsaturated Fats
... animals. Those triglycerides that are liquid are called oils and originate chiefly in plants. Fats and oils are made up of two different kinds of molecules: glycerol and fatty acids Build a Model of Glycerol- the backbone of fats and oils ● before you begin, draw a diagram of a glycerol molecule ● o ...
... animals. Those triglycerides that are liquid are called oils and originate chiefly in plants. Fats and oils are made up of two different kinds of molecules: glycerol and fatty acids Build a Model of Glycerol- the backbone of fats and oils ● before you begin, draw a diagram of a glycerol molecule ● o ...
Examination III Key
... have too many essential amino acids and not enough non-essential amino acids This may be the cause, but is not always the cause have inadequate levels of glucogenic amino acids available from his/her diet This may be the cause, but is not always the cause 18. Though it can function in several diff ...
... have too many essential amino acids and not enough non-essential amino acids This may be the cause, but is not always the cause have inadequate levels of glucogenic amino acids available from his/her diet This may be the cause, but is not always the cause 18. Though it can function in several diff ...
Membrane lipids
... -- add H2 to the double bonds -- complete hydrogenation converts all double bonds to single bonds (fully hydrogenated) --reaction saturates the oil --partial hydrogenation occurs when some of the double bonds are hydrogenated --remaining double bonds are often converted in to trans form O ...
... -- add H2 to the double bonds -- complete hydrogenation converts all double bonds to single bonds (fully hydrogenated) --reaction saturates the oil --partial hydrogenation occurs when some of the double bonds are hydrogenated --remaining double bonds are often converted in to trans form O ...
lipids
... diphosphate, a C15 sesquiterpene, by addition of a fivecarbon unit. Farnesyl diphosphate is the starting material for all sesquiterpenes and diterpenes. [3] Two molecules of farnesyl diphosphate are converted to squalene, a C30 triterpene. Squalene is the starting material for all triterpenes and st ...
... diphosphate, a C15 sesquiterpene, by addition of a fivecarbon unit. Farnesyl diphosphate is the starting material for all sesquiterpenes and diterpenes. [3] Two molecules of farnesyl diphosphate are converted to squalene, a C30 triterpene. Squalene is the starting material for all triterpenes and st ...
Lipids: Membrane Structure
... Unsaturated Fatty acids • One or more double bonds • Cis: cis-∆9, double bond between 9 and 10 carbon • Trans: trans- ∆2, double bond between 2 and 3 carbon • ω-3 counting from the distal end. ...
... Unsaturated Fatty acids • One or more double bonds • Cis: cis-∆9, double bond between 9 and 10 carbon • Trans: trans- ∆2, double bond between 2 and 3 carbon • ω-3 counting from the distal end. ...
Fatty acids and their derivatives
... organisms that dissolve in nonpolar solvents eg. Ether, chloroform, acetone but not in water. ...
... organisms that dissolve in nonpolar solvents eg. Ether, chloroform, acetone but not in water. ...
PPT
... Protective wax coatings found on some plants Energy-rich compounds with low densities Storage form of energy for plants and animals Structural components, especially in cellular membrane formation ...
... Protective wax coatings found on some plants Energy-rich compounds with low densities Storage form of energy for plants and animals Structural components, especially in cellular membrane formation ...
5.6. membrane lipids
... • Carboxylic acids with long-chain hydrocarbon side groups. • They can be branched and saturated, unsaturated or polyunsaturated (contain ...
... • Carboxylic acids with long-chain hydrocarbon side groups. • They can be branched and saturated, unsaturated or polyunsaturated (contain ...
Lipids2
... formed. Note the usage of some energy to achieve this. Odd-numbered fatty acids yields propionylCoA, which is converted to succinylCoA to enter the TCA. ...
... formed. Note the usage of some energy to achieve this. Odd-numbered fatty acids yields propionylCoA, which is converted to succinylCoA to enter the TCA. ...
4. Essential fatty acid
... atherosclerosis is (A) Low density of lipoproteins (B) very low density lipoproteins (C) High density lipoproteins (D) Chylomicrons ...
... atherosclerosis is (A) Low density of lipoproteins (B) very low density lipoproteins (C) High density lipoproteins (D) Chylomicrons ...
Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
Lipids and Their Structures - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Definition: Organic molecule of biological origin that is insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. Solubility Explained: Lipids do have both nonpolar and polar regions; however, the majority of the molecule is nonpolar (due to large nonpolar tails). Since "like dissolves like", lipid ...
... Definition: Organic molecule of biological origin that is insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents. Solubility Explained: Lipids do have both nonpolar and polar regions; however, the majority of the molecule is nonpolar (due to large nonpolar tails). Since "like dissolves like", lipid ...
FATS - Catherine Huff`s Site
... 1) fatty acids : * saturated (milk fat) no double bonds in the fatty acid chain * unsaturated (corn oil) one or more double bonds in the fatty acid chain 2) prostaglandins : any member of a group of lipid compounds 3) lipid soluble vitamins : (A, D, E and K) Monounsaturated fats contain a single dou ...
... 1) fatty acids : * saturated (milk fat) no double bonds in the fatty acid chain * unsaturated (corn oil) one or more double bonds in the fatty acid chain 2) prostaglandins : any member of a group of lipid compounds 3) lipid soluble vitamins : (A, D, E and K) Monounsaturated fats contain a single dou ...
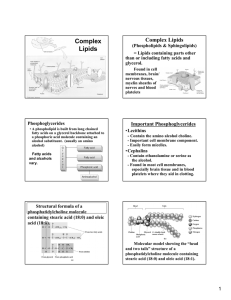
L2 - Complex Lipids
... • A phospholipid is built from long chained fatty acids on a glycerol backbone attached to a phosphoric acid molecule containing an alcohol substituent. (usually an amino ...
... • A phospholipid is built from long chained fatty acids on a glycerol backbone attached to a phosphoric acid molecule containing an alcohol substituent. (usually an amino ...
Lipids
... have been identified as essential fatty acids They have important roles in immune function and vision, help form cell membranes, and produce hormone-like compounds called eicosanoids The body has no means to produce double bonds between any carbon atoms from the first to the ninth carbon Alpha ...
... have been identified as essential fatty acids They have important roles in immune function and vision, help form cell membranes, and produce hormone-like compounds called eicosanoids The body has no means to produce double bonds between any carbon atoms from the first to the ninth carbon Alpha ...
Qualitative tests of lipids 2
... Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds ,side chian are a)Short chain From 4 to 10 Carbon atoms ,and present as liquid in room Temp. e.g acetic acid and butyric acid a)Long chain: More than 10 Carbone atoms, present in solid at room Temp. e.g. Palmatic (16) acid and Stearic(18) acid ...
... Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds ,side chian are a)Short chain From 4 to 10 Carbon atoms ,and present as liquid in room Temp. e.g acetic acid and butyric acid a)Long chain: More than 10 Carbone atoms, present in solid at room Temp. e.g. Palmatic (16) acid and Stearic(18) acid ...
Hein and Arena - University of Wisconsin–Eau Claire
... digestion by forming emulsions with dietary lipids. ...
... digestion by forming emulsions with dietary lipids. ...
Saturated fatty acid
... 36 carbons, whereas the alcohols have an even number from 24 to 36 carbons. ► A component in beeswax is the ester formed from a 30-C alcohol (triacontanol) and a 16-C acid (palmitic acid). ...
... 36 carbons, whereas the alcohols have an even number from 24 to 36 carbons. ► A component in beeswax is the ester formed from a 30-C alcohol (triacontanol) and a 16-C acid (palmitic acid). ...
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... Synthetic detergents are alkylbenzene sulfonates that dissolve dirt like soaps but do not form scums with Mg+2 and Ca+2 . ...
... Synthetic detergents are alkylbenzene sulfonates that dissolve dirt like soaps but do not form scums with Mg+2 and Ca+2 . ...
Lipids (fats)
... Also known as fats Made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen When your body breaks down lipids, it turns it into fatty acids and glycerol ...
... Also known as fats Made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen When your body breaks down lipids, it turns it into fatty acids and glycerol ...
3. LIPIDS
... decrease HDL-cholesterol Current concerns about trans fatty acid intake and attempt to ↓ their dietary intake ...
... decrease HDL-cholesterol Current concerns about trans fatty acid intake and attempt to ↓ their dietary intake ...
Eicosanoid
In biochemistry, eicosanoids (preferred IUPAC name icosanoids) are signaling molecules made by oxidation of 20-carbon fatty acids.They exert complex control over many bodily systems; mainly in growth during and after physical activity, inflammation or immunity after the intake of toxic compounds and pathogens, and as messengers in the central nervous system.The networks of controls that depend upon eicosanoids are among the most complex in the human body.Eicosanoids are derived from either omega-3 (ω-3) or omega-6 (ω-6) fatty acids.In general, the ω-6 eicosanoids are pro-inflammatory; ω-3s are much less so.The amounts and balance of these fats in a person's diet will affect the body's eicosanoid-controlled functions, with effects on cardiovascular disease, triglycerides, blood pressure, and arthritis. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and other NSAIDs act by downregulating eicosanoid synthesis.There are multiple subfamilies of eicosanoids, including the prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes, as well as the lipoxins and eoxins, and others. For each, there are two or three separate series, derived from either an ω-3 or an ω-6 EFA. These series' different activities largely explain the health effects of ω-3 and ω-6 fats.