Lecture no. 3 - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... Where was radioactive sulfur found at the end of experiment 1? Where was it found at the end of experiment 2? Based on the Hershey–Chase experiments, is it reasonable to assume that Griffith’s “transforming factor” was DNA, not protein? Why or why not? What is the connection between the two ex ...
... Where was radioactive sulfur found at the end of experiment 1? Where was it found at the end of experiment 2? Based on the Hershey–Chase experiments, is it reasonable to assume that Griffith’s “transforming factor” was DNA, not protein? Why or why not? What is the connection between the two ex ...
DNA REPLICATION HANDOUT
... 1) Template strands: Original DNA strands that were ripped apart. 2) Replication Fork: Y-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongated 3) Okazaki Fragments: Only found on the lagging strand. Since DNA is connected by base pairs, as the original strand “unzips” one of the templates is running ...
... 1) Template strands: Original DNA strands that were ripped apart. 2) Replication Fork: Y-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongated 3) Okazaki Fragments: Only found on the lagging strand. Since DNA is connected by base pairs, as the original strand “unzips” one of the templates is running ...
Gene Interactions – Extensions to Mendelian Genetics
... • A pair of genes can often work together to create a specific phenotype. We call this complementary interaction. • With this type of interaction we see 2 different phenotypes instead of the 4 seen in 2 genes 1 phenotype • Two or more genotypic classes may display an identical phenotype. – Example: ...
... • A pair of genes can often work together to create a specific phenotype. We call this complementary interaction. • With this type of interaction we see 2 different phenotypes instead of the 4 seen in 2 genes 1 phenotype • Two or more genotypic classes may display an identical phenotype. – Example: ...
Unit Plan Template - Gates County Schools
... Unit Plan Reflection Describe any adaptations or “tweaks” to the resource or lesson plan that were needed: What do you plan to do differently the next time you teach this unit?: ...
... Unit Plan Reflection Describe any adaptations or “tweaks” to the resource or lesson plan that were needed: What do you plan to do differently the next time you teach this unit?: ...
Chapter 24 - The Origin of Species - Bio-Guru
... •Unless populations are geographically isolated they will continue to interbreed ...then genetic isolation •Populations diverge to the point where they no longer interbreed •This may be due to adaptation to different environments, or genetic drift ...
... •Unless populations are geographically isolated they will continue to interbreed ...then genetic isolation •Populations diverge to the point where they no longer interbreed •This may be due to adaptation to different environments, or genetic drift ...
REVIEW 5 Heredity Modern society uses scientific knowledge to
... So far we have looked at traits controlled by a single gene pair (two alleles). Many traits are controlled by more than just a single gene pair. For example, scientists have located three gene pairs (six alleles) that control eye color, and they suspect that there may be more. By tracking two of th ...
... So far we have looked at traits controlled by a single gene pair (two alleles). Many traits are controlled by more than just a single gene pair. For example, scientists have located three gene pairs (six alleles) that control eye color, and they suspect that there may be more. By tracking two of th ...
SIMULATING NATURAL SELECTION
... We know from the fossil record that species change (evolve) over time. Darwin argued, and this has subsequently been confirmed, that the primary mechanism of evolutionary change is the process of natural selection. Given that evolutionary theory is the most important unifying principle in biology, t ...
... We know from the fossil record that species change (evolve) over time. Darwin argued, and this has subsequently been confirmed, that the primary mechanism of evolutionary change is the process of natural selection. Given that evolutionary theory is the most important unifying principle in biology, t ...
Alien Protein Synthesis
... In a process known as transcription (takes place in the nucleus) messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA. mRNA then takes the message out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm and finally to the ribosome (rRNA), the site of protein synthesis in a process known as translation. It is at the ribosome ...
... In a process known as transcription (takes place in the nucleus) messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA. mRNA then takes the message out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm and finally to the ribosome (rRNA), the site of protein synthesis in a process known as translation. It is at the ribosome ...
Number 4 - Laboratory Animal Boards Study Group
... information about the problem, 3) formulate a hypothesis that can be tested, 4) gather objective data to test the hypothesis, and 5) interpret the data in regard to the identified problem. However, funding agencies require hypotheses in the proposal, perhaps assuming steps 1 & 2 were already carried ...
... information about the problem, 3) formulate a hypothesis that can be tested, 4) gather objective data to test the hypothesis, and 5) interpret the data in regard to the identified problem. However, funding agencies require hypotheses in the proposal, perhaps assuming steps 1 & 2 were already carried ...
The chromosomal theory of inheritance
... • Accidental changes in genes are called mutations mutations occur only rarely and almost always result in recessive alleles • not eliminated from the population because they are not usually expressed in most individuals (heterozygotes) • in some cases, particular mutant alleles have become more c ...
... • Accidental changes in genes are called mutations mutations occur only rarely and almost always result in recessive alleles • not eliminated from the population because they are not usually expressed in most individuals (heterozygotes) • in some cases, particular mutant alleles have become more c ...
Genetic Diversity of ploidy level Miscanthus species in Japan
... Giant Miscanthus (Miscanthus × giganteus), a highly productive sterile triploid hybrid grass that was discovered in Japan several decades ago, has considerable potential as an alternative source of energy. The aim of this study is to measure DNA content variation of each species using flow cytometry ...
... Giant Miscanthus (Miscanthus × giganteus), a highly productive sterile triploid hybrid grass that was discovered in Japan several decades ago, has considerable potential as an alternative source of energy. The aim of this study is to measure DNA content variation of each species using flow cytometry ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... whether a child will be a girl (X) or a boy (Y). So…. The father determines the sex of the baby!!!!!! Figure 3- Complete the Punnett square to show the possible genotypes and phenotypes of a child. Determine- What is the probability that the child will be a girl? A boy? Interpret Diagrams- What sex ...
... whether a child will be a girl (X) or a boy (Y). So…. The father determines the sex of the baby!!!!!! Figure 3- Complete the Punnett square to show the possible genotypes and phenotypes of a child. Determine- What is the probability that the child will be a girl? A boy? Interpret Diagrams- What sex ...
Dissection of a DNA-damage-induced transcriptional network using
... knocked-down for Rel-A, p53 and ATM), each probed at two time points: without treatment and 4 h after exposure to NCS.14 (All samples were probed in independent triplicates) ...
... knocked-down for Rel-A, p53 and ATM), each probed at two time points: without treatment and 4 h after exposure to NCS.14 (All samples were probed in independent triplicates) ...
DNA REVIEW SHEET
... 14. What are the three kinds of RNA? 15. Where is an anticodon located? 16. A codon that has no anticodon match would be called a ___________________. 17. What does DNA polymerase do? 18. Anything ending in –ase would be classified as an ____________________> 19. What 3 things make up DNA? 20. DNA i ...
... 14. What are the three kinds of RNA? 15. Where is an anticodon located? 16. A codon that has no anticodon match would be called a ___________________. 17. What does DNA polymerase do? 18. Anything ending in –ase would be classified as an ____________________> 19. What 3 things make up DNA? 20. DNA i ...
Chromosome Mapping The following data were collected from
... Chromosome Mapping The following data were collected from repeated matings of fruit flies (D. melanogaster). The data record the frequency, to 0.1 percent, of the recombinant characteristics for seven genes located on the same side of the centromere on chromosome 3. The veinlet gene is located one m ...
... Chromosome Mapping The following data were collected from repeated matings of fruit flies (D. melanogaster). The data record the frequency, to 0.1 percent, of the recombinant characteristics for seven genes located on the same side of the centromere on chromosome 3. The veinlet gene is located one m ...
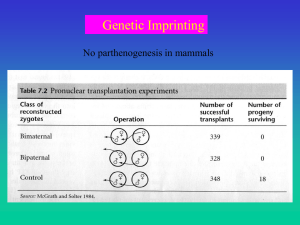
מצגת של PowerPoint
... Imprinted genes are expressed either from the maternally or paternally inherited copy only, and they play a key role in regulating complex biological processes, including offspring development and mother-offspring interactions. There are several competing theories attempting to explain the evolution ...
... Imprinted genes are expressed either from the maternally or paternally inherited copy only, and they play a key role in regulating complex biological processes, including offspring development and mother-offspring interactions. There are several competing theories attempting to explain the evolution ...
Genetic Analysis of Phytophthora Rot Resistance in the
... disease in soybeans for many years. Recent crop loss estimates have ranked Phytophthora root rot as the second or third most destructive disease for soybeans (Doupnik, 1993). Resistance to Phytophthora in soybeans is controlled by thirteen dominant genes. There are fifty-three known races of the pat ...
... disease in soybeans for many years. Recent crop loss estimates have ranked Phytophthora root rot as the second or third most destructive disease for soybeans (Doupnik, 1993). Resistance to Phytophthora in soybeans is controlled by thirteen dominant genes. There are fifty-three known races of the pat ...
Genetic Basis of Cancer Student Handout ACTIVITY 1
... and what do they do? Cancer consists of a group of diseases caused by mutations in the DNA of cells. Some mutations are inherited, but most occur during a person’s lifetime as a result of random errors in replication. Environmental factors that damage DNA, such as smoking and sunlight, can also caus ...
... and what do they do? Cancer consists of a group of diseases caused by mutations in the DNA of cells. Some mutations are inherited, but most occur during a person’s lifetime as a result of random errors in replication. Environmental factors that damage DNA, such as smoking and sunlight, can also caus ...
EOC Review Part 3
... This can also be done to find relativesthe closer the patterns the closer the relative This can be used to find the parents of a childthe child cannot not have any bands that it didn’t get from mom or dad. Larry you are the Father! ...
... This can also be done to find relativesthe closer the patterns the closer the relative This can be used to find the parents of a childthe child cannot not have any bands that it didn’t get from mom or dad. Larry you are the Father! ...
Genes Are Only Part of the Story | Print Article
... more than doubled the risk of having a heart attack in men who were less than 50 years old and women less than 60 years old. In the first study, scientists at deCODE Genetics in Iceland examined blood samples from more than 17,000 people and compared those who had heart disease with those who did no ...
... more than doubled the risk of having a heart attack in men who were less than 50 years old and women less than 60 years old. In the first study, scientists at deCODE Genetics in Iceland examined blood samples from more than 17,000 people and compared those who had heart disease with those who did no ...
Slide 1
... GJB2, MYO7A, CDH23, OTOF, SLC26A4, TMC1, are quite common and can be tested in individuals with hearing loss. Mutations in many other genes are extraordinarily rare, some of which have been reported in only one or two consanguineous families. ...
... GJB2, MYO7A, CDH23, OTOF, SLC26A4, TMC1, are quite common and can be tested in individuals with hearing loss. Mutations in many other genes are extraordinarily rare, some of which have been reported in only one or two consanguineous families. ...
Essential Standard: 1.1 Understanding the relationship between
... method of sexual reproduction within cells that increases the genetic variation of a population ...
... method of sexual reproduction within cells that increases the genetic variation of a population ...
Free Response Review
... (b) Information flow can be altered by mutation. Describe THREE different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis. (c) Identify TWO environmental factors that increase the mutation rate in an organism, and discuss their effect on the genome of the organism. (d) Epigenetics is the st ...
... (b) Information flow can be altered by mutation. Describe THREE different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis. (c) Identify TWO environmental factors that increase the mutation rate in an organism, and discuss their effect on the genome of the organism. (d) Epigenetics is the st ...