BITC1311 Intro to Biotechnology Name
... Describe 2 ways in which genetically engineered plants can improve the quality and safety of food production. a. In what way can they increase crop production? b. What makes plants attractive hosts for the production of recombinant proteins? Transgenic animals are being used as “bioreactors” for the ...
... Describe 2 ways in which genetically engineered plants can improve the quality and safety of food production. a. In what way can they increase crop production? b. What makes plants attractive hosts for the production of recombinant proteins? Transgenic animals are being used as “bioreactors” for the ...
Week 5: The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, population differences
... genotype frequencies, but the combination of the two populations did not there was a deficiency of heterozygotes from what would be expected under HW. This is what’s called the Wahlund effect. ● Populations differ: ○ May have different allele and genotype frequencies ○ But they may also have ...
... genotype frequencies, but the combination of the two populations did not there was a deficiency of heterozygotes from what would be expected under HW. This is what’s called the Wahlund effect. ● Populations differ: ○ May have different allele and genotype frequencies ○ But they may also have ...
Expression Analysis of the Sphingolipid Metabolism
... GenMAPP v2.1, a Windows operating program, provides a technique for conducting a genomic analysis through the visualization of gene expression data within a metabolic pathway. Expression data derived from microarray and other similar genomic experiments can be imported and recognized by GenMAPP usin ...
... GenMAPP v2.1, a Windows operating program, provides a technique for conducting a genomic analysis through the visualization of gene expression data within a metabolic pathway. Expression data derived from microarray and other similar genomic experiments can be imported and recognized by GenMAPP usin ...
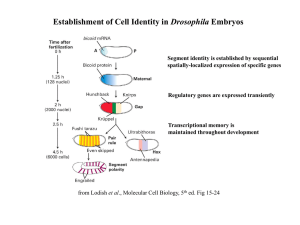
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
... Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
Unit: Equilibrium Differentiated (Tiered) Task What Is Happening To
... 1. Assign a letter to each of the normal and lethal alleles, and use the letters to form the genotypes of the salamanders. Produce a Punnett square showing the cross of two salamanders, both of which are heterozygous for the lethal gene. Provide a key to the symbols you use in the cross and identify ...
... 1. Assign a letter to each of the normal and lethal alleles, and use the letters to form the genotypes of the salamanders. Produce a Punnett square showing the cross of two salamanders, both of which are heterozygous for the lethal gene. Provide a key to the symbols you use in the cross and identify ...
Natural Selection in Spatially Structured Populations Case for
... The main purpose of theoretical population genetics is to understand the complex patterns of genetic variation that we observe in the world around us, and to show how these lead to the evolution of adaptation and diversity. Its origins can be traced to the pioneering work of Fisher, Haldane and Wrig ...
... The main purpose of theoretical population genetics is to understand the complex patterns of genetic variation that we observe in the world around us, and to show how these lead to the evolution of adaptation and diversity. Its origins can be traced to the pioneering work of Fisher, Haldane and Wrig ...
“Indeed, the Homeobox has been called the `Rosetta Stone` of
... Figure 11.42(1) Evolutionary Conservation of Homeotic Gene Organization and Transcriptional Expression ...
... Figure 11.42(1) Evolutionary Conservation of Homeotic Gene Organization and Transcriptional Expression ...
Genetics Concept Inventory
... 1) state that DNA and chromosomes are made of protein or that DNA is composed of genes, 2) are confused over the difference between chromosomes and chromatids and don’t correlate alleles with chromatids, 3) think that cells contain only the genetic material they need to carry out their functions or ...
... 1) state that DNA and chromosomes are made of protein or that DNA is composed of genes, 2) are confused over the difference between chromosomes and chromatids and don’t correlate alleles with chromatids, 3) think that cells contain only the genetic material they need to carry out their functions or ...
File - Biology 30 DIploma Prep
... • Density-dependent, limits growth of a population • Aids in natural selection • Some individuals have a “competitive advantage” which makes them better able to survive, and therefore reproduce ...
... • Density-dependent, limits growth of a population • Aids in natural selection • Some individuals have a “competitive advantage” which makes them better able to survive, and therefore reproduce ...
population
... • Duplication of small pieces of DNA increases genome size and is usually less harmful • Duplicated genes can take on new functions by further mutation • An ancestral odor-detecting gene has been duplicated many times: humans have 1,000 copies of the gene, mice have 1,300 ...
... • Duplication of small pieces of DNA increases genome size and is usually less harmful • Duplicated genes can take on new functions by further mutation • An ancestral odor-detecting gene has been duplicated many times: humans have 1,000 copies of the gene, mice have 1,300 ...
Test Info Sheet
... offered in two tiers. Tier 1 comprises the two main exons 31 and 32, while Tier 2 includes bi-directional sequence analysis of the remaining 30 exons. Mutations found in the first person of a family to be tested are confirmed by repeat analysis using sequencing, restriction fragment analysis, or ano ...
... offered in two tiers. Tier 1 comprises the two main exons 31 and 32, while Tier 2 includes bi-directional sequence analysis of the remaining 30 exons. Mutations found in the first person of a family to be tested are confirmed by repeat analysis using sequencing, restriction fragment analysis, or ano ...
Faithful meiotic chromosome segregation in Caenorhabditis elegans
... We use the genetic model system C. elegans to identify genes that are essential for proper meiotic prophase cell cycle progression and faithful meiotic chromosome segregation. Characterization of the encoded factors, their interaction partners and identification of mammalian (human) homologues will ...
... We use the genetic model system C. elegans to identify genes that are essential for proper meiotic prophase cell cycle progression and faithful meiotic chromosome segregation. Characterization of the encoded factors, their interaction partners and identification of mammalian (human) homologues will ...
Chapter 13 outline
... variation - offsprings differ somewhat in appearance from parents and siblings. genetics - the scientific study of heredity and hereditary variation. gene pool - the total aggregate of genes in a population at any one time. asexual reproduction - a type of reproduction involving only one parent that ...
... variation - offsprings differ somewhat in appearance from parents and siblings. genetics - the scientific study of heredity and hereditary variation. gene pool - the total aggregate of genes in a population at any one time. asexual reproduction - a type of reproduction involving only one parent that ...
RECOMBINANT DNA
... 1. Obtain ONE strip of plasmid DNA and ONE strip of a human gene. 2. Genetic engineers use plasmids to introduce new genes into bacteria. The plasmid DNA is actually circular and the two ends are normally connected. Tape together the two ends of the plasmid DNA molecule to form a ring. 3. Genetic en ...
... 1. Obtain ONE strip of plasmid DNA and ONE strip of a human gene. 2. Genetic engineers use plasmids to introduce new genes into bacteria. The plasmid DNA is actually circular and the two ends are normally connected. Tape together the two ends of the plasmid DNA molecule to form a ring. 3. Genetic en ...
File
... DNA molecules can build an exact copy of itself. This is called replication. (ATP is the energy source) Replication is important for reproduction and must occur every time a cell divides. That way each cell has a complete set of instructions for making proteins. ...
... DNA molecules can build an exact copy of itself. This is called replication. (ATP is the energy source) Replication is important for reproduction and must occur every time a cell divides. That way each cell has a complete set of instructions for making proteins. ...
Genetic Algorithms
... strings (chromosomes) that undergo -- selection (based on their fitness) -- crossover (mutually among themselves randomly) -- mutation (randomly) Note – crossover and mutation destroy old solutions Elitism – Some elite (good) solutions are carried onto the next generation without being destroyed. It ...
... strings (chromosomes) that undergo -- selection (based on their fitness) -- crossover (mutually among themselves randomly) -- mutation (randomly) Note – crossover and mutation destroy old solutions Elitism – Some elite (good) solutions are carried onto the next generation without being destroyed. It ...
I. Microbial Genetics (Chapter 7) A. Overview 1. all of the information
... a. if the cell has low concentrations of tryptophan, the ribosomes pause in region 1 and region 2 binds to region 3 (1) the termination loop (region 3 binding to region 4) does not form (2) RNA polymerase continues to transcribe the gene b. if the cell has high levels of tryptophan, the ribosomes fo ...
... a. if the cell has low concentrations of tryptophan, the ribosomes pause in region 1 and region 2 binds to region 3 (1) the termination loop (region 3 binding to region 4) does not form (2) RNA polymerase continues to transcribe the gene b. if the cell has high levels of tryptophan, the ribosomes fo ...
File
... • There are over eight million combinations possible from the 23 chromosomes you inherit from your mom and 23 you inherit from your dad. • The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called heredity. ...
... • There are over eight million combinations possible from the 23 chromosomes you inherit from your mom and 23 you inherit from your dad. • The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called heredity. ...
A NOTE ON EFFECTIVE POPULATION SIZE WITH
... order terms were included, to give N e = (N-I ) L/un2. Monoecious diploids: Assuming random mating, but without any need to specify the joint age distribution of mates, the analysis extends readily to monecious diploids with random selfing. If N individuals are born in each cohort, the probability o ...
... order terms were included, to give N e = (N-I ) L/un2. Monoecious diploids: Assuming random mating, but without any need to specify the joint age distribution of mates, the analysis extends readily to monecious diploids with random selfing. If N individuals are born in each cohort, the probability o ...
013368718X_CH11_159-178.indd
... A. Specific characteristics that vary among individuals B. The offspring of true-breeding parents with different traits C. Factors that determine traits D. Sex cells, egg or sperm E. The different forms of a gene ...
... A. Specific characteristics that vary among individuals B. The offspring of true-breeding parents with different traits C. Factors that determine traits D. Sex cells, egg or sperm E. The different forms of a gene ...
1-2-13 Genetics PPT -FILL IN THE BLANK NOTES
... He observed that the _________ generation were all __________________ flowers. ______________________________ the ______ generation he found that the _______ generation had a ratio of______________. * One __________ for every three_____________. He concluded that the ________________________________ ...
... He observed that the _________ generation were all __________________ flowers. ______________________________ the ______ generation he found that the _______ generation had a ratio of______________. * One __________ for every three_____________. He concluded that the ________________________________ ...
GENETIC ENGINEERING: WHERE DOES IT STOP? Nada
... soon be able to create the "perfect" individual. We must now face the question: is this choice morally correct? The technological breakthrough is already altering the way in which people approach having children. Soon babies will no longer be wonderful creations of God's choice, but instead products ...
... soon be able to create the "perfect" individual. We must now face the question: is this choice morally correct? The technological breakthrough is already altering the way in which people approach having children. Soon babies will no longer be wonderful creations of God's choice, but instead products ...
Chapter 6 Genes and Gene Technology Section 1 We now know
... 11. Make sure you understand that one side of the DNA molecule is complimentary to the other side regarding the bases that pair up. 12. When a DNA molecule makes a copy of itself it “unzips” resembling a zipper or an upside down Y. When DNA makes a copy of itself we say it ________________ or has un ...
... 11. Make sure you understand that one side of the DNA molecule is complimentary to the other side regarding the bases that pair up. 12. When a DNA molecule makes a copy of itself it “unzips” resembling a zipper or an upside down Y. When DNA makes a copy of itself we say it ________________ or has un ...