Chap 11 Student Notes - Blair Community Schools
... E. ________________ – a new individual splits off from existing one F. Parthenogenesis – process in which female makes viable egg that grows into an adult without being fertilized by a male II. Sexual Reproduction A. ...
... E. ________________ – a new individual splits off from existing one F. Parthenogenesis – process in which female makes viable egg that grows into an adult without being fertilized by a male II. Sexual Reproduction A. ...
Document
... of chromosomes and chromatin varies through the cell cycle. Chromosomes are the essential unit for cellular division and must be replicated, divided, and passed successfully to their daughter cells so as to ensure the genetic diversity and survival of their progeny. Chromosomes may exist as either d ...
... of chromosomes and chromatin varies through the cell cycle. Chromosomes are the essential unit for cellular division and must be replicated, divided, and passed successfully to their daughter cells so as to ensure the genetic diversity and survival of their progeny. Chromosomes may exist as either d ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Test
... 3. Diploid refers to? The amount of chromosomes 4. The two halves of a replicated chromosome are referred to as – Sister Chromatids 5. The T-shaped organelle responsible for pulling a chromosome apart - Centrioles Column A _b_6. The final phase of mitosis, in which two daughter cells are formed, eac ...
... 3. Diploid refers to? The amount of chromosomes 4. The two halves of a replicated chromosome are referred to as – Sister Chromatids 5. The T-shaped organelle responsible for pulling a chromosome apart - Centrioles Column A _b_6. The final phase of mitosis, in which two daughter cells are formed, eac ...
09ans - Evergreen Archives
... move to one pole during anaphase, leaving one daughter cell with one extra copy and the other daughter cell lacking a copy. Both daughter cells then have an imbalance with respect to the normal gene complement. Too many copies of a set of genes can cause abnormalities, such as Down syndrome. The abs ...
... move to one pole during anaphase, leaving one daughter cell with one extra copy and the other daughter cell lacking a copy. Both daughter cells then have an imbalance with respect to the normal gene complement. Too many copies of a set of genes can cause abnormalities, such as Down syndrome. The abs ...
Meosis Definitions – Let`s talk about sex
... Recall that chromosomes are composed of DNA and contain the genetic blueprint for an organism. Each species has its own unique set of chromosome, and all individuals in a particular species typically have the same number of chromosomes. Humans have 46 chromosomes. The domestic dog has 78 chromosomes ...
... Recall that chromosomes are composed of DNA and contain the genetic blueprint for an organism. Each species has its own unique set of chromosome, and all individuals in a particular species typically have the same number of chromosomes. Humans have 46 chromosomes. The domestic dog has 78 chromosomes ...
Exam practice answers 8
... (ii) Prophase of division 1. (iii) If the chiasma forms between non-sister chromatids, the alleles on homologous chromosomes can be exchanged. This produces new combinations of alleles in the gametes. New combinations of alleles mean that there is genetic variation. Selection can occur and the speci ...
... (ii) Prophase of division 1. (iii) If the chiasma forms between non-sister chromatids, the alleles on homologous chromosomes can be exchanged. This produces new combinations of alleles in the gametes. New combinations of alleles mean that there is genetic variation. Selection can occur and the speci ...
Brooker Chapter 9
... • Late 1800’s – microscopy studies – egg and sperm nuclei unite and contribute equally (e.g. frogs, sea urchins) – dyes used to stain the nucleus and observed long, threadlike bodies = Chromosomes (“colored bodies) – Mitosis described (nucleus is equally partitioned into daughter cells) – Sex Deter ...
... • Late 1800’s – microscopy studies – egg and sperm nuclei unite and contribute equally (e.g. frogs, sea urchins) – dyes used to stain the nucleus and observed long, threadlike bodies = Chromosomes (“colored bodies) – Mitosis described (nucleus is equally partitioned into daughter cells) – Sex Deter ...
IB Biology--Chromosome Review Activity
... 24. Use drawings to compare telocentric ,metacentric , submetacentric , and acrocentric chromosomes .Give 1 example of the last 3 in humans. ...
... 24. Use drawings to compare telocentric ,metacentric , submetacentric , and acrocentric chromosomes .Give 1 example of the last 3 in humans. ...
Reading Guide for Chapter 10
... a. What is the number of chromosomes in a gamete (haploid – n) cell for: i. An apple: _________ ii. A fern: _________ iii. A fruit fly: _______ iv. A human: ________ v. A chimpanzee: _______ vi. A dog: ___________ b. What is the number of chromosomes in a body cell (diploid-2n) for: vii. An apple: _ ...
... a. What is the number of chromosomes in a gamete (haploid – n) cell for: i. An apple: _________ ii. A fern: _________ iii. A fruit fly: _______ iv. A human: ________ v. A chimpanzee: _______ vi. A dog: ___________ b. What is the number of chromosomes in a body cell (diploid-2n) for: vii. An apple: _ ...
RevShtFinalBio160
... A cell which has a diploid (2n) number of 6 undergoes either mitosis or meiosis. Use the pictures below to answer questions about the stages of division for this cell. (Note: if the correct answer below is more than one letter long, like “ae.”, mark both a AND e on your answer sheet for that questio ...
... A cell which has a diploid (2n) number of 6 undergoes either mitosis or meiosis. Use the pictures below to answer questions about the stages of division for this cell. (Note: if the correct answer below is more than one letter long, like “ae.”, mark both a AND e on your answer sheet for that questio ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
File
... Lecture 2: Population Genetic and Evolution: 1.5 One statement is correct about founder population: A. It is larger than the parent population B. less rare allele or absent C. The effect of genetic drift will be small D. All of the above ...
... Lecture 2: Population Genetic and Evolution: 1.5 One statement is correct about founder population: A. It is larger than the parent population B. less rare allele or absent C. The effect of genetic drift will be small D. All of the above ...
Review - Peoria Public Schools
... 13. If separation of chromosomes does not occur, either in the first meiotic division or the second, an occurrence referred to as non-disjunction is said to occur. 14. One of the most common examples of non-disjunction is Down’s syndrome. These individuals have an extra 21st chromosome and the condi ...
... 13. If separation of chromosomes does not occur, either in the first meiotic division or the second, an occurrence referred to as non-disjunction is said to occur. 14. One of the most common examples of non-disjunction is Down’s syndrome. These individuals have an extra 21st chromosome and the condi ...
Mitosis/Meiosis Modeling Lab Analysis Questions – Answer Key
... Mitosis/Meiosis Modeling Lab Analysis Questions – Answer Key Mitosis Modeling If a cell contains a set of duplicated chromosomes, does it contain any more genetic information than the cell before the chromosomes were duplicated? No. There is twice the amount of genetic material but no additional dif ...
... Mitosis/Meiosis Modeling Lab Analysis Questions – Answer Key Mitosis Modeling If a cell contains a set of duplicated chromosomes, does it contain any more genetic information than the cell before the chromosomes were duplicated? No. There is twice the amount of genetic material but no additional dif ...
Meiosis and Genetics
... Diploid (2n) = 2 Haploid (n) = 1 •Explain how this diagram of meiosis could relate to Mendel’s idea that two “factors” must control a trait. ...
... Diploid (2n) = 2 Haploid (n) = 1 •Explain how this diagram of meiosis could relate to Mendel’s idea that two “factors” must control a trait. ...
Activating Strategy AP Lesson #65
... – new species form in an empty environment – competition between species is minimal but increases with time – differences are selected for ...
... – new species form in an empty environment – competition between species is minimal but increases with time – differences are selected for ...
Meiosis Student Notes • Organisms have tens of thousands of
... _____________________ – A different type of cell division where gametes have half the number of chromosomes as the parents. ...
... _____________________ – A different type of cell division where gametes have half the number of chromosomes as the parents. ...
D2 Species and Speciation
... Another barrier between gene pools can occur due to polyploidy. A polyploidy organism has more than two sets of chromosomes. The normal number of sets is 2, known as diploid (2n), polyploidy organism could contain 3 or more sets. 3n triploid, 4n tetraploid. Polyploidy is widespread in plants but rar ...
... Another barrier between gene pools can occur due to polyploidy. A polyploidy organism has more than two sets of chromosomes. The normal number of sets is 2, known as diploid (2n), polyploidy organism could contain 3 or more sets. 3n triploid, 4n tetraploid. Polyploidy is widespread in plants but rar ...
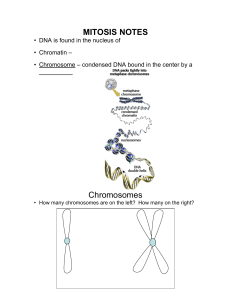
Mitosis Notes
... Cell starts to pinch at Spindle fibers disappear Chromosomes unwind to become ______ _______ forms in plant cells ...
... Cell starts to pinch at Spindle fibers disappear Chromosomes unwind to become ______ _______ forms in plant cells ...
Honors Biology Final Exam-‐Part 2-‐Semester 2
... 36. Changes in allele frequencies within a population are referred to as: 37. Organisms that look alike and interbreed to produce fertile offspring 38. Any trait that better enables an organism ...
... 36. Changes in allele frequencies within a population are referred to as: 37. Organisms that look alike and interbreed to produce fertile offspring 38. Any trait that better enables an organism ...
Chapter 14 – Human Genome
... Males only have one X chromosome so they will have black spots or orange spots but not both ...
... Males only have one X chromosome so they will have black spots or orange spots but not both ...
A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism
... 1. A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. 2. A karyotype shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes grouped together in pairs, arranged in order of decreasing size. 3. Two of the 46 chromosomes in the human genome are known as sex chromosomes, because ...
... 1. A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. 2. A karyotype shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes grouped together in pairs, arranged in order of decreasing size. 3. Two of the 46 chromosomes in the human genome are known as sex chromosomes, because ...
Human Heredity - Catawba County Schools
... carry other traits besides the one determining the male sex characteristics • Males MUST always express all of their X genes • ** You can tell a trait is sex-linked if more males than females have it in the population!!** ...
... carry other traits besides the one determining the male sex characteristics • Males MUST always express all of their X genes • ** You can tell a trait is sex-linked if more males than females have it in the population!!** ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.