Compounds of Chlorine
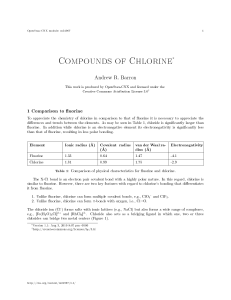
... Hydrogen chloride (HCl) is prepared by the reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2 SO4 ) with either NaCl or concentrated HCl solution. Hydrogen chloride is a polar molecule with a dipole of 1.08 D. However, the lower polarity as compared to that of hydrogen uoride (1.91 D) is consistent with th ...
... Hydrogen chloride (HCl) is prepared by the reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2 SO4 ) with either NaCl or concentrated HCl solution. Hydrogen chloride is a polar molecule with a dipole of 1.08 D. However, the lower polarity as compared to that of hydrogen uoride (1.91 D) is consistent with th ...
BIOC203W1_Lecture Slides_Enzymes
... as they were such as- Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, pepsin etc. The above nomenclature was confusing considering the vast number of enzymes. Finally, the Enzyme Commission (EC) of the International Union of Biochemistry (IUB) developed a new naming system. Each enzyme will have a code and a systemic name c ...
... as they were such as- Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, pepsin etc. The above nomenclature was confusing considering the vast number of enzymes. Finally, the Enzyme Commission (EC) of the International Union of Biochemistry (IUB) developed a new naming system. Each enzyme will have a code and a systemic name c ...
Theoretical Study of Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe(CO)5 with OH
... explored for the last stages of this chemical process as a mechanistic alternative to regenerate the starting catalyst. Introduction The water gas shift reaction (WGSR), eq 1, is a key process in the worldwide chemical industry.1 Its importance derives from its role both as a means for enriching the ...
... explored for the last stages of this chemical process as a mechanistic alternative to regenerate the starting catalyst. Introduction The water gas shift reaction (WGSR), eq 1, is a key process in the worldwide chemical industry.1 Its importance derives from its role both as a means for enriching the ...
____ 1. The energy required to convert a ground
... 72. The phase diagram for the pure substance X is shown above. The temperature of a sample of pure solid X is slowly raised from 10oC to 100oC constant pressure of 0.5 atm. What is the expected behavior of the substance? a. It first melts to a liquid and then boils at d. It sublimes to a vapor at an ...
... 72. The phase diagram for the pure substance X is shown above. The temperature of a sample of pure solid X is slowly raised from 10oC to 100oC constant pressure of 0.5 atm. What is the expected behavior of the substance? a. It first melts to a liquid and then boils at d. It sublimes to a vapor at an ...
mole concept and stoichiometry
... 2.4 Law of Reciprocal Proportions Jeremiasa Richter German scientist in 1972 proposed a law known as “Law of Reciprocal Proportions “ The Law States that , “The ratio of the weights of two elements, A and B which combine separately with a fixed weight of the third element C is either the same or som ...
... 2.4 Law of Reciprocal Proportions Jeremiasa Richter German scientist in 1972 proposed a law known as “Law of Reciprocal Proportions “ The Law States that , “The ratio of the weights of two elements, A and B which combine separately with a fixed weight of the third element C is either the same or som ...
Unit 7 Homework and Lab Packet
... rinse off any remaining copper from the nails before removing them completely from the beaker. If necessary, use a stirring rod to scrape any excess copper from the nails. Set the nails aside on a paper towel to dry. 7. After the nails are completely dry find the mass of the nails and record. 8. Dec ...
... rinse off any remaining copper from the nails before removing them completely from the beaker. If necessary, use a stirring rod to scrape any excess copper from the nails. Set the nails aside on a paper towel to dry. 7. After the nails are completely dry find the mass of the nails and record. 8. Dec ...
From Organometallic Zinc and Copper Complexes to Highly
... tank reactor (CSTR), under an atmosphere of N2 at 298 K. A 3:1 H2:CO2 mixture, at 50 bar, was added and the reactor was heated to 523 K. The reaction was monitored using an in-line GC to detect the formation of methanol. During the first 120 mins the quantity of methanol produced steadily increased ...
... tank reactor (CSTR), under an atmosphere of N2 at 298 K. A 3:1 H2:CO2 mixture, at 50 bar, was added and the reactor was heated to 523 K. The reaction was monitored using an in-line GC to detect the formation of methanol. During the first 120 mins the quantity of methanol produced steadily increased ...
1984 Advanced Placement Exam
... 54. Which of the following statements is always true about the phase diagram of any one–component system? (A) The slope of the curve representing equilibrium between the vapor and liquid phases is positive. (B) The slope of the curve representing equilibrium between the liquid and solid phases is ne ...
... 54. Which of the following statements is always true about the phase diagram of any one–component system? (A) The slope of the curve representing equilibrium between the vapor and liquid phases is positive. (B) The slope of the curve representing equilibrium between the liquid and solid phases is ne ...
STUDY GUIDE
... multiple bonds, and they are more reactive than alkanes. They may participate in addition reactions, including hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, and hydration. A naming scheme has been established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) to name the organic comp ...
... multiple bonds, and they are more reactive than alkanes. They may participate in addition reactions, including hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, and hydration. A naming scheme has been established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) to name the organic comp ...
Chemical Thermodynamics - Winona State University
... • A process that is spontaneous in one direction is not spontaneous in the opposite direction. • The direction of a spontaneous process can depend on temperature: Ice turning to water is spontaneous at T > 0C, Water turning to ice is spontaneous at T < 0C. Reversible and Irreversible Processes • A ...
... • A process that is spontaneous in one direction is not spontaneous in the opposite direction. • The direction of a spontaneous process can depend on temperature: Ice turning to water is spontaneous at T > 0C, Water turning to ice is spontaneous at T < 0C. Reversible and Irreversible Processes • A ...
Chapter12
... c. Moles - The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation tells us the number of moles of reactants and products. The equation tells us that 1 mol of N2(g) reacts with 3mol of H2(g) to yield 2 mol of NH3(g). Using this information, we can calculate the amounts of reactants and products. Note: the ...
... c. Moles - The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation tells us the number of moles of reactants and products. The equation tells us that 1 mol of N2(g) reacts with 3mol of H2(g) to yield 2 mol of NH3(g). Using this information, we can calculate the amounts of reactants and products. Note: the ...
2. The Magic of Chemical Reactions
... are TRUE or FALSE. When oils and fats are allowed to stand for a long time, they become rancid. Respiration is a physical change. According to the law of constant proportion, the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. Antioxidants are used to prevent oxidation of foo ...
... are TRUE or FALSE. When oils and fats are allowed to stand for a long time, they become rancid. Respiration is a physical change. According to the law of constant proportion, the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. Antioxidants are used to prevent oxidation of foo ...
chap-4-atomic-weights
... second experiment above wasn’t quite so bad: it would suggest that adding 2 O atoms to an N (since it used twice the volume of oxygen) made a product twice as large as the N. ...
... second experiment above wasn’t quite so bad: it would suggest that adding 2 O atoms to an N (since it used twice the volume of oxygen) made a product twice as large as the N. ...
Gas Laws
... What is a solid – solid solution of two or more metals called? alloy A mixture in which the particles are so small that they will not reflect the “light” from a laser are called solution. A solution that contains a large amount of solute per amount of solvent is called a concentrated solution. What ...
... What is a solid – solid solution of two or more metals called? alloy A mixture in which the particles are so small that they will not reflect the “light” from a laser are called solution. A solution that contains a large amount of solute per amount of solvent is called a concentrated solution. What ...
Gas Laws
... What is a solid – solid solution of two or more metals called? alloy A mixture in which the particles are so small that they will not reflect the “light” from a laser are called solution. A solution that contains a large amount of solute per amount of solvent is called a concentrated solution. What ...
... What is a solid – solid solution of two or more metals called? alloy A mixture in which the particles are so small that they will not reflect the “light” from a laser are called solution. A solution that contains a large amount of solute per amount of solvent is called a concentrated solution. What ...
Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective
... Esterification of tert-butanol by acetic anhydride, a typical acid–base catalytic reaction, was conducted with excellent selectivity and high yield in a neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate). Many other tertiary alcohols could also be successfully converted t ...
... Esterification of tert-butanol by acetic anhydride, a typical acid–base catalytic reaction, was conducted with excellent selectivity and high yield in a neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate). Many other tertiary alcohols could also be successfully converted t ...
Sample Exercise 19.1 Identifying Spontaneous Processes
... (thermal equilibrium), will be somewhere between the initial temperatures of the metal and the water. (b) Experience tells us that this process is not spontaneous—we certainly have never seen hydrogen and oxygen gases spontaneously bubbling up out of water! Rather, the reverse process—the reaction o ...
... (thermal equilibrium), will be somewhere between the initial temperatures of the metal and the water. (b) Experience tells us that this process is not spontaneous—we certainly have never seen hydrogen and oxygen gases spontaneously bubbling up out of water! Rather, the reverse process—the reaction o ...
Nikolai N. Semenov - Nobel Lecture
... chain reactions with degenerate branching. These reactions are characterized in that their primary product is a molecular intermediate which enters relatively slowly into the reaction leading to the formation of free radicals. The existence of such reactions was proved even in the thirties, when it ...
... chain reactions with degenerate branching. These reactions are characterized in that their primary product is a molecular intermediate which enters relatively slowly into the reaction leading to the formation of free radicals. The existence of such reactions was proved even in the thirties, when it ...
19 BROWN Chemical Thermodynamics PPTSExercise
... (thermal equilibrium), will be somewhere between the initial temperatures of the metal and the water. (b) Experience tells us that this process is not spontaneous—we certainly have never seen hydrogen and oxygen gases spontaneously bubbling up out of water! Rather, the reverse process—the reaction o ...
... (thermal equilibrium), will be somewhere between the initial temperatures of the metal and the water. (b) Experience tells us that this process is not spontaneous—we certainly have never seen hydrogen and oxygen gases spontaneously bubbling up out of water! Rather, the reverse process—the reaction o ...
Slide 1
... (thermal equilibrium), will be somewhere between the initial temperatures of the metal and the water. (b) Experience tells us that this process is not spontaneous—we certainly have never seen hydrogen and oxygen gases spontaneously bubbling up out of water! Rather, the reverse process—the reaction o ...
... (thermal equilibrium), will be somewhere between the initial temperatures of the metal and the water. (b) Experience tells us that this process is not spontaneous—we certainly have never seen hydrogen and oxygen gases spontaneously bubbling up out of water! Rather, the reverse process—the reaction o ...
4. chemical kinetics
... In case of solids, rate increases with decrease in the size of particle. Rate is faster in powdered state than that of undivided state because surface area increases and the possibility of contact between reactant molecules increases. ...
... In case of solids, rate increases with decrease in the size of particle. Rate is faster in powdered state than that of undivided state because surface area increases and the possibility of contact between reactant molecules increases. ...
Photogeneration of Hydride Donors and Their Use Toward CO2
... [1•HH]•+ species with a dramatically increased hydricity that can donate its hydride to [CpRe(NO)(CO)2]+ to form CpRe(NO)(CO)(CHO), the most difficult step in CO2 reduction to methanol. Our experiments indicate that the excited state of [1•HH]2+ lives 70 ns and can be reductively quenched by amine t ...
... [1•HH]•+ species with a dramatically increased hydricity that can donate its hydride to [CpRe(NO)(CO)2]+ to form CpRe(NO)(CO)(CHO), the most difficult step in CO2 reduction to methanol. Our experiments indicate that the excited state of [1•HH]2+ lives 70 ns and can be reductively quenched by amine t ...
Hydrogen: An Assessment of Its Potential for Energy Use
... national security standpoints is driven primarily by the possibility of developing practical transportation solutions. Hydrogen‐powered vehicles will use a hydrogen fuel cell or hydrogen combustion engine. Hydrogen storage must be developed to be much more efficient, and ve ...
... national security standpoints is driven primarily by the possibility of developing practical transportation solutions. Hydrogen‐powered vehicles will use a hydrogen fuel cell or hydrogen combustion engine. Hydrogen storage must be developed to be much more efficient, and ve ...
Exam - Vcaa
... Large deposits of methane hydrate have been discovered deep under the sediment on the ocean floor. It has been suggested that methane hydrate deposits could be commercially mined to provide a clean fuel once the trapped methane is extracted. Methane hydrate has a complex structure. The simplified fo ...
... Large deposits of methane hydrate have been discovered deep under the sediment on the ocean floor. It has been suggested that methane hydrate deposits could be commercially mined to provide a clean fuel once the trapped methane is extracted. Methane hydrate has a complex structure. The simplified fo ...
WA AP Chem gas law IMF MC Set C
... B. The intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonds, between the H2O (l) molecules require energy to be overcome, and the molecules can only separate to become a gas once these intermolecular forces are overcome. C. Water vapor is hotter than or equal in temperature to water at constant pressure, a ...
... B. The intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonds, between the H2O (l) molecules require energy to be overcome, and the molecules can only separate to become a gas once these intermolecular forces are overcome. C. Water vapor is hotter than or equal in temperature to water at constant pressure, a ...
Catalytic reforming

Catalytic reforming is a chemical process used to convert petroleum refinery naphthas distilled from crude oil (typically having low octane ratings) into high-octane liquid products called reformates, which are premium blending stocks for high-octane gasoline. The process converts low-octane linear hydrocarbons (paraffins) into branched alkanes (isoparaffins) and cyclic naphthenes, which are then partially dehydrogenated to produce high-octane aromatic hydrocarbons. The dehydrogenation also produces significant amounts of byproduct hydrogen gas, which is fed into other refinery processes such as hydrocracking. A side reaction is hydrogenolysis, which produces light hydrocarbons of lower value, such as methane, ethane, propane and butanes.In addition to a gasoline blending stock, reformate is the main source of aromatic bulk chemicals such as benzene, toluene, xylene and ethylbenzene which have diverse uses, most importantly as raw materials for conversion into plastics. However, the benzene content of reformate makes it carcinogenic, which has led to governmental regulations effectively requiring further processing to reduce its benzene content.This process is quite different from and not to be confused with the catalytic steam reforming process used industrially to produce products such as hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol from natural gas, naphtha or other petroleum-derived feedstocks. Nor is this process to be confused with various other catalytic reforming processes that use methanol or biomass-derived feedstocks to produce hydrogen for fuel cells or other uses.











![Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017897985_1-047f9869d5604c115b21339541ccfffe-300x300.png)








