21 More About Amines • Heterocyclic Compounds
... Some amines are heterocyclic compounds (or heterocycles)—cyclic compounds in which one or more of the atoms of the ring are heteroatoms. A heteroatom is an atom other than carbon. The name comes from the Greek word heteros, which means “different.” A variety of atoms, such as N, O, S, Se, P, Si, B, ...
... Some amines are heterocyclic compounds (or heterocycles)—cyclic compounds in which one or more of the atoms of the ring are heteroatoms. A heteroatom is an atom other than carbon. The name comes from the Greek word heteros, which means “different.” A variety of atoms, such as N, O, S, Se, P, Si, B, ...
Enhancement of anaerobic digestion of actual industrial
... Oxygen Demand (BOD) or Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) of the streams. It has become increasingly expensive for industry to meet stringent regulatory standards. One solution to reduce this cost is to anaerobically degrade the COD content, which in turn generates useful methane gas that can be used to g ...
... Oxygen Demand (BOD) or Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) of the streams. It has become increasingly expensive for industry to meet stringent regulatory standards. One solution to reduce this cost is to anaerobically degrade the COD content, which in turn generates useful methane gas that can be used to g ...
Stoichiometry
... formed. The reaction will stop when all of the limiting reactant is consumed. Example: I want to assemble a gadget that requires one nut, one bolt and two washers for every hole. I have in my garage a bucket filled with 12 washers, 4 bolts and five nuts. What is the LIMITING SMALL METAL ...
... formed. The reaction will stop when all of the limiting reactant is consumed. Example: I want to assemble a gadget that requires one nut, one bolt and two washers for every hole. I have in my garage a bucket filled with 12 washers, 4 bolts and five nuts. What is the LIMITING SMALL METAL ...
Chemistry
... one response which you want to mark on the Response Sheet. In case you feel that there is more than one correct response, mark the response which you consider the best. In any case, choose ONLY ONE response for each item. 5. In case you find any discrepancy in this test booklet in any question(s) or ...
... one response which you want to mark on the Response Sheet. In case you feel that there is more than one correct response, mark the response which you consider the best. In any case, choose ONLY ONE response for each item. 5. In case you find any discrepancy in this test booklet in any question(s) or ...
Part A Completion
... ________ 10. A positive value for a standard reduction potential means hydrogen ions have a greater tendency to be reduced than the ions in this half-cell. ________ 11. If the cell potential for a given redox reaction is negative, the reaction is ...
... ________ 10. A positive value for a standard reduction potential means hydrogen ions have a greater tendency to be reduced than the ions in this half-cell. ________ 11. If the cell potential for a given redox reaction is negative, the reaction is ...
Formic acid oxidation reaction on a PdxNiy bimetallic nanoparticle
... ribbon (GR), in which Na2PdCl4 was employed as the precursor and graphene ribbon itself served as the reducing reagent, stabilizer, and catalyst support for Pd. And the as-synthesized Pd/GR electrocatalysts showed increased electrochemical surface area and significantly enhanced catalytic activity f ...
... ribbon (GR), in which Na2PdCl4 was employed as the precursor and graphene ribbon itself served as the reducing reagent, stabilizer, and catalyst support for Pd. And the as-synthesized Pd/GR electrocatalysts showed increased electrochemical surface area and significantly enhanced catalytic activity f ...
Recent Developments on the Mechanism and Kinetics
... Krause et al., 2009; Martínez et al., 2011). The vast majority of esters can be prepared using esterification reaction in the chemical engineering industry. Esterification has acquired further improvement from the engineering side; this mainly depends on the research of esterification kinetics. On ...
... Krause et al., 2009; Martínez et al., 2011). The vast majority of esters can be prepared using esterification reaction in the chemical engineering industry. Esterification has acquired further improvement from the engineering side; this mainly depends on the research of esterification kinetics. On ...
Answers - Pearson-Global
... pairs of electrons around one of the atoms – in other words, it is nothing like a noble gas structure. Despite the impression often given at GCSE, such compounds are very common – although in the great majority of cases, there are more than 8 electrons around one atom rather than fewer. Students mig ...
... pairs of electrons around one of the atoms – in other words, it is nothing like a noble gas structure. Despite the impression often given at GCSE, such compounds are very common – although in the great majority of cases, there are more than 8 electrons around one atom rather than fewer. Students mig ...
Thermodynamics - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... Which of the following statements concerning the change in ∆G° and ∆G during a chemical reaction is most correct? a. ∆G° remains constant while ∆G changes and becomes equal to ∆G° at equilibrium. b. Both ∆G° and ∆G remain constant during a chemical reaction. c. Initially both ∆G and ∆G° are equal to ...
... Which of the following statements concerning the change in ∆G° and ∆G during a chemical reaction is most correct? a. ∆G° remains constant while ∆G changes and becomes equal to ∆G° at equilibrium. b. Both ∆G° and ∆G remain constant during a chemical reaction. c. Initially both ∆G and ∆G° are equal to ...
chemical reaction equation - parmod cobra insititution.
... (a) Chemical reaction must be associated with change in temperature i.e. Heat should be either evolved or absorbed. (b) The reaction must occur between fixed quantities of the reactants. (c) The chemical reaction should follow the law of conservation of mass. (d) The products obtained must have prop ...
... (a) Chemical reaction must be associated with change in temperature i.e. Heat should be either evolved or absorbed. (b) The reaction must occur between fixed quantities of the reactants. (c) The chemical reaction should follow the law of conservation of mass. (d) The products obtained must have prop ...
Ch 10 Practice Problems 1. Consider the process A(l) A(s). Which
... C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. q is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. H is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. E is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater th ...
... C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. q is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. H is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. E is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater th ...
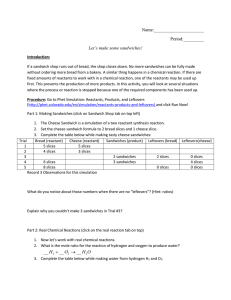
Name: Period:______ Let`s make some sandwiches! Introduction: If
... If a sandwich shop runs out of bread, the shop closes down. No more sandwiches can be fully made without ordering more bread from a bakery. A similar thing happens in a chemical reaction. If there are fixed amounts of reactants to work with in a chemical reaction, one of the reactants may be used up ...
... If a sandwich shop runs out of bread, the shop closes down. No more sandwiches can be fully made without ordering more bread from a bakery. A similar thing happens in a chemical reaction. If there are fixed amounts of reactants to work with in a chemical reaction, one of the reactants may be used up ...
Thermochemistry Exam Review Questions
... an unknown solution. What is the pH for the unknown solution likely to be? A. 1.2 B. 3.0 C. 5.3 D. 9.0 12. What is the name of the ion when a positively charged proton combines with a water molecule? A. ammonium ion B. hydrogen ion C. hydronium ion D. hydroxide ion 13. What is the term for a substan ...
... an unknown solution. What is the pH for the unknown solution likely to be? A. 1.2 B. 3.0 C. 5.3 D. 9.0 12. What is the name of the ion when a positively charged proton combines with a water molecule? A. ammonium ion B. hydrogen ion C. hydronium ion D. hydroxide ion 13. What is the term for a substan ...
Hydrothermal conversion of xylose, glucose, and
... products could cause many problems in following separation and utilization of these products. Catalysts can increase the rate of chemical reactions and change the reaction selectivity by reducing the activation barrier of specific pathway. Catalytic HTC processes have been applied to convert biomass ...
... products could cause many problems in following separation and utilization of these products. Catalysts can increase the rate of chemical reactions and change the reaction selectivity by reducing the activation barrier of specific pathway. Catalytic HTC processes have been applied to convert biomass ...
Chemical Reactions
... What is a chemical reaction composed of? 1) Contains reactants and products 2) Formulas must be written correctly with symbols and subscripts 3) Law of conservation of matter requires that coefficients be used to ensure that atoms ...
... What is a chemical reaction composed of? 1) Contains reactants and products 2) Formulas must be written correctly with symbols and subscripts 3) Law of conservation of matter requires that coefficients be used to ensure that atoms ...
contact - DTU Kemi
... instance tryptamine) will undergo ring closure after condensation with an aldehyde to give important precursor molecules (for instance THBCs, tetra-hydro-β-carbolines) for the synthesis of alkaloids. Usually, a strongly acidic catalyst is employed and the reaction mixture is heated to promote the ov ...
... instance tryptamine) will undergo ring closure after condensation with an aldehyde to give important precursor molecules (for instance THBCs, tetra-hydro-β-carbolines) for the synthesis of alkaloids. Usually, a strongly acidic catalyst is employed and the reaction mixture is heated to promote the ov ...
The Process of Chemical Reactions
... Why, then, does it take place rapidly at 1200 °C? Similarly, why does the combustion of gasoline take place more quickly when the fuel air mixture in a cylinder of your car is compressed into a smaller volume by a moving piston? How does your car’s catalytic converter speed the conversion of NO( g) ...
... Why, then, does it take place rapidly at 1200 °C? Similarly, why does the combustion of gasoline take place more quickly when the fuel air mixture in a cylinder of your car is compressed into a smaller volume by a moving piston? How does your car’s catalytic converter speed the conversion of NO( g) ...
The Process of Chemical Reactions
... Why, then, does it take place rapidly at 1200 °C? Similarly, why does the combustion of gasoline take place more quickly when the fuel air mixture in a cylinder of your car is compressed into a smaller volume by a moving piston? How does your car’s catalytic converter speed the conversion of NO( g) ...
... Why, then, does it take place rapidly at 1200 °C? Similarly, why does the combustion of gasoline take place more quickly when the fuel air mixture in a cylinder of your car is compressed into a smaller volume by a moving piston? How does your car’s catalytic converter speed the conversion of NO( g) ...
CHM203 - National Open University of Nigeria
... increase in the molecular weight. This can be explained due to increase in the London forces between the larger molecules of higher molecular weight. Thus, each additional methylene (-CH2) unit contributes to the increase in melting point. In a homologous series, the higher the molecular weight, the ...
... increase in the molecular weight. This can be explained due to increase in the London forces between the larger molecules of higher molecular weight. Thus, each additional methylene (-CH2) unit contributes to the increase in melting point. In a homologous series, the higher the molecular weight, the ...
Chapter 14
... mol/L, it takes __________ s for the concentration to decrease to 0.11 mol/L. A) 0.017 B) 0.68 C) 9.1 D) 40. E) 5.2 Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium 1) At equilibrium, __________. A) all chemical reactions have ceased B) the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal C) the rate constants o ...
... mol/L, it takes __________ s for the concentration to decrease to 0.11 mol/L. A) 0.017 B) 0.68 C) 9.1 D) 40. E) 5.2 Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium 1) At equilibrium, __________. A) all chemical reactions have ceased B) the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal C) the rate constants o ...
A Review of Surface Analysis Techniques for the
... chemistry, which in turn governs the catalytic performance. The deep understanding at the atomic level of a catalyst surface could pave the way towards the design of novel catalytic systems for real-life energy and environmental applications. Thanks to surface science we can obtain profound insight ...
... chemistry, which in turn governs the catalytic performance. The deep understanding at the atomic level of a catalyst surface could pave the way towards the design of novel catalytic systems for real-life energy and environmental applications. Thanks to surface science we can obtain profound insight ...
chapter 16
... the oxygen atoms that are forming the new bond move closer together, attracting each other more strongly and releasing more energy. At a certain stage in the progress of the reaction, bond breaking and bond making are of equal importance. In other words, the energy necessary for bond breaking is bal ...
... the oxygen atoms that are forming the new bond move closer together, attracting each other more strongly and releasing more energy. At a certain stage in the progress of the reaction, bond breaking and bond making are of equal importance. In other words, the energy necessary for bond breaking is bal ...
2015 Dr. Jay L. Wile, All rights reserved.
... 9. If a chemist reacts 6.4 g of copper with 1.6 grams of oxygen, cupric oxide is made. It is composed of one copper atom and one oxygen atom. However, copper and oxygen can also combine to make cuprous oxide, which is made of two copper atoms and one oxygen atom. Suppose you react 1.6 grams of oxyge ...
... 9. If a chemist reacts 6.4 g of copper with 1.6 grams of oxygen, cupric oxide is made. It is composed of one copper atom and one oxygen atom. However, copper and oxygen can also combine to make cuprous oxide, which is made of two copper atoms and one oxygen atom. Suppose you react 1.6 grams of oxyge ...
Stoichiometry - HCC Learning Web
... 1) write the units on all numbers and check that the units cancel properly to give the correct unit for the answer, and 2) avoid rounding numbers too much during the calculation, or you will have roundoff error in your answer. ...
... 1) write the units on all numbers and check that the units cancel properly to give the correct unit for the answer, and 2) avoid rounding numbers too much during the calculation, or you will have roundoff error in your answer. ...
Catalytic reforming

Catalytic reforming is a chemical process used to convert petroleum refinery naphthas distilled from crude oil (typically having low octane ratings) into high-octane liquid products called reformates, which are premium blending stocks for high-octane gasoline. The process converts low-octane linear hydrocarbons (paraffins) into branched alkanes (isoparaffins) and cyclic naphthenes, which are then partially dehydrogenated to produce high-octane aromatic hydrocarbons. The dehydrogenation also produces significant amounts of byproduct hydrogen gas, which is fed into other refinery processes such as hydrocracking. A side reaction is hydrogenolysis, which produces light hydrocarbons of lower value, such as methane, ethane, propane and butanes.In addition to a gasoline blending stock, reformate is the main source of aromatic bulk chemicals such as benzene, toluene, xylene and ethylbenzene which have diverse uses, most importantly as raw materials for conversion into plastics. However, the benzene content of reformate makes it carcinogenic, which has led to governmental regulations effectively requiring further processing to reduce its benzene content.This process is quite different from and not to be confused with the catalytic steam reforming process used industrially to produce products such as hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol from natural gas, naphtha or other petroleum-derived feedstocks. Nor is this process to be confused with various other catalytic reforming processes that use methanol or biomass-derived feedstocks to produce hydrogen for fuel cells or other uses.