Unit 7 Reaction Rates and Equilibrium Notes
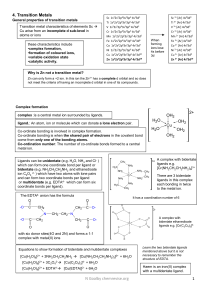
... Le Châtelier’s Principle: - a qualitative method to predict the shift on an equilibrium system if it is disturbed by means of changing concentration, pressure and temperature. - the equilibrium will shift in the direction that minimizes the change imposed on the system. 1. Effects of a Change in Con ...
... Le Châtelier’s Principle: - a qualitative method to predict the shift on an equilibrium system if it is disturbed by means of changing concentration, pressure and temperature. - the equilibrium will shift in the direction that minimizes the change imposed on the system. 1. Effects of a Change in Con ...
Reaction Kinetics - National Open University of Nigeria
... chemical reactions. The study of reaction rates allows for the prediction of how fast it will take a reaction mixture to reach equilibrium. It also account for how the reaction rate would be optimised by controlling certain factors such as temperature, pressure and the presence of a catalyst. The st ...
... chemical reactions. The study of reaction rates allows for the prediction of how fast it will take a reaction mixture to reach equilibrium. It also account for how the reaction rate would be optimised by controlling certain factors such as temperature, pressure and the presence of a catalyst. The st ...
mod-5-revision-guide-4-transition-metals
... Adsorption of reactants at active sites on the surface may lead to catalytic action. The active site is the place where the reactants adsorb on to the surface of the catalyst. This can result in the bonds within the reactant molecules becoming weaker, or the molecules being held in a more reactive c ...
... Adsorption of reactants at active sites on the surface may lead to catalytic action. The active site is the place where the reactants adsorb on to the surface of the catalyst. This can result in the bonds within the reactant molecules becoming weaker, or the molecules being held in a more reactive c ...
Catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen
... deposition in most countries. However emission of ammonia from intensive agricultural activities, e.g. cattle breeding, makes a significant contribution to the acidification of the environment in The Netherlands. About 94% of the ammonia emitted originates from agricultural sources in The Netherland ...
... deposition in most countries. However emission of ammonia from intensive agricultural activities, e.g. cattle breeding, makes a significant contribution to the acidification of the environment in The Netherlands. About 94% of the ammonia emitted originates from agricultural sources in The Netherland ...
Amines - ncert
... group. Hence, alkylamines are stronger bases than ammonia. Thus, the basic nature of aliphatic amines should increase with increase in the number of alkyl groups. This trend is followed in the gaseous phase. The order of basicity of amines in the gaseous phase follows the expected order: tertiary am ...
... group. Hence, alkylamines are stronger bases than ammonia. Thus, the basic nature of aliphatic amines should increase with increase in the number of alkyl groups. This trend is followed in the gaseous phase. The order of basicity of amines in the gaseous phase follows the expected order: tertiary am ...
Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... carbon dioxide produced from the combustion of one mole of propane. Relating masses of reactants and products: calculation of the mass of propane needed to produce a given amount of water. Calculating a quantity of reactant: the reaction of hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide. Calculating react ...
... carbon dioxide produced from the combustion of one mole of propane. Relating masses of reactants and products: calculation of the mass of propane needed to produce a given amount of water. Calculating a quantity of reactant: the reaction of hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide. Calculating react ...
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
... • This technique is suitable for the manufacture of coatings, powders, fibers and monolithic components. • This technique is often used in many thin film applications. • By varying the experimental conditions—substrate material, substrate temperature, composition of the reaction gas mixture, total p ...
... • This technique is suitable for the manufacture of coatings, powders, fibers and monolithic components. • This technique is often used in many thin film applications. • By varying the experimental conditions—substrate material, substrate temperature, composition of the reaction gas mixture, total p ...
Rh(acac)(CO)(PR1R2R3) - University of the Free State
... octahedral geometries. The oxidative addition and reductive elimination reactions from Rh(I) to Rh(III) and vice versa, has transformed the catalytic industry and has produced many fascinating reactions over the years. ...
... octahedral geometries. The oxidative addition and reductive elimination reactions from Rh(I) to Rh(III) and vice versa, has transformed the catalytic industry and has produced many fascinating reactions over the years. ...
Chapter 1 – Reaction Kinetics Answer Key
... 3. The concentrations of pure solids and liquids are fixed. That is they do not change (appreciably for the liquid if it is the solvent and at all for the solid) during a chemical reaction. ...
... 3. The concentrations of pure solids and liquids are fixed. That is they do not change (appreciably for the liquid if it is the solvent and at all for the solid) during a chemical reaction. ...
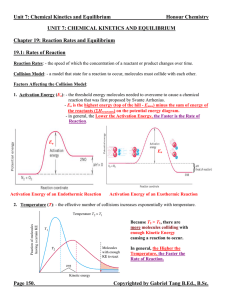
revised Chemical Kinetics
... the number of molecular collisions. Not every molecular collision between reactant molecules will lead to reaction, but some fraction of them will. Certainly, increasing the total number of molecular collisions will increase the number of successful collisions. "Successful collisions" are defined as ...
... the number of molecular collisions. Not every molecular collision between reactant molecules will lead to reaction, but some fraction of them will. Certainly, increasing the total number of molecular collisions will increase the number of successful collisions. "Successful collisions" are defined as ...
chemistry - Textbooks Online
... Alchemy was a mixture of scientific investigation and mystical quest, with strands of philosophy from Greece, China, Egypt and Arabia mixed in. The main aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), an ...
... Alchemy was a mixture of scientific investigation and mystical quest, with strands of philosophy from Greece, China, Egypt and Arabia mixed in. The main aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), an ...
GAS LAW PROBLEMS
... 1. Calcium hydride reacts with water to form hydrogen gas and calcium hydroxide. This reaction is sometimes used to inflate life rafts, weather balloons, and the like where a simple, compact means of generating H2 is desired. How many grams of calcium hydride are needed to generate 10.0 L of H2 gas ...
... 1. Calcium hydride reacts with water to form hydrogen gas and calcium hydroxide. This reaction is sometimes used to inflate life rafts, weather balloons, and the like where a simple, compact means of generating H2 is desired. How many grams of calcium hydride are needed to generate 10.0 L of H2 gas ...
kcse chemistry questions
... obtained in this experiment is different from the theoretical value. On the axis below draw an energy level diagram for the combustion of ...
... obtained in this experiment is different from the theoretical value. On the axis below draw an energy level diagram for the combustion of ...
Test bank questions
... a. If hydrogen gas is added to the above system at equilibrium, which direction will the reaction shift? b. If nitrogen is added to the system at equilibrium, what will happen to the ammonia concentration? c. If nitrogen is removed from the system at equilibrium, what will happen to the hydrogen (H2 ...
... a. If hydrogen gas is added to the above system at equilibrium, which direction will the reaction shift? b. If nitrogen is added to the system at equilibrium, what will happen to the ammonia concentration? c. If nitrogen is removed from the system at equilibrium, what will happen to the hydrogen (H2 ...
08272012BC Science Chem 12 Chapter 1 Answer Key
... 2. There is a common misconception that a significant increase in the volume of water will occur as water is formed in a reaction that occurs in aqueous solution. This is, of course, nonsense! As the entire reaction occurs in the solvent water, there will simply be a small amount of water formed, re ...
... 2. There is a common misconception that a significant increase in the volume of water will occur as water is formed in a reaction that occurs in aqueous solution. This is, of course, nonsense! As the entire reaction occurs in the solvent water, there will simply be a small amount of water formed, re ...
Chapter 14 Review
... Which of these statements is false? A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total ...
... Which of these statements is false? A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total ...
Answer Key - mrkelleher
... 2. C4H8 3. a. Na2S2O3 b. neither 4. a. 36 b. 5 c. The second heating is to ensure that all the water in the sample has been driven off. If the mass is less after the second heating, water was still present after the first |heating. 5. a. CF2 b. C4F8 6. a. CuClO3 b. copper(I) chlorate ...
... 2. C4H8 3. a. Na2S2O3 b. neither 4. a. 36 b. 5 c. The second heating is to ensure that all the water in the sample has been driven off. If the mass is less after the second heating, water was still present after the first |heating. 5. a. CF2 b. C4F8 6. a. CuClO3 b. copper(I) chlorate ...
The integration of flow reactors into synthetic organic chemistry
... best use of these tools and associated pieces of equipment. A standard sequence for a reaction today and over a century ago would still be easily recognizable to both bench chemists (Figure 1). From a simple analysis of the individual processing steps it is evident that for a single chemical transfo ...
... best use of these tools and associated pieces of equipment. A standard sequence for a reaction today and over a century ago would still be easily recognizable to both bench chemists (Figure 1). From a simple analysis of the individual processing steps it is evident that for a single chemical transfo ...
Chapter 16
... Discussion We conclude that 10 percent of H2 dissociates into H when the temperature is raised to 3535 K. If the temperature is increased further, the percentage of H2 that dissociates into H will also increase. ...
... Discussion We conclude that 10 percent of H2 dissociates into H when the temperature is raised to 3535 K. If the temperature is increased further, the percentage of H2 that dissociates into H will also increase. ...
Study Guide for Chapter 22 - Hydrocarbon Compounds
... • Because carbon has four valence electrons, carbon atoms always form four covalent bonds. • The carbon atoms in an alkane can be arranged in a straight chain or in a chain that has branches. • Molecules of hydrocarbons, such as alkanes, are nonpolar molecules. ...
... • Because carbon has four valence electrons, carbon atoms always form four covalent bonds. • The carbon atoms in an alkane can be arranged in a straight chain or in a chain that has branches. • Molecules of hydrocarbons, such as alkanes, are nonpolar molecules. ...
Oxygen Carriers Materials for Chemical
... biomass and by electrolysis of water, where electricity is produced without CO2 emissions. However, at present these options are not preferred because of high cost and some technical problems. Consequently, it is likely that the production of H2 from steam reforming of natural gas will be a dominant ...
... biomass and by electrolysis of water, where electricity is produced without CO2 emissions. However, at present these options are not preferred because of high cost and some technical problems. Consequently, it is likely that the production of H2 from steam reforming of natural gas will be a dominant ...
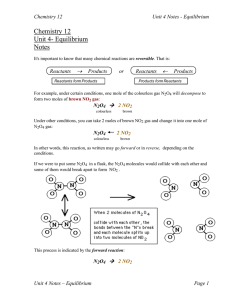
unit-4-notes-1_enthalpy-and-entropy
... Can you guess what would happen if we had started with pure NO2 instead (no N2O4 )? The reverse rate would start out high and the forward rate, zero. In time, the forward rate would " catch up ". When the rates became equal, again equilibrium would be established. We can summarize all this by saying ...
... Can you guess what would happen if we had started with pure NO2 instead (no N2O4 )? The reverse rate would start out high and the forward rate, zero. In time, the forward rate would " catch up ". When the rates became equal, again equilibrium would be established. We can summarize all this by saying ...
Equilibrium Booklet - mrstorie
... 3. Chemists have determined the equilibrium constants for several reactions. In which of these reactions are the products favoured over the reactants? a. KC = 1.0×102 ...
... 3. Chemists have determined the equilibrium constants for several reactions. In which of these reactions are the products favoured over the reactants? a. KC = 1.0×102 ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry STOICHIOMETRY: The chemical arithmetic
... With a 50 % Yield, How many moles of NH3 are produced from (a) 3 grams of H2 and ½ mole of N2? ½ mole = (½ mole)x(17 g/mole) grams of NH3 (b) 3 grams of H2 and 28 grams of N2? ...
... With a 50 % Yield, How many moles of NH3 are produced from (a) 3 grams of H2 and ½ mole of N2? ½ mole = (½ mole)x(17 g/mole) grams of NH3 (b) 3 grams of H2 and 28 grams of N2? ...
File
... 15. Physical properties of elements depend upon the number of __________. (Protons in the nucleus, neutrons in the nucleus, electrons in the valence shell, both protons and neutrons in the nucleus) 16. Chemical properties of elements depend upon the number of __________. (electrons in the valence sh ...
... 15. Physical properties of elements depend upon the number of __________. (Protons in the nucleus, neutrons in the nucleus, electrons in the valence shell, both protons and neutrons in the nucleus) 16. Chemical properties of elements depend upon the number of __________. (electrons in the valence sh ...
Catalytic reforming

Catalytic reforming is a chemical process used to convert petroleum refinery naphthas distilled from crude oil (typically having low octane ratings) into high-octane liquid products called reformates, which are premium blending stocks for high-octane gasoline. The process converts low-octane linear hydrocarbons (paraffins) into branched alkanes (isoparaffins) and cyclic naphthenes, which are then partially dehydrogenated to produce high-octane aromatic hydrocarbons. The dehydrogenation also produces significant amounts of byproduct hydrogen gas, which is fed into other refinery processes such as hydrocracking. A side reaction is hydrogenolysis, which produces light hydrocarbons of lower value, such as methane, ethane, propane and butanes.In addition to a gasoline blending stock, reformate is the main source of aromatic bulk chemicals such as benzene, toluene, xylene and ethylbenzene which have diverse uses, most importantly as raw materials for conversion into plastics. However, the benzene content of reformate makes it carcinogenic, which has led to governmental regulations effectively requiring further processing to reduce its benzene content.This process is quite different from and not to be confused with the catalytic steam reforming process used industrially to produce products such as hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol from natural gas, naphtha or other petroleum-derived feedstocks. Nor is this process to be confused with various other catalytic reforming processes that use methanol or biomass-derived feedstocks to produce hydrogen for fuel cells or other uses.