BIOL 157 * BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Lecture 6
... ketones in nucleophilic reactions partly due to the presence of more bulky groups in the ketones. • For reactions that occur in two phases (gas/solid or liquid/solid), the ...
... ketones in nucleophilic reactions partly due to the presence of more bulky groups in the ketones. • For reactions that occur in two phases (gas/solid or liquid/solid), the ...
Theoretical Investigation of the Water
... for his encouragements to be strong. I thank God for helping me all the time. ...
... for his encouragements to be strong. I thank God for helping me all the time. ...
Organic Chemistry
... condition, the difficulty to remove the iodobenzene byproduct from the desired disulfide makes the reuse of the diacetoxyiodo(benzene) reagent cumbersome. To overcome this problem, the hypervalent iodine is bound onto a polymeric support. The desired product can be obtained by simple filtration and ...
... condition, the difficulty to remove the iodobenzene byproduct from the desired disulfide makes the reuse of the diacetoxyiodo(benzene) reagent cumbersome. To overcome this problem, the hypervalent iodine is bound onto a polymeric support. The desired product can be obtained by simple filtration and ...
Chemical Equilibrium - The Gurukul Institute
... At a certain elevated temperature, the total pressure of the gases generated was 0.42 atm. At equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction. 10. if a given quantity of phosphorus pentachloride is heated at 250o C and allowed to come to equilibrium at atmospheric pressure it is fou ...
... At a certain elevated temperature, the total pressure of the gases generated was 0.42 atm. At equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction. 10. if a given quantity of phosphorus pentachloride is heated at 250o C and allowed to come to equilibrium at atmospheric pressure it is fou ...
Mole-Volume Conversion Assignment
... If we use 2 litres of nitrogen oxide, how many litres of hydrogen would be needed? How many litres of Water vapour? How many litres of nitrogen? ...
... If we use 2 litres of nitrogen oxide, how many litres of hydrogen would be needed? How many litres of Water vapour? How many litres of nitrogen? ...
Review Unit 8 Test (Chp 15,17)
... increases until it becomes the same as the reverse reaction rate at equilibrium. stays constant before and after equilibrium is reached. A is half true, but “decreases”, decreases to become a constant nonzero rate at equilibrium. not “increases.” decreases to become zero at equilibrium. Greater pres ...
... increases until it becomes the same as the reverse reaction rate at equilibrium. stays constant before and after equilibrium is reached. A is half true, but “decreases”, decreases to become a constant nonzero rate at equilibrium. not “increases.” decreases to become zero at equilibrium. Greater pres ...
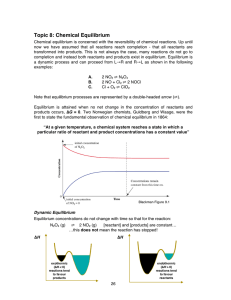
Topic 8: Chemical Equilibrium
... The best way to think about this is to consider temperature as one of the reactants in an endothermic reaction or as one of the products in an exothermic reaction: An endothermic takes in heat, so: +58 kJ mol-1 + 2NO2 (g) ⇌ N2O4 (g) So, if temperature is raised the system will react to oppose th ...
... The best way to think about this is to consider temperature as one of the reactants in an endothermic reaction or as one of the products in an exothermic reaction: An endothermic takes in heat, so: +58 kJ mol-1 + 2NO2 (g) ⇌ N2O4 (g) So, if temperature is raised the system will react to oppose th ...
heterogeneous chiral catalyst derived from hydrolyzed
... development of efficient routes to enantiopure compounds was perceived as cumbersome and expensive. However, following the understanding that different enantiomers may have qualitatively distinct physiological effects, [16-20] and instigated by stricter regulations from health authorities, a growing ...
... development of efficient routes to enantiopure compounds was perceived as cumbersome and expensive. However, following the understanding that different enantiomers may have qualitatively distinct physiological effects, [16-20] and instigated by stricter regulations from health authorities, a growing ...
Appendices - Mattson Creighton
... 1. (a) NaHCO3; (b) HC2H3O2; and (c) CO2 2. (a) NaHCO3(s); (b) HC2H3O2(aq); (c) CO2(g) 3. It is actually the syringe containing the gas that must be washed in order to remove all traces of chemicals that were used to make the gas. After that has happened, the syringe contains our desired gas (CO2), a ...
... 1. (a) NaHCO3; (b) HC2H3O2; and (c) CO2 2. (a) NaHCO3(s); (b) HC2H3O2(aq); (c) CO2(g) 3. It is actually the syringe containing the gas that must be washed in order to remove all traces of chemicals that were used to make the gas. After that has happened, the syringe contains our desired gas (CO2), a ...
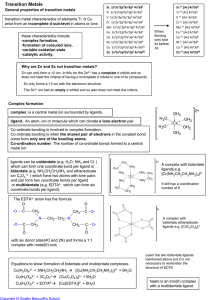
Transition Metals
... Poisoning has a cost implication e.g. poisoning by sulphur in the Haber Process and by lead in catalytic converters in cars means that catalysts lose their efficiency and may need to be replaced ...
... Poisoning has a cost implication e.g. poisoning by sulphur in the Haber Process and by lead in catalytic converters in cars means that catalysts lose their efficiency and may need to be replaced ...
Bk2P06EE
... forward precipitation step removes SO42 from the solution, it is favoured and the white precipitate of calcium sulphate appears. 2NO2(g) N2O4(g) H < 0 Since cooling favours the exothermic reaction which gives out heat, the dimerisation of brown NO2 to form the colourless N2O4 is an exothermic proc ...
... forward precipitation step removes SO42 from the solution, it is favoured and the white precipitate of calcium sulphate appears. 2NO2(g) N2O4(g) H < 0 Since cooling favours the exothermic reaction which gives out heat, the dimerisation of brown NO2 to form the colourless N2O4 is an exothermic proc ...
Ch. 11-12 Supplements
... HOMEWORK OPTIONS: 1) Do all problems a-f and have your total score out of 48 points. 2) Do all problems, but omit parts d,e,f for a total of 32 points. (I will have two different columns in my grade book. One with the larger point total, and one with the smaller point total.) Do what you feel is an ...
... HOMEWORK OPTIONS: 1) Do all problems a-f and have your total score out of 48 points. 2) Do all problems, but omit parts d,e,f for a total of 32 points. (I will have two different columns in my grade book. One with the larger point total, and one with the smaller point total.) Do what you feel is an ...
- Boreskov Institute of Catalysis
... Institute of Catalysis in the main fields of its academic and R&D activities covers the year 2009 and follows the scheme which has been accepted for such kinds of reviews many years ago. The Boreskov Institute of Catalysis, or BIC, is well known to experts in both academic and industrial catalysis n ...
... Institute of Catalysis in the main fields of its academic and R&D activities covers the year 2009 and follows the scheme which has been accepted for such kinds of reviews many years ago. The Boreskov Institute of Catalysis, or BIC, is well known to experts in both academic and industrial catalysis n ...
Hydrolases as Catalysts for Green Chemistry and
... synthesis of a chiral pharmaceutical compound, S-clopidogrel, by selective hydrolysis of the racemic precursor. Current production of the pure S- clopidogrel isomer involves the use of a resolving agent, L-camphorsulfonic acid, and organic solvents. Screening of different hydrolases revealed that cr ...
... synthesis of a chiral pharmaceutical compound, S-clopidogrel, by selective hydrolysis of the racemic precursor. Current production of the pure S- clopidogrel isomer involves the use of a resolving agent, L-camphorsulfonic acid, and organic solvents. Screening of different hydrolases revealed that cr ...
Topic 1 Quantitative Chemistry File
... 18. The red colour of blood is due to haemoglobin. It contains 0.335% by mass of iron. Four atoms of iron are present in each molecule of haemoglobin. If the molar mass of iron is 55.84 g mol–1, estimate the molar mass of haemoglobin. ...
... 18. The red colour of blood is due to haemoglobin. It contains 0.335% by mass of iron. Four atoms of iron are present in each molecule of haemoglobin. If the molar mass of iron is 55.84 g mol–1, estimate the molar mass of haemoglobin. ...
1. dia
... • occurs at spring when the melted acidic snow flows suddenly into the rivers of catchments area. • If natural water is in contact with limestone, dolomite, the pH does not change → buffer effect. The living organisms are killed by the increased CO2 content • In case of week buffer effect (small Ca- ...
... • occurs at spring when the melted acidic snow flows suddenly into the rivers of catchments area. • If natural water is in contact with limestone, dolomite, the pH does not change → buffer effect. The living organisms are killed by the increased CO2 content • In case of week buffer effect (small Ca- ...
Untitled
... d. If you add 125 g of C2H6O to your fuel, how many grams of CO2 and H2O can be produced from the ethanol? ...
... d. If you add 125 g of C2H6O to your fuel, how many grams of CO2 and H2O can be produced from the ethanol? ...
Honors Chemistry: Ch. 12 – Stoichiometry Some useful terms
... 4.) Calculate the mass of silver needed to react with chlorine to produce 84 g of silver chloride (Hint: Write a balanced equation first). 5.) Calculate the number of liters of oxygen gas needed to produce 15.0 liters of dinitrogen trioxide. Assume all gases are at STP. 2N2(g) + 3O2(g) 2N2O3(g) 6. ...
... 4.) Calculate the mass of silver needed to react with chlorine to produce 84 g of silver chloride (Hint: Write a balanced equation first). 5.) Calculate the number of liters of oxygen gas needed to produce 15.0 liters of dinitrogen trioxide. Assume all gases are at STP. 2N2(g) + 3O2(g) 2N2O3(g) 6. ...
C:\SUBJECTS\SUBJECTS\Chemistry
... copper ions to form copper. This is due to the fact that A. iron is in the metallic form while dthe copper is in the ionic form B. the atomic weight of copper is greater than that of ion C. copper metal has more electrons than ion metal D. iron is an inert metal E. iron is higher in the electrochemi ...
... copper ions to form copper. This is due to the fact that A. iron is in the metallic form while dthe copper is in the ionic form B. the atomic weight of copper is greater than that of ion C. copper metal has more electrons than ion metal D. iron is an inert metal E. iron is higher in the electrochemi ...
Chemistry JAMB Past Questions
... heated to about 1000oC CO may be prepared by heating charcoal with a limited amount of O2 CO is a good reducing agent. ...
... heated to about 1000oC CO may be prepared by heating charcoal with a limited amount of O2 CO is a good reducing agent. ...
Type - Enrico Fermi High
... points increase. Account for this based on IMF’s. As go down, MM goes up, so dispersion forces go up, so VP down and BP up. Why does water have an unusually high boiling point? Water forms lots of hydrogen bonds with itself. ...
... points increase. Account for this based on IMF’s. As go down, MM goes up, so dispersion forces go up, so VP down and BP up. Why does water have an unusually high boiling point? Water forms lots of hydrogen bonds with itself. ...
Chemical Reactions
... than one reactant, and asked to calculate the amount of product formed. The quantities of reactants might be such that both react completely, or one might react completely, and the other(s) might be in excess. These are called limiting reagent problems, since the quantity of one of the reacts will l ...
... than one reactant, and asked to calculate the amount of product formed. The quantities of reactants might be such that both react completely, or one might react completely, and the other(s) might be in excess. These are called limiting reagent problems, since the quantity of one of the reacts will l ...
Study guide for final
... 15) Liquid and gas molecules can easily be compressed, while in a solid the molecules are incompressible. 16) A chemical change occurs when matter does not change its composition. 17) When a cold ice cube is dropped into a warm cup of water, energy is transferred as heat from the ice to the water. 1 ...
... 15) Liquid and gas molecules can easily be compressed, while in a solid the molecules are incompressible. 16) A chemical change occurs when matter does not change its composition. 17) When a cold ice cube is dropped into a warm cup of water, energy is transferred as heat from the ice to the water. 1 ...
Acids, bases and combustion
... To prevent filament from burning out. Provides an atmosphere in which burning cannot occur i.e. inert atmosphere a) Halogens (b) X & Y (c) Z is the largest atom with the highest number of energy levels occupied by electrons. The longer an atom is the higher the forces of attraction that hold the mol ...
... To prevent filament from burning out. Provides an atmosphere in which burning cannot occur i.e. inert atmosphere a) Halogens (b) X & Y (c) Z is the largest atom with the highest number of energy levels occupied by electrons. The longer an atom is the higher the forces of attraction that hold the mol ...
Catalytic reforming

Catalytic reforming is a chemical process used to convert petroleum refinery naphthas distilled from crude oil (typically having low octane ratings) into high-octane liquid products called reformates, which are premium blending stocks for high-octane gasoline. The process converts low-octane linear hydrocarbons (paraffins) into branched alkanes (isoparaffins) and cyclic naphthenes, which are then partially dehydrogenated to produce high-octane aromatic hydrocarbons. The dehydrogenation also produces significant amounts of byproduct hydrogen gas, which is fed into other refinery processes such as hydrocracking. A side reaction is hydrogenolysis, which produces light hydrocarbons of lower value, such as methane, ethane, propane and butanes.In addition to a gasoline blending stock, reformate is the main source of aromatic bulk chemicals such as benzene, toluene, xylene and ethylbenzene which have diverse uses, most importantly as raw materials for conversion into plastics. However, the benzene content of reformate makes it carcinogenic, which has led to governmental regulations effectively requiring further processing to reduce its benzene content.This process is quite different from and not to be confused with the catalytic steam reforming process used industrially to produce products such as hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol from natural gas, naphtha or other petroleum-derived feedstocks. Nor is this process to be confused with various other catalytic reforming processes that use methanol or biomass-derived feedstocks to produce hydrogen for fuel cells or other uses.