Athens and Sparta - Greenon Local Schools
... Returned home and expected to marry Continued to train for combat ...
... Returned home and expected to marry Continued to train for combat ...
9.2 Cornell Notes with Questions and Summary
... Compare and contrast the lives of Spartans and Athenians. ...
... Compare and contrast the lives of Spartans and Athenians. ...
Class Activities - Walsingham Academy
... •Credited with having established democracy in Athens, •His reforms (end of the 6th Century BC) made possible the Golden Age of Athenian civilization (5th Century BC.) •Born into one of the city's foremost political dynasties (brother-in-law to Peisistratus:) an unlikely champion of the people when ...
... •Credited with having established democracy in Athens, •His reforms (end of the 6th Century BC) made possible the Golden Age of Athenian civilization (5th Century BC.) •Born into one of the city's foremost political dynasties (brother-in-law to Peisistratus:) an unlikely champion of the people when ...
Sparta and Athens Questions
... 2. Women had more rights and responsibilities in Spartan than women of Athens because while the boys and young men in the military were away from home serving as soldiers, women filled the roles, such as property owners and heads of households, that men filled in other societies. 3. Spartan men stay ...
... 2. Women had more rights and responsibilities in Spartan than women of Athens because while the boys and young men in the military were away from home serving as soldiers, women filled the roles, such as property owners and heads of households, that men filled in other societies. 3. Spartan men stay ...
Women in Ancient Times Athens and Sparta were the two great
... Greek cities. Indeed, one of the criticisms of Athens was that its slaves and freemen were difficult to tell apart. Slaves were excluded from the religious festivals of Athens, could not own land, were denied some civil rights and could not participate in political activities. They were able to hold ...
... Greek cities. Indeed, one of the criticisms of Athens was that its slaves and freemen were difficult to tell apart. Slaves were excluded from the religious festivals of Athens, could not own land, were denied some civil rights and could not participate in political activities. They were able to hold ...
(Section II): Greek City-States Rise to Power
... To fight against the Persians (in many battles). Sparta and Athens even fought together against the Persians (in the Persian War). At one time Athens and Sparta weren’t doing to well. But they re-grouped and in the battle of Salamis (first naval battle ever recorded) beat the Persians (300 sunk ship ...
... To fight against the Persians (in many battles). Sparta and Athens even fought together against the Persians (in the Persian War). At one time Athens and Sparta weren’t doing to well. But they re-grouped and in the battle of Salamis (first naval battle ever recorded) beat the Persians (300 sunk ship ...
The Persian Wars
... • The outnumbered Greeks staged a surprise attack and defeated the Persians! • In 480B.C., the Persians returned to Greece (now led by Xerxes I) • 7,000 Greeks (Spartans/Athenians) vs. 100,000 Persians • Greek navy destroyed the entire Persian fleet. • The Persians responded with a sneak attack on t ...
... • The outnumbered Greeks staged a surprise attack and defeated the Persians! • In 480B.C., the Persians returned to Greece (now led by Xerxes I) • 7,000 Greeks (Spartans/Athenians) vs. 100,000 Persians • Greek navy destroyed the entire Persian fleet. • The Persians responded with a sneak attack on t ...
4th Century Greece - Eastern New Mexico University
... Reforms of Lycurgus (6th century BC) 2 hereditary kings Council of Elders (Garousia) (28 men over 60 years of age) Five Ephors (annually elected magistrates) Assembly of Equals (free adult male citizensHomoioi): mess mates (sysstion) ...
... Reforms of Lycurgus (6th century BC) 2 hereditary kings Council of Elders (Garousia) (28 men over 60 years of age) Five Ephors (annually elected magistrates) Assembly of Equals (free adult male citizensHomoioi): mess mates (sysstion) ...
Greece: Athens/Sparta Reading
... Spartan Government:Usually classified as an "oligarchy" (rule by a few), but it had elements of monarchy (rule by kings), democracy (through the election of council/senators), and aristocracy (rule by the upper class or land owning class). Two kings who were generals in command of the armies and wit ...
... Spartan Government:Usually classified as an "oligarchy" (rule by a few), but it had elements of monarchy (rule by kings), democracy (through the election of council/senators), and aristocracy (rule by the upper class or land owning class). Two kings who were generals in command of the armies and wit ...
Fifth Century Greece
... Reforms of Lycurgus (6th century BC) 2 hereditary kings Council of Elders (Garousia) (28 men over 60 years of age) Five Ephors (annually elected magistrates) Assembly of Equals (free adult male citizensHomoioi): mess mates (sysstion) ...
... Reforms of Lycurgus (6th century BC) 2 hereditary kings Council of Elders (Garousia) (28 men over 60 years of age) Five Ephors (annually elected magistrates) Assembly of Equals (free adult male citizensHomoioi): mess mates (sysstion) ...
Warring City States - Dr. Afxendiou`s Classes
... Women also taught to put service to Sparta above all else “come back with your shield or on it” Given considerable freedom in the house when men ...
... Women also taught to put service to Sparta above all else “come back with your shield or on it” Given considerable freedom in the house when men ...
File - Caleb Westveer
... Our region of study will be the Greek City State Sparta, at the time period 650 BCE. We will also compare the other Greek City State Athens who was powerful. The prevalent religion was Greek polytheism, many gods and goddesses such as Zeus, Hades, etc. Sparta was an oligarchy with 2 hereditary kings ...
... Our region of study will be the Greek City State Sparta, at the time period 650 BCE. We will also compare the other Greek City State Athens who was powerful. The prevalent religion was Greek polytheism, many gods and goddesses such as Zeus, Hades, etc. Sparta was an oligarchy with 2 hereditary kings ...
The Ancient Greeks and the battle of Marathon
... The Spartan army did not come for several days because of a religious festival. The Athenians fought the Persians without help. The Athenians defeated the Persians at Marathon. The Spartans arrived the next day. ...
... The Spartan army did not come for several days because of a religious festival. The Athenians fought the Persians without help. The Athenians defeated the Persians at Marathon. The Spartans arrived the next day. ...
Chapter 4, Section 2 Sparta & Athens
... • #1—taught them to read, write, and ______________. • #2—____________ • #3—taught them to sing & play stringed instrument called a ________. ...
... • #1—taught them to read, write, and ______________. • #2—____________ • #3—taught them to sing & play stringed instrument called a ________. ...
The Greek City
... • A council of elders, composed of the two kings and 28 citizens over the age of 60, decided on the issues that would be presented to an assembly made of male citizens. This assembly did not debate; it only voted on the issues. ...
... • A council of elders, composed of the two kings and 28 citizens over the age of 60, decided on the issues that would be presented to an assembly made of male citizens. This assembly did not debate; it only voted on the issues. ...
4.2 guided notes
... Noncitizens (_______________, slaves, and resident aliens ) Aristotle argued that a citizen did not belong to himself or herself but to the _______________ ...
... Noncitizens (_______________, slaves, and resident aliens ) Aristotle argued that a citizen did not belong to himself or herself but to the _______________ ...
The Spartans and Women in Ancient Greece
... “‘For it was not by imitating other states, but by devising a system utterly different from that of most others, that he [Lycurgus] made his country prosperous…he insisted on physical training for the female no less than for the male sex: moreover, he instituted races and trials of strength for wome ...
... “‘For it was not by imitating other states, but by devising a system utterly different from that of most others, that he [Lycurgus] made his country prosperous…he insisted on physical training for the female no less than for the male sex: moreover, he instituted races and trials of strength for wome ...
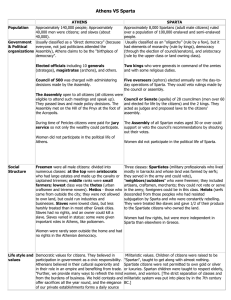
Athens and Sparta comparisons
... mostly in barracks and whose land was farmed by serfs; they served in the army and could vote), "neighbors/outsiders" who were freemen; they included artisans, craftsmen, merchants; they could not vote or serve in the army; foreigners could be in this class. Helots (serfs descended from those people ...
... mostly in barracks and whose land was farmed by serfs; they served in the army and could vote), "neighbors/outsiders" who were freemen; they included artisans, craftsmen, merchants; they could not vote or serve in the army; foreigners could be in this class. Helots (serfs descended from those people ...
The Peloponnesian War
... sailing off to Sicily . . . And at the same time we shall become either masters, as we very easily may, of the whole of Hellas . . . Or in any case ruin the Syracusians, to no small advantage to us and our allies.” ...
... sailing off to Sicily . . . And at the same time we shall become either masters, as we very easily may, of the whole of Hellas . . . Or in any case ruin the Syracusians, to no small advantage to us and our allies.” ...
Topic(s): Cues – themes, terms, people, places, events, ideas
... : Education - very limited - only basic reading and writing - purpose of education is only to have basic skills for service to the state : Social structure - 3 basic classes - Equals - full Spartan citizens - descended from original Spartan settlers (Dorians) - full voting rights for men - may serve ...
... : Education - very limited - only basic reading and writing - purpose of education is only to have basic skills for service to the state : Social structure - 3 basic classes - Equals - full Spartan citizens - descended from original Spartan settlers (Dorians) - full voting rights for men - may serve ...
Greece`s Golden Age
... Early Greek Olympics were done in the nude, and only men participated…”sounds dangerous” Which U.S. state is named after a Greek Island? ...
... Early Greek Olympics were done in the nude, and only men participated…”sounds dangerous” Which U.S. state is named after a Greek Island? ...
Spartan army
The Spartan army stood at the centre of the Spartan state, whose male and female citizens were trained in the discipline and honor of the warrior society. Subject to military drill from early manhood, the Spartans were one of the most feared military forces in the Greek world. At the height of Sparta's power – between the 6th and 4th centuries BC – it was commonly accepted that, ""one Spartan was worth several men of any other state."" According to Thucydides, the famous moment of Spartan surrender at the island of Sphacteria off of Pylos was highly unexpected. He said that ""it was the common perception at the time that Spartans would never lay down their weapons for any reason, be it hunger, or danger.""The iconic army was first coined by the Spartan legislator Lycurgus. In his famous quote of Sparta having a ""wall of men, instead of bricks"", he proposed to create a military-focused lifestyle reformation in the Spartan society in accordance to proper virtues such as equality for the male citizens, austerity, strength, and fitness. A Spartan man's involvement with the army began in infancy when he was inspected by the Gerousia. If the baby was found to be weak or deformed he was left at Mount Taygetus to die, since the world of the Spartans was no place for those who could not already fend for themselves. It should be noted, however, that the practice of discarding children at birth took place in Athens as well. Those deemed strong were then put in the agoge at the age of seven. Under the agoge the young boys or Spartiates were kept under intense and rigorous military training. Their education focused primarily on cunning, sports and war tactics, but also included poetry, music, academics, and sometimes politics. Those who passed the agoge by the age of 30 were given full Spartan citizenship.The term ""spartan"" became synonymous with multiple meanings such as: fearlessness, harsh and cruel life, bland and lacking creativity, or simplicity by design.