Guide
... Judaism: “B’Rit” = covenant between Jews, God Judaic belief in selves as “Chosen people” of God: What does that mean / not mean? ...
... Judaism: “B’Rit” = covenant between Jews, God Judaic belief in selves as “Chosen people” of God: What does that mean / not mean? ...
Chapter 6- Ancient Greece Test Review
... 24.Socrates was concerned with A.The atoms that things are made of B.The meaning of justice and courage C.The difference between tragedy and comedy ...
... 24.Socrates was concerned with A.The atoms that things are made of B.The meaning of justice and courage C.The difference between tragedy and comedy ...
Chapter 6- Ancient Greece Test Review
... * What was your favorite part about the field trip yesterday? * Put your completed Bellringer in the tray * Put your notes in the correct order and staple them. turn these in on Monday before your test. ...
... * What was your favorite part about the field trip yesterday? * Put your completed Bellringer in the tray * Put your notes in the correct order and staple them. turn these in on Monday before your test. ...
TheGreeks
... – Probably for economic reasons – Troy controlled the vital straits or narrow water passages that connected the Mediterranean and Black ...
... – Probably for economic reasons – Troy controlled the vital straits or narrow water passages that connected the Mediterranean and Black ...
The Rise of Greek Cities - Our Lady of the Wayside
... questions than absolutely necessary.” They stayed at home at helped their mothers. They weaved, and helped on the farms at harvest time. Boys worked each day with their fathers. They worked in the fields, or in pottery or stone working shops. They only went to school to learn reading and writing i ...
... questions than absolutely necessary.” They stayed at home at helped their mothers. They weaved, and helped on the farms at harvest time. Boys worked each day with their fathers. They worked in the fields, or in pottery or stone working shops. They only went to school to learn reading and writing i ...
Greek Art
... Only men could be citizens; men ran government Open expression of homosexuality (words, behaviour, literature and visual arts) especially between older men and young boys Advancements in culture, thinking, literature, philosophy, ...
... Only men could be citizens; men ran government Open expression of homosexuality (words, behaviour, literature and visual arts) especially between older men and young boys Advancements in culture, thinking, literature, philosophy, ...
Greece Test 2010
... C. They were focused on the rights and pleasure of the individual D. They did not practice any form of slavery. In 500 bc, the only thing that stood in the way of Persia taking over all of Europe was: A. Deserts B. Greece C. Oceans D. Jungles Which of the following shows us that the Minoans were obs ...
... C. They were focused on the rights and pleasure of the individual D. They did not practice any form of slavery. In 500 bc, the only thing that stood in the way of Persia taking over all of Europe was: A. Deserts B. Greece C. Oceans D. Jungles Which of the following shows us that the Minoans were obs ...
Guided Notes: Ancient Greece Early Civilization: Ancient Greece
... after years of fighting each other, only the city-states of Athens and Thebes could agree on a policy join forces against Phillip but by then it was too late. The Macedonians soundly defeated and conquered the _______ at the Battle of Chaeronea. Phillip next planned to invade the Persian empire but ...
... after years of fighting each other, only the city-states of Athens and Thebes could agree on a policy join forces against Phillip but by then it was too late. The Macedonians soundly defeated and conquered the _______ at the Battle of Chaeronea. Phillip next planned to invade the Persian empire but ...
Greek City-States and Culture
... _________ people lived simple lives of hard work and physical activity. It had a standing army led by two kings who were part of a governing council. ...
... _________ people lived simple lives of hard work and physical activity. It had a standing army led by two kings who were part of a governing council. ...
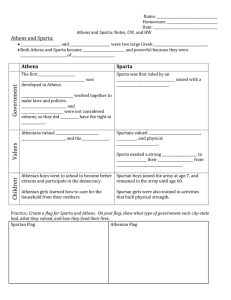
Athens vs Spartan society DBQ
... had were differed from those of the women in Athens. This is because the men were always out either training for war, or fighting a war. Spartan women had greater freedom than Athenian women had. Different from Athens, Spartan women could own land just like the men could. In fact, they owned more th ...
... had were differed from those of the women in Athens. This is because the men were always out either training for war, or fighting a war. Spartan women had greater freedom than Athenian women had. Different from Athens, Spartan women could own land just like the men could. In fact, they owned more th ...
Athens` Choices - Middle School World History
... presented to rulers who decided whether the baby had the potential to be a great soldier or the mother of strong children. Those who failed the test were abandoned to die. For men, daily life was focused on the military. At age seven, boys left home and moved into military barracks. Their schooling ...
... presented to rulers who decided whether the baby had the potential to be a great soldier or the mother of strong children. Those who failed the test were abandoned to die. For men, daily life was focused on the military. At age seven, boys left home and moved into military barracks. Their schooling ...
Sparta and Athens Questions: self-discipline and obedience While
... soldiers, women filled the roles, such as property owners and heads of households, that men filled in other societies. 3. 40 years 4. Boys trained for military service from age 18 to 20, and men served in the army from age 20 to 60. Spartan women had more rights than other Greek women. 5. Rich Athen ...
... soldiers, women filled the roles, such as property owners and heads of households, that men filled in other societies. 3. 40 years 4. Boys trained for military service from age 18 to 20, and men served in the army from age 20 to 60. Spartan women had more rights than other Greek women. 5. Rich Athen ...
Directions: Fill in the boxes with concrete details as you research
... protect the city-state Valued discipline and strength At age 7 all children (even girls) trained to fight Boys were taught to read and write, but it was unimportant Taught to endure pain without complaining Needed to sneak around and steal from other people but were punished harshly if caught Men at ...
... protect the city-state Valued discipline and strength At age 7 all children (even girls) trained to fight Boys were taught to read and write, but it was unimportant Taught to endure pain without complaining Needed to sneak around and steal from other people but were punished harshly if caught Men at ...
File
... Women’s Roles: Spartan society expected its women to be tough emotionally and physically. Mothers told their sons, “bring back the shield yourself or be brought back on it.” Education for girls in Sparta focused on making them physically strong; they had athletic training and learned to defend thems ...
... Women’s Roles: Spartan society expected its women to be tough emotionally and physically. Mothers told their sons, “bring back the shield yourself or be brought back on it.” Education for girls in Sparta focused on making them physically strong; they had athletic training and learned to defend thems ...
Ancient Greece Review
... Helots – people taken during war time and forced to work for the whole polis Assembly- gathering of citizens Sparta is located on what peninsula: Peloponnesian What age to Spartan warrior enter military training and what age do they return home: 7 and 30 Describe the roles of Spartan women? What did ...
... Helots – people taken during war time and forced to work for the whole polis Assembly- gathering of citizens Sparta is located on what peninsula: Peloponnesian What age to Spartan warrior enter military training and what age do they return home: 7 and 30 Describe the roles of Spartan women? What did ...
Greek Warfare
... Greece. They were always fighting for supremacy. The men were trained to be ready to fight at any time. Sparta’s troops fought on land Athens’ troops fought overseas. ...
... Greece. They were always fighting for supremacy. The men were trained to be ready to fight at any time. Sparta’s troops fought on land Athens’ troops fought overseas. ...
Presentation 6 - Athens vs Sparta Chart with readings packet
... Athenians really focused on individual. This means that they thought it was important to recognize each individual person and it was okay to different everyone else. They also thought it was very important that they were education, and always kept their minds open to learn new things. They also thou ...
... Athenians really focused on individual. This means that they thought it was important to recognize each individual person and it was okay to different everyone else. They also thought it was very important that they were education, and always kept their minds open to learn new things. They also thou ...
The Rise of Greek Civilization Homer, Sparta, Athens, and the
... Whereas the Spartans thought that trade was below them, Athenians excelled in it Athens allowed a citizen the right to govern the polis Moved through a series of political developments ...
... Whereas the Spartans thought that trade was below them, Athenians excelled in it Athens allowed a citizen the right to govern the polis Moved through a series of political developments ...
Chapter 7 Lesson 2 Sparta and Athens: City
... -‐merchants and artisans did not own land, not considered citizens -‐tyrant-‐ someone who seizes power and rules with total authority -‐common people supported tyrant leaders in 600 B.C. -‐oligarchy-‐ few ...
... -‐merchants and artisans did not own land, not considered citizens -‐tyrant-‐ someone who seizes power and rules with total authority -‐common people supported tyrant leaders in 600 B.C. -‐oligarchy-‐ few ...
Each city-state or
... rich. This gave the poor the feeling that they could and should be able to make their own political decisions. By the 6th century B.C. some city-states, led by ATHENS, had some form of DEMOCRACY or rule by the PEOPLE. The beginning of democracy in Athens was in 621 B.C. when DRACO wrote down the law ...
... rich. This gave the poor the feeling that they could and should be able to make their own political decisions. By the 6th century B.C. some city-states, led by ATHENS, had some form of DEMOCRACY or rule by the PEOPLE. The beginning of democracy in Athens was in 621 B.C. when DRACO wrote down the law ...
Part 1 Multiple Choice
... In Greece, small independent city-states developed. This occurred because Greek families did not get along with each other The topography of the land forced the city-states to develop separately Foreign invaders divided the Greeks up so they could control them Each city-state had a different languag ...
... In Greece, small independent city-states developed. This occurred because Greek families did not get along with each other The topography of the land forced the city-states to develop separately Foreign invaders divided the Greeks up so they could control them Each city-state had a different languag ...
I. Greek Civilization
... c. Military Training i. Age 7, ALL boys sent to barracks for training ii. Beaten, coarse diet, hard exercise iii. Marry at 20, move out of barracks at 30, stop eating there at 40 d. Women i. Exercise and strength important ii. Expected to produce healthy sons ...
... c. Military Training i. Age 7, ALL boys sent to barracks for training ii. Beaten, coarse diet, hard exercise iii. Marry at 20, move out of barracks at 30, stop eating there at 40 d. Women i. Exercise and strength important ii. Expected to produce healthy sons ...
Greece documentary pitch
... Base Overview: Thermopylae • Leonidas, King of Sparta, refused offers of land and power if he surrendered, prompting the dignitary to demand that he and his men lay down their arms. This was the dialogue: • Persian: “Give up your weapons!” • Leonidas: “Come and get them!” • Four days later, Xerxes ...
... Base Overview: Thermopylae • Leonidas, King of Sparta, refused offers of land and power if he surrendered, prompting the dignitary to demand that he and his men lay down their arms. This was the dialogue: • Persian: “Give up your weapons!” • Leonidas: “Come and get them!” • Four days later, Xerxes ...
the golden age part i
... within the bounds of its current power (for it was unlikely further gains could be made against Persia), or break with Sparta and turn towards other Greek states to expand. It was this decision which would define the future of the Greek world. The Western Greeks: While the Persian Wars were being fo ...
... within the bounds of its current power (for it was unlikely further gains could be made against Persia), or break with Sparta and turn towards other Greek states to expand. It was this decision which would define the future of the Greek world. The Western Greeks: While the Persian Wars were being fo ...
Spartan army
The Spartan army stood at the centre of the Spartan state, whose male and female citizens were trained in the discipline and honor of the warrior society. Subject to military drill from early manhood, the Spartans were one of the most feared military forces in the Greek world. At the height of Sparta's power – between the 6th and 4th centuries BC – it was commonly accepted that, ""one Spartan was worth several men of any other state."" According to Thucydides, the famous moment of Spartan surrender at the island of Sphacteria off of Pylos was highly unexpected. He said that ""it was the common perception at the time that Spartans would never lay down their weapons for any reason, be it hunger, or danger.""The iconic army was first coined by the Spartan legislator Lycurgus. In his famous quote of Sparta having a ""wall of men, instead of bricks"", he proposed to create a military-focused lifestyle reformation in the Spartan society in accordance to proper virtues such as equality for the male citizens, austerity, strength, and fitness. A Spartan man's involvement with the army began in infancy when he was inspected by the Gerousia. If the baby was found to be weak or deformed he was left at Mount Taygetus to die, since the world of the Spartans was no place for those who could not already fend for themselves. It should be noted, however, that the practice of discarding children at birth took place in Athens as well. Those deemed strong were then put in the agoge at the age of seven. Under the agoge the young boys or Spartiates were kept under intense and rigorous military training. Their education focused primarily on cunning, sports and war tactics, but also included poetry, music, academics, and sometimes politics. Those who passed the agoge by the age of 30 were given full Spartan citizenship.The term ""spartan"" became synonymous with multiple meanings such as: fearlessness, harsh and cruel life, bland and lacking creativity, or simplicity by design.