Introduction to Greek and Roman History
... jumped up three times from the throne in fear for his army. This, then, is how the fighting progressed, and on the next day the barbarians fought no better. They joined battle supposing that their enemies, being so few, were now disabled by wounds and could no longer resist. [2] The Hellenes, howeve ...
... jumped up three times from the throne in fear for his army. This, then, is how the fighting progressed, and on the next day the barbarians fought no better. They joined battle supposing that their enemies, being so few, were now disabled by wounds and could no longer resist. [2] The Hellenes, howeve ...
Athens V Sparta - Primary Resources
... However when it came to Athens and Sparta against each other… Sparta won! But, they did not take over Athens they said they would not burn it as long as Athens promised not to keep trying to take over. Athens was therefore left as it was and even now is one of the most famous cities in the world. ...
... However when it came to Athens and Sparta against each other… Sparta won! But, they did not take over Athens they said they would not burn it as long as Athens promised not to keep trying to take over. Athens was therefore left as it was and even now is one of the most famous cities in the world. ...
File - Coach Franco World History
... o Many were prisoners of war or debt slaves. Athenian Economy was based on agriculture and trade. Trade: Grapes and Olives were the two main exports. Family Life and the Role of Women The Athenian family was the husband, wife, and children. It also sometimes included extended relatives and slaves. ...
... o Many were prisoners of war or debt slaves. Athenian Economy was based on agriculture and trade. Trade: Grapes and Olives were the two main exports. Family Life and the Role of Women The Athenian family was the husband, wife, and children. It also sometimes included extended relatives and slaves. ...
AthenianDemocracy.wars_
... Athens evacuated, with the aid of Allied fleet, to Salamis. Athens fell to Persians The Persians had now captured much of Greece. But needed to capture navy. Destruction of some of Persian fleet in battle and storm at Artemisium Peloponnesians fortify Isthmus of Corinth “Eurybiades presented the pro ...
... Athens evacuated, with the aid of Allied fleet, to Salamis. Athens fell to Persians The Persians had now captured much of Greece. But needed to capture navy. Destruction of some of Persian fleet in battle and storm at Artemisium Peloponnesians fortify Isthmus of Corinth “Eurybiades presented the pro ...
The Persian Wars: From the Ionian Revolt to Eion
... Athens evacuated, with the aid of Allied fleet, to Salamis. Athens fell to Persians The Persians had now captured much of Greece. But needed to capture navy. Destruction of some of Persian fleet in battle and storm at Artemisium Peloponnesians fortify Isthmus of Corinth “Eurybiades presented the pro ...
... Athens evacuated, with the aid of Allied fleet, to Salamis. Athens fell to Persians The Persians had now captured much of Greece. But needed to capture navy. Destruction of some of Persian fleet in battle and storm at Artemisium Peloponnesians fortify Isthmus of Corinth “Eurybiades presented the pro ...
ANCIENT AND CLASSICAL GREECE
... • Founded by Dorians (Greeks who invaded the Peloponnesus in the Dark Ages) • Conquered and enslaved their neighbors/Helots “Capture” • By 6th century B.C.E., helots outnumbered Spartans by 10 to 1 • Located on Peloponnesus • No interest in statues, temples, education, arts, travel • Willing to DIE ...
... • Founded by Dorians (Greeks who invaded the Peloponnesus in the Dark Ages) • Conquered and enslaved their neighbors/Helots “Capture” • By 6th century B.C.E., helots outnumbered Spartans by 10 to 1 • Located on Peloponnesus • No interest in statues, temples, education, arts, travel • Willing to DIE ...
File
... They were given little food or clothing. They were expected to survive by stealing whatever they ...
... They were given little food or clothing. They were expected to survive by stealing whatever they ...
CH 5.CLASSICAL GREECE.HWH
... i. Only free male Athenians over the age of 20, who completed military training could vote 1. Expected to take part in 4 areas a. Vote in all elections b. Serve in office if elected c. Serve on juries d. Serve in the military during war ...
... i. Only free male Athenians over the age of 20, who completed military training could vote 1. Expected to take part in 4 areas a. Vote in all elections b. Serve in office if elected c. Serve on juries d. Serve in the military during war ...
Chapter 28
... As the Persians approached, the Greek ships seemed to retreat in order to throw them off. Really, they were just trying to lure them deeper into the channel. Soon, the Persian ships were surrounded, and the Greeks sank 300 Persian ...
... As the Persians approached, the Greek ships seemed to retreat in order to throw them off. Really, they were just trying to lure them deeper into the channel. Soon, the Persian ships were surrounded, and the Greeks sank 300 Persian ...
CHAPTER 5: Classical Greece - Mr. Hammond: Social Studies
... where they would stand side by side with a shield in one hand and a spear in the other. The phalanx would make the Spartans the best fighting force in the world. Battle at Marathon • Persian Wars—between Greece and Persian Empire—begin in Ionia • After being conquered by the Persians, Ionian Greeks ...
... where they would stand side by side with a shield in one hand and a spear in the other. The phalanx would make the Spartans the best fighting force in the world. Battle at Marathon • Persian Wars—between Greece and Persian Empire—begin in Ionia • After being conquered by the Persians, Ionian Greeks ...
Unit 4 Mediterranean Empires
... 29. Define Pericles. 30. Define Sparta. 31. (√) What details show that Sparta was governed differently than Athens? 32. Define helot. 33. At what age were Spartan boys sent to military camps to begin training for the army e. Women in Sparta (page 256) Main Idea: Spartan women had more rights and res ...
... 29. Define Pericles. 30. Define Sparta. 31. (√) What details show that Sparta was governed differently than Athens? 32. Define helot. 33. At what age were Spartan boys sent to military camps to begin training for the army e. Women in Sparta (page 256) Main Idea: Spartan women had more rights and res ...
The Peloponnesian War
... Pericles “never really had any clear strategy for how to mount an offensive…” (Hanson, ...
... Pericles “never really had any clear strategy for how to mount an offensive…” (Hanson, ...
Peloponnesian War
... Athens was also effective in land combat. They would strategically set up in an area where they could both flank the enemy and yet also defend. The strategy was very much like the one used in the Battle of Marathon. ...
... Athens was also effective in land combat. They would strategically set up in an area where they could both flank the enemy and yet also defend. The strategy was very much like the one used in the Battle of Marathon. ...
The Persian Wars
... "My men have become women, and my women men.“ Artemesia rammed one if its own ships so she could escape ...
... "My men have become women, and my women men.“ Artemesia rammed one if its own ships so she could escape ...
Warrick 1 Ancient Greek Childhood and the Pursuit of Polis Identity
... visit the Agora…public opinion will likewise frown upon the man who allowed his wife to appear in public too freely”.35 Athenian women were typically not educated outside of those functions required for the proper management of the household, and this lack of education contrasts sharply with the ext ...
... visit the Agora…public opinion will likewise frown upon the man who allowed his wife to appear in public too freely”.35 Athenian women were typically not educated outside of those functions required for the proper management of the household, and this lack of education contrasts sharply with the ext ...
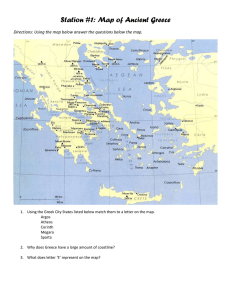
Station 3: City States
... Life was very different in ancient Sparta than it was in the rest of ancient Greek city-states. The Spartans were proud, fierce, capable warriors. No great works of art came out of Sparta. But the Spartans, both men and women, were tough, and the Greeks admired strength. Sparta's government was an o ...
... Life was very different in ancient Sparta than it was in the rest of ancient Greek city-states. The Spartans were proud, fierce, capable warriors. No great works of art came out of Sparta. But the Spartans, both men and women, were tough, and the Greeks admired strength. Sparta's government was an o ...
Main Ideas - John Q. Adams Middle School
... Ancient Greeks made lasting contributions in the arts, philosophy, and science. Main Ideas • The Greeks made great contributions to the arts. • The teachings of Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle are the basis ...
... Ancient Greeks made lasting contributions in the arts, philosophy, and science. Main Ideas • The Greeks made great contributions to the arts. • The teachings of Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle are the basis ...
Ancient Greece - Class Notes For Mr. Pantano
... Hoplites ran in this formation and crash into the enemy or the opposing phalanx. Fought in formation until one side retreated. ...
... Hoplites ran in this formation and crash into the enemy or the opposing phalanx. Fought in formation until one side retreated. ...
Ancient Greece 2012 chapter 4
... Spartan’s ability in open battles 2nd year – deadly disease Pericles dies. Standoff continues for 25 years Spartan deal with Persians Spartan navy defeats Athens Athens surrenders. ...
... Spartan’s ability in open battles 2nd year – deadly disease Pericles dies. Standoff continues for 25 years Spartan deal with Persians Spartan navy defeats Athens Athens surrenders. ...
Ancient Greece - Class Notes For Mr. Pantano
... Hoplites ran in this formation and crash into the enemy or the opposing phalanx. Fought in formation until one side retreated. ...
... Hoplites ran in this formation and crash into the enemy or the opposing phalanx. Fought in formation until one side retreated. ...
Ancient Greece - Class Notes For Mr. Pantano
... Hoplites ran in this formation and crash into the enemy or the opposing phalanx. Fought in formation until one side retreated. ...
... Hoplites ran in this formation and crash into the enemy or the opposing phalanx. Fought in formation until one side retreated. ...
Greek History
... 5. After the death of Cyrus, who led The Ten Thousand, a band of Greek mercenaries, out of Persia? a. Alcibiades b. Iphicrates c. Philomelus d. Xenophon 6. Who was known as "The Father of History" because he was the first to organize his materials in a systematic way and to test their veracity? a. L ...
... 5. After the death of Cyrus, who led The Ten Thousand, a band of Greek mercenaries, out of Persia? a. Alcibiades b. Iphicrates c. Philomelus d. Xenophon 6. Who was known as "The Father of History" because he was the first to organize his materials in a systematic way and to test their veracity? a. L ...
Name Chapter 28 Fighting the Persian Wars Review Introduction
... 2. What is an ally? States that agree to help each other against a common enemy 3. What was the Persian’s advantage during the wars? Land mass and population Ionian Revolt 4. Was it wise for King Darius to allow conquered people to keep their own customs and religions? Why or why not? Yes, they were ...
... 2. What is an ally? States that agree to help each other against a common enemy 3. What was the Persian’s advantage during the wars? Land mass and population Ionian Revolt 4. Was it wise for King Darius to allow conquered people to keep their own customs and religions? Why or why not? Yes, they were ...
Olympic Games Assembly
... well but will they be able to keep it up in the long term? It’s a close race…..but, as predicted, Argos are fading, they put too much into their start, they’ve literally run out of puff (Argive runner passes out on floor). So, it’s a three man race now…almost at the end and, although Corinth and Spa ...
... well but will they be able to keep it up in the long term? It’s a close race…..but, as predicted, Argos are fading, they put too much into their start, they’ve literally run out of puff (Argive runner passes out on floor). So, it’s a three man race now…almost at the end and, although Corinth and Spa ...
File
... locales. Mindarus was killed in the fighting, the Peloponnesian and Persian forces fled, and the Athenians regained control of the land. The entire Peloponnesian fleet was captured or destroyed. ...
... locales. Mindarus was killed in the fighting, the Peloponnesian and Persian forces fled, and the Athenians regained control of the land. The entire Peloponnesian fleet was captured or destroyed. ...
Spartan army
The Spartan army stood at the centre of the Spartan state, whose male and female citizens were trained in the discipline and honor of the warrior society. Subject to military drill from early manhood, the Spartans were one of the most feared military forces in the Greek world. At the height of Sparta's power – between the 6th and 4th centuries BC – it was commonly accepted that, ""one Spartan was worth several men of any other state."" According to Thucydides, the famous moment of Spartan surrender at the island of Sphacteria off of Pylos was highly unexpected. He said that ""it was the common perception at the time that Spartans would never lay down their weapons for any reason, be it hunger, or danger.""The iconic army was first coined by the Spartan legislator Lycurgus. In his famous quote of Sparta having a ""wall of men, instead of bricks"", he proposed to create a military-focused lifestyle reformation in the Spartan society in accordance to proper virtues such as equality for the male citizens, austerity, strength, and fitness. A Spartan man's involvement with the army began in infancy when he was inspected by the Gerousia. If the baby was found to be weak or deformed he was left at Mount Taygetus to die, since the world of the Spartans was no place for those who could not already fend for themselves. It should be noted, however, that the practice of discarding children at birth took place in Athens as well. Those deemed strong were then put in the agoge at the age of seven. Under the agoge the young boys or Spartiates were kept under intense and rigorous military training. Their education focused primarily on cunning, sports and war tactics, but also included poetry, music, academics, and sometimes politics. Those who passed the agoge by the age of 30 were given full Spartan citizenship.The term ""spartan"" became synonymous with multiple meanings such as: fearlessness, harsh and cruel life, bland and lacking creativity, or simplicity by design.