2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
MEDICAL EMBRYOLOGY
... filaments that are composed of DNA chain bound to basic proteins (mainly histone) The basic unit is the nucleosome (histone + 140 base pairs of DNA). Heterochromatin: inactive state the chromatin appear as beads of nucleosomes on a string of DNA. Euchromatin: active state, the DNA uncoild from ...
... filaments that are composed of DNA chain bound to basic proteins (mainly histone) The basic unit is the nucleosome (histone + 140 base pairs of DNA). Heterochromatin: inactive state the chromatin appear as beads of nucleosomes on a string of DNA. Euchromatin: active state, the DNA uncoild from ...
Sex Linked Traits
... Sex Linked Traits • When X and Y chromosomes meet at fertilization, each sex-linked gene on the X chromosome (whether recessive or dominant) becomes expressed in the phenotype. • This is because the Y chromosome does not possess alleles of any of these genes and cannot offer dominance to them. ...
... Sex Linked Traits • When X and Y chromosomes meet at fertilization, each sex-linked gene on the X chromosome (whether recessive or dominant) becomes expressed in the phenotype. • This is because the Y chromosome does not possess alleles of any of these genes and cannot offer dominance to them. ...
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis–Inheritance Connection
... Nondisjunction of Sex Chromosomes • Do not generally experience severe developmental abnormalities • Individuals have somewhat abnormal features, but often reach maturity and in some cases may be fertile • XXX – triple-X females • XXY – males (Klinefelter syndrome) • XO – females (Turner syndrome) • ...
... Nondisjunction of Sex Chromosomes • Do not generally experience severe developmental abnormalities • Individuals have somewhat abnormal features, but often reach maturity and in some cases may be fertile • XXX – triple-X females • XXY – males (Klinefelter syndrome) • XO – females (Turner syndrome) • ...
sex-linked traits
... Uses 3 loci instead of 2 to construct maps Gene in the middle allows us to see recombination events on either side In any three-point cross, the class of offspring with two crossovers is the least frequent class In practice, geneticists use three-point crosses to determine the order of genes, ...
... Uses 3 loci instead of 2 to construct maps Gene in the middle allows us to see recombination events on either side In any three-point cross, the class of offspring with two crossovers is the least frequent class In practice, geneticists use three-point crosses to determine the order of genes, ...
Human Heridity
... *The very last chromosomes (23rd) are the _________________ (X’s and Y’s) *All human _____ cells carry an ___ chromosome *________ cells carry either an _______________ *Human females are _____, males are _____ ...
... *The very last chromosomes (23rd) are the _________________ (X’s and Y’s) *All human _____ cells carry an ___ chromosome *________ cells carry either an _______________ *Human females are _____, males are _____ ...
Chapter 15 practice Questions AP Biology
... 10) Cinnabar eyes is a sex-linked recessive characteristic in fruit flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a wild-type male, what percentage of the F1 males will have cinnabar eyes? A) 0% B) 25% C) 50% D) 75% E) 100% Refer to the following information to answer the questions below. ...
... 10) Cinnabar eyes is a sex-linked recessive characteristic in fruit flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a wild-type male, what percentage of the F1 males will have cinnabar eyes? A) 0% B) 25% C) 50% D) 75% E) 100% Refer to the following information to answer the questions below. ...
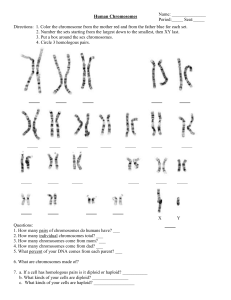
Human Chromosomes
... 7. a. If a cell has homologous pairs is it diploid or haploid? ___________ b. What kinds of your cells are diploid? ________________ c. What kinds of your cells are haploid? __________________ ...
... 7. a. If a cell has homologous pairs is it diploid or haploid? ___________ b. What kinds of your cells are diploid? ________________ c. What kinds of your cells are haploid? __________________ ...
Chapter 9 I am - Mrs Smith`s Biology
... I am the symbol used to represent the fact that a cell is diploid n ...
... I am the symbol used to represent the fact that a cell is diploid n ...
29 - Karmayog .org
... to continue the species. Male organs called testis make sperm. Female organs called ovaries make eggs. Sperms and eggs unite to create babies. The process of uniting the two reproductive cells is called fertilisation. In man, animals and plant life cycles, all species need to reproduce, so that the ...
... to continue the species. Male organs called testis make sperm. Female organs called ovaries make eggs. Sperms and eggs unite to create babies. The process of uniting the two reproductive cells is called fertilisation. In man, animals and plant life cycles, all species need to reproduce, so that the ...
Document
... Linked genes can assort separately from on another only through crossing over The closer to genes are to each other on a chromosome, the more tightly linked they are (i.e. the more likely they are to assort together during meiosis ...
... Linked genes can assort separately from on another only through crossing over The closer to genes are to each other on a chromosome, the more tightly linked they are (i.e. the more likely they are to assort together during meiosis ...
Polygenic Traits
... – 95% of non-disjunctions occur with the ovum. • Most Down syndrome babies are born to women younger than 35 because those are the ages that most women have children. • Dogma: all your oocytes are present at birth; meiosis is arrested in Prophase I and not completed until adulthood, once a month. – ...
... – 95% of non-disjunctions occur with the ovum. • Most Down syndrome babies are born to women younger than 35 because those are the ages that most women have children. • Dogma: all your oocytes are present at birth; meiosis is arrested in Prophase I and not completed until adulthood, once a month. – ...
The Mechanism of X inactivation
... – It results in a diploid cell and one without chromosomes – The chromosome-less cell is nonviable – The diploid cell can participate in fertilization with a normal gamete • This yields a triploid individual ...
... – It results in a diploid cell and one without chromosomes – The chromosome-less cell is nonviable – The diploid cell can participate in fertilization with a normal gamete • This yields a triploid individual ...
CHAPTER 14: Genes in Action Essential Ideas
... Polyploidy when extra chromosomes are found in an individual, for example trisomy 21 or Downs syndrome Non disjunction event during Anaphase of Meiosis in which chromosomes fail to separate that can lead to polyploidy DOWNS SYNDROME =TRISOMY21 (3 copies of a chromosome 21) mental delays, changes in ...
... Polyploidy when extra chromosomes are found in an individual, for example trisomy 21 or Downs syndrome Non disjunction event during Anaphase of Meiosis in which chromosomes fail to separate that can lead to polyploidy DOWNS SYNDROME =TRISOMY21 (3 copies of a chromosome 21) mental delays, changes in ...
“IPMATC” Activity Directions: Use complete, meaning
... What are the phases of mitosis? Use page 131 to draw and label a chromosome. What happens to the amount of DNA during “Replication” phase of interphase? Where in the cell is the chromatin during interphase? In what phase are the chromosomes completely separated in their own nuclear envelope? How doe ...
... What are the phases of mitosis? Use page 131 to draw and label a chromosome. What happens to the amount of DNA during “Replication” phase of interphase? Where in the cell is the chromatin during interphase? In what phase are the chromosomes completely separated in their own nuclear envelope? How doe ...
Chromosome Theory Sex Chromosomes
... 2 X chromosomes = female 1 X and 1 Y chromosome = male Sex determination in humans is based on the presence of a Y chromosome 2 X chromosomes = female having a Y chromosome (XY) = male ...
... 2 X chromosomes = female 1 X and 1 Y chromosome = male Sex determination in humans is based on the presence of a Y chromosome 2 X chromosomes = female having a Y chromosome (XY) = male ...
PGS: 274 – 284
... b. They experience problems with bleeding to death. c. This was a disorder associated with the “Royal Blue-Bloods of Europe” – They were inbreeding to keep the crown “ In the Family”. d. Treatment? These individuals have to keep AHF with them at all times in case they get hurt. If they do get hurt a ...
... b. They experience problems with bleeding to death. c. This was a disorder associated with the “Royal Blue-Bloods of Europe” – They were inbreeding to keep the crown “ In the Family”. d. Treatment? These individuals have to keep AHF with them at all times in case they get hurt. If they do get hurt a ...
Chromosomes Key - Iowa State University
... The coiling in question 3 is caused by what type of protein? _topoisomerase___ 4. Prokaryotic chromosomes are different than Eukaryotic chromosomes because: a) they are single stranded b) they are located in the nucleus c) they are circular 5. Explain the difference between a nucleosome and a chroma ...
... The coiling in question 3 is caused by what type of protein? _topoisomerase___ 4. Prokaryotic chromosomes are different than Eukaryotic chromosomes because: a) they are single stranded b) they are located in the nucleus c) they are circular 5. Explain the difference between a nucleosome and a chroma ...
The Human Chromosome
... by the presence of all or part of an extra 21 chromosome, known as trisomy 21. Down’s syndrome is associated with some impairment of cognitive ability and physical growth. ...
... by the presence of all or part of an extra 21 chromosome, known as trisomy 21. Down’s syndrome is associated with some impairment of cognitive ability and physical growth. ...
Cytogenetics
... Analysis of the banding pattern of each individual chromosome in selected cells. Total chr. Count is determined in 10-15 cells, but if mosaicism is suspected then 30 or more cell count will be undertaken. Detailed analysis of the banding pattern of the individual chromosomes is carried out in ...
... Analysis of the banding pattern of each individual chromosome in selected cells. Total chr. Count is determined in 10-15 cells, but if mosaicism is suspected then 30 or more cell count will be undertaken. Detailed analysis of the banding pattern of the individual chromosomes is carried out in ...
14.1 ws - Woodstown.org
... The alleles for many human genes display codominant inheritance. Many human genes, including the genes for blood group, have multiple alleles. A gene located on a sex chromosome is a __________________________________. The genes on sex chromosomes show a sex-linked pattern of inheritance, since fema ...
... The alleles for many human genes display codominant inheritance. Many human genes, including the genes for blood group, have multiple alleles. A gene located on a sex chromosome is a __________________________________. The genes on sex chromosomes show a sex-linked pattern of inheritance, since fema ...
Foundations of Biology
... The cos site signals for packaging into l phage, thus the plasmid, including a large insert can be packaged into phage particles without having to waste space on l genes A cosmid combined with a cloned insert cannot exceed the 53 kb limit on how much can be packaged into the l phage head ©2000 Timot ...
... The cos site signals for packaging into l phage, thus the plasmid, including a large insert can be packaged into phage particles without having to waste space on l genes A cosmid combined with a cloned insert cannot exceed the 53 kb limit on how much can be packaged into the l phage head ©2000 Timot ...