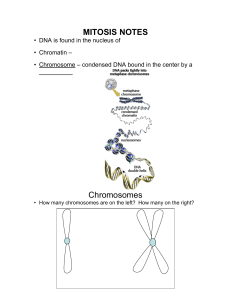
Mitosis Vocab
... 1. Chromosome- package of DNA & proteins that stores genetic information and “tells” cell how to function. 2. Chromatid – One part of a chromosome 3. Spindle fibers- protein filaments (part of cytoskeleton) that move the chromosomes apart during cell division. ...
... 1. Chromosome- package of DNA & proteins that stores genetic information and “tells” cell how to function. 2. Chromatid – One part of a chromosome 3. Spindle fibers- protein filaments (part of cytoskeleton) that move the chromosomes apart during cell division. ...
Modeling Meiosis with Pop Beads
... Assemble two strands of yellow beads connected to magnetic centromeres and two strands of red beads connected to magnetic centromeres. One of the red strands represents the chromosome contribution of the female parent, and one of the yellow strands represents the chromosome contribution of the male ...
... Assemble two strands of yellow beads connected to magnetic centromeres and two strands of red beads connected to magnetic centromeres. One of the red strands represents the chromosome contribution of the female parent, and one of the yellow strands represents the chromosome contribution of the male ...
Detachments from duplication bearing females
... The occurrence in these experiments of several “atypical cases” in which the ratio after test with a weak centromere is depressed somewhat below the 3 : 2 expectation may have some significance in this connection. 174-1 3,9-1 Oe, 9-1 00, 9-20i, and 9-24d can be explained as instances in which the re ...
... The occurrence in these experiments of several “atypical cases” in which the ratio after test with a weak centromere is depressed somewhat below the 3 : 2 expectation may have some significance in this connection. 174-1 3,9-1 Oe, 9-1 00, 9-20i, and 9-24d can be explained as instances in which the re ...
The Case of the Cumbersome Chromosomes
... attached at the centromere. Make sure that the centromere is located between A and B on each chromosome. Synapse the homologs, again remembering that your goal is to align each and every gene region with its homolog. Show your synapsed chromosomes to your instructor. Now, simulate a single crossover ...
... attached at the centromere. Make sure that the centromere is located between A and B on each chromosome. Synapse the homologs, again remembering that your goal is to align each and every gene region with its homolog. Show your synapsed chromosomes to your instructor. Now, simulate a single crossover ...
Brooker Chapter 8
... – Allelic variations are due to mutations in particular genes – Chromosomal aberrations are substantial changes in chromosome structure • These typically affect more than one gene • They are also called chromosomal mutations ...
... – Allelic variations are due to mutations in particular genes – Chromosomal aberrations are substantial changes in chromosome structure • These typically affect more than one gene • They are also called chromosomal mutations ...
ExamView - Unit 2 pracitce test.tst
... Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ...
... Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ...
Human karyotype
... Stabilize chromosome movement during cell division Site where chromosome attaches to spindle Acentric chromosome: Chromosome that lacks a centromere; segregates abnormally in mitosis or meiosis. Dicentric chromosome: Chromosome with two centromeres; unstable, usually breaks during cell division. ...
... Stabilize chromosome movement during cell division Site where chromosome attaches to spindle Acentric chromosome: Chromosome that lacks a centromere; segregates abnormally in mitosis or meiosis. Dicentric chromosome: Chromosome with two centromeres; unstable, usually breaks during cell division. ...
Chapter 14 Human Genetics
... Human Karyotype • Cells are photographed in mitosis when chromosomes are condensed and easy to see • 46 chromosomes (23 pair) ▫ 2 sex chromosomes (determine male or female) XX = Female XY = Male 1200 genes are found on the X chromosome 140 genes are found on the Y chromosome ...
... Human Karyotype • Cells are photographed in mitosis when chromosomes are condensed and easy to see • 46 chromosomes (23 pair) ▫ 2 sex chromosomes (determine male or female) XX = Female XY = Male 1200 genes are found on the X chromosome 140 genes are found on the Y chromosome ...
Name: Biology I: Chapter 14 Guided Reading Chapter 12.4 When
... Males/Females are more likely to have colorblindness. (Circle One) ...
... Males/Females are more likely to have colorblindness. (Circle One) ...
Enter the weird world of the imagination!
... different types of cells in different parts of your body.You can only see human cells by looking at them down a microscope, which makes them look much bigger than they really are. Inside each cell there is something called a nucleus – this is where the chromosomes are found. Chromosomes look like lo ...
... different types of cells in different parts of your body.You can only see human cells by looking at them down a microscope, which makes them look much bigger than they really are. Inside each cell there is something called a nucleus – this is where the chromosomes are found. Chromosomes look like lo ...
Cell Division Cancer review 14-15
... 3. What could cause a cell to enter later stages of interphase (from G1, S, G2)? 4. What happens in later interphase stages (G1, S, and G2)? 5. What are the stages of mitosis and what happens in each of the stages? 6. Be able to recognize the stage that different cells are in from a picture and sequ ...
... 3. What could cause a cell to enter later stages of interphase (from G1, S, G2)? 4. What happens in later interphase stages (G1, S, and G2)? 5. What are the stages of mitosis and what happens in each of the stages? 6. Be able to recognize the stage that different cells are in from a picture and sequ ...
Cell Division Cancer review 16-17
... 3. What could cause a cell to enter later stages of interphase (from G1, S, G2)? 4. What happens in later interphase stages (G1, S, and G2)? 5. What are the stages of mitosis and what happens in each of the stages? 6. Be able to recognize the stage that different cells are in from a picture and sequ ...
... 3. What could cause a cell to enter later stages of interphase (from G1, S, G2)? 4. What happens in later interphase stages (G1, S, and G2)? 5. What are the stages of mitosis and what happens in each of the stages? 6. Be able to recognize the stage that different cells are in from a picture and sequ ...
Answers to “A Closer Look at Conception”
... particles called chromosomes 3. 23 chromosomes come from the father or sperm 23 chromosomes come from the mother or egg 4. Each chromosomes contains thousands of genes. ...
... particles called chromosomes 3. 23 chromosomes come from the father or sperm 23 chromosomes come from the mother or egg 4. Each chromosomes contains thousands of genes. ...
Causes of Variation PPT
... http://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/var/sciencelearn/storage/images/contexts/uniquely-me/sci-media/images/chromosomes-crossing-over/464438-1-engNZ/Chromosomes-crossing-over.jpg ...
... http://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/var/sciencelearn/storage/images/contexts/uniquely-me/sci-media/images/chromosomes-crossing-over/464438-1-engNZ/Chromosomes-crossing-over.jpg ...
DNA FRQ practice
... ______Chromatin Form (heterochromatin/ euchromatin) structure: condensed supercoiled vs. loosely coiled. ______ Chromatin Form (heterochromatin/ euchromatin) function: proper distribution in cell division (not during replication)/ gene expression during interphase/ replication occurs when loosely pa ...
... ______Chromatin Form (heterochromatin/ euchromatin) structure: condensed supercoiled vs. loosely coiled. ______ Chromatin Form (heterochromatin/ euchromatin) function: proper distribution in cell division (not during replication)/ gene expression during interphase/ replication occurs when loosely pa ...
Sex linked traits and autosomal diseases
... II. Sex-linked traits A. First discovered by T. Morgan in fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) B. He figured out that the gene for white eyes was carried on the X chromosome ...
... II. Sex-linked traits A. First discovered by T. Morgan in fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) B. He figured out that the gene for white eyes was carried on the X chromosome ...
pdf version
... enzymes that target accidental DNA breaks in need of repair. The cell is, indeed, equipped with a sensitive surveillance system that recognizes and corrects abnormalities occurring within our genome. This system includes patrolling proteins, molecules that set off an alarm, as well as damage-repairi ...
... enzymes that target accidental DNA breaks in need of repair. The cell is, indeed, equipped with a sensitive surveillance system that recognizes and corrects abnormalities occurring within our genome. This system includes patrolling proteins, molecules that set off an alarm, as well as damage-repairi ...
Full Lecture 2 pdf - Institute for Behavioral Genetics
... potential to become part of the human genome? ...
... potential to become part of the human genome? ...