What do these 3 people have in common?
... During an 8 month period in 1984, he murdered at least ten women in Tampa Bay area of Florida. The murders were extremely brutal. ...
... During an 8 month period in 1984, he murdered at least ten women in Tampa Bay area of Florida. The murders were extremely brutal. ...
Gene Section AF1q (ALL1 fused gene from chromosome 1q)
... probes are welcome : contact [email protected]. ...
... probes are welcome : contact [email protected]. ...
doc Summer 2010 Lecture 3
... - many involved with energy production - some play roles in heredity - chromosomal inheritance is 50% male and 50% female - organelle DNA: male contribution is low o random distribution—no spindle dividing it get a segregation of mitochondria into 2 daughters if the dominant allele is on the L a ...
... - many involved with energy production - some play roles in heredity - chromosomal inheritance is 50% male and 50% female - organelle DNA: male contribution is low o random distribution—no spindle dividing it get a segregation of mitochondria into 2 daughters if the dominant allele is on the L a ...
Female Genitourinary System
... proteins [+ charge] & non-histone proteins. Bind very tightly. Chromosomes contain thousands of genes; smallest units of heredity information Cells express only some of their genes. Genes expressed determine function of cell. If genes have incorrect information, defects follow. ...
... proteins [+ charge] & non-histone proteins. Bind very tightly. Chromosomes contain thousands of genes; smallest units of heredity information Cells express only some of their genes. Genes expressed determine function of cell. If genes have incorrect information, defects follow. ...
Heredity Inherited Traits - Saint Mary Catholic School
... represented with a lower case letter. ...
... represented with a lower case letter. ...
File - Ms. Richards IB Biology HL
... 2. Meiosis creates genetic variation: 4 daughter cells genetically different from parent cell and from each other 3. Meiosis is 2 successive nuclear divisions ...
... 2. Meiosis creates genetic variation: 4 daughter cells genetically different from parent cell and from each other 3. Meiosis is 2 successive nuclear divisions ...
Algebra 1 - Edublogs
... 2. Which of the following does NOT describe how genetic information is organized in the cell? A. A gene contains the coded information for building a protein B. A nucleus contains chromosomes which are made of genes C. The sequence of bases in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in protein D. ...
... 2. Which of the following does NOT describe how genetic information is organized in the cell? A. A gene contains the coded information for building a protein B. A nucleus contains chromosomes which are made of genes C. The sequence of bases in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in protein D. ...
Procaryotic chromosome
... 1. Specialized DNA sequences which form the ends of the linear DNA of the eukaryotic chromosome 2. Contains up to hundreds copies of a short repeated sequence (5’-TTAGGG-3’in human) 3. Synthesized by the enzyme telomerase (a ribonucleoprotein) independent of normal DNA ...
... 1. Specialized DNA sequences which form the ends of the linear DNA of the eukaryotic chromosome 2. Contains up to hundreds copies of a short repeated sequence (5’-TTAGGG-3’in human) 3. Synthesized by the enzyme telomerase (a ribonucleoprotein) independent of normal DNA ...
Cell cycle to Sexual Reproduction
... • Prophase 1: Each chromosome duplicates and remains closely associated. These are called sister chromatids. Crossing-over can occur during the latter part of this stage. • Metaphase 1: Homologous chromosomes align at the equatorial plate. (Tetrads or two full chromosomes pair up) • Anaphase 1: Homo ...
... • Prophase 1: Each chromosome duplicates and remains closely associated. These are called sister chromatids. Crossing-over can occur during the latter part of this stage. • Metaphase 1: Homologous chromosomes align at the equatorial plate. (Tetrads or two full chromosomes pair up) • Anaphase 1: Homo ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... Certain previously described CCRs (Table 1) in female cases were also ascertained by recurrent miscarriages were all phenotypically normal, it is likely that these chromosomal breakpoints might not include genes or gene regulatory regions whose disruptions may give rise to physical dysfunction and c ...
... Certain previously described CCRs (Table 1) in female cases were also ascertained by recurrent miscarriages were all phenotypically normal, it is likely that these chromosomal breakpoints might not include genes or gene regulatory regions whose disruptions may give rise to physical dysfunction and c ...
10.2: Dihybrid Crosses
... chromosome other than a sex chromosome; come in pairs. Sex chromosomes- Come in pairs also, but there are two types, X & Y. For humans, the Y chromosome is the “determining factor” as it determines whether or not the embryo is male or female. ...
... chromosome other than a sex chromosome; come in pairs. Sex chromosomes- Come in pairs also, but there are two types, X & Y. For humans, the Y chromosome is the “determining factor” as it determines whether or not the embryo is male or female. ...
HEREDITY
... HEREDITY • Heredity Is the passing of traits from parents to offspring. • Genes on chromosomes control the traits that show up in an organism. • The different forms of a traits that a gene may have are alleles. ...
... HEREDITY • Heredity Is the passing of traits from parents to offspring. • Genes on chromosomes control the traits that show up in an organism. • The different forms of a traits that a gene may have are alleles. ...
Cell Division, Chromosomes, and Inheritance Worksheet BIO/410
... Complete all four sections of this worksheet. Section I: Mitosis and Meiosis Part 1: Review the following images on mitosis and meiosis. ...
... Complete all four sections of this worksheet. Section I: Mitosis and Meiosis Part 1: Review the following images on mitosis and meiosis. ...
Meiosis and Genetic Variation
... pairs of chromosomes, and that each pair assorts independently from the others. As a result, there are about 8 million different combinations of chromosomes that can be produced during meiosis of one human cell. Suppose a human sperm cell that has one of 8 million different possible combinations f ...
... pairs of chromosomes, and that each pair assorts independently from the others. As a result, there are about 8 million different combinations of chromosomes that can be produced during meiosis of one human cell. Suppose a human sperm cell that has one of 8 million different possible combinations f ...
Unit 3 Review Notes
... Linked genes vs. sex-linked genes o How do they differ?, where are they found, how are they passed on? linked genes are located on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together; sex-linked genes are any genes on sex chromosomes Parental type offspring vs. recombinant type offspring o How ...
... Linked genes vs. sex-linked genes o How do they differ?, where are they found, how are they passed on? linked genes are located on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together; sex-linked genes are any genes on sex chromosomes Parental type offspring vs. recombinant type offspring o How ...
meiosis - Citrus College
... • Gametes have half the # of chromosomes. chromosomes • Occurs only in gonads (testes or ovaries). Male: spermatogenesis Female: oogenesis ...
... • Gametes have half the # of chromosomes. chromosomes • Occurs only in gonads (testes or ovaries). Male: spermatogenesis Female: oogenesis ...
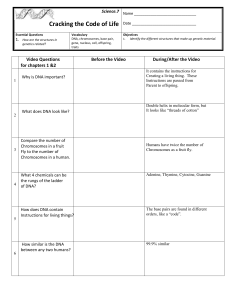
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... Double helix in molecular form, but It looks like “threads of cotton” ...
... Double helix in molecular form, but It looks like “threads of cotton” ...
Mutations
... • Many types of rays can cause mutations – Xrays, ultraviolet rays, microwaves, etc. • Chemicals can also cause mutations – Toxins, hazardous chemicals, carcinogens • Additional mutagenic factor: – The sun! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o9 BqrSAHbTc ...
... • Many types of rays can cause mutations – Xrays, ultraviolet rays, microwaves, etc. • Chemicals can also cause mutations – Toxins, hazardous chemicals, carcinogens • Additional mutagenic factor: – The sun! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o9 BqrSAHbTc ...
Topic 3 powerpoint notes
... • ______ ___________also creates variation because of which of the different sperm cells ______________ the egg cell. • The number of different gametes a human could produce is _____ or 8,388,608. That doesn’t include _________ _______. ...
... • ______ ___________also creates variation because of which of the different sperm cells ______________ the egg cell. • The number of different gametes a human could produce is _____ or 8,388,608. That doesn’t include _________ _______. ...
Unit 7 Genetics Review
... 4. A heterozygous man for blood type B marries a woman heterozygous for blood type A. The chance that their first child will have type O blood is… A. 0% B. 25% C. 50% D. 75% ...
... 4. A heterozygous man for blood type B marries a woman heterozygous for blood type A. The chance that their first child will have type O blood is… A. 0% B. 25% C. 50% D. 75% ...
Document
... addition to the basic medium that supports growth of wild-type. 7. The function of a protein is strongly dependent upon its __tertiary__________ structure that consists of prominent foldings of the polypeptide chain that are stabilized by non-covalent and, sometime, covalent interactions. 8. __eukar ...
... addition to the basic medium that supports growth of wild-type. 7. The function of a protein is strongly dependent upon its __tertiary__________ structure that consists of prominent foldings of the polypeptide chain that are stabilized by non-covalent and, sometime, covalent interactions. 8. __eukar ...
Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
... 24. How would it be possible for two healthy parents pass on a recessive disorder to their children? 25. What is a pedigree? What would you look for on that pedigree to identify a dominant trait? A recessive trait? A sex-linked trait? 26. The letters on the outside of the Punnett chart are the paren ...
... 24. How would it be possible for two healthy parents pass on a recessive disorder to their children? 25. What is a pedigree? What would you look for on that pedigree to identify a dominant trait? A recessive trait? A sex-linked trait? 26. The letters on the outside of the Punnett chart are the paren ...
Genetic Mutations
... number of varied side effects. There are characteristic physical abnormalities, such as ‘short stature, swelling, broad chest, low hairline, low-set ears, and webbed necks. Girls with Turner syndrome typically experience non-working ovaries, which results in an absence of menstrual cycle and sterili ...
... number of varied side effects. There are characteristic physical abnormalities, such as ‘short stature, swelling, broad chest, low hairline, low-set ears, and webbed necks. Girls with Turner syndrome typically experience non-working ovaries, which results in an absence of menstrual cycle and sterili ...