Things to Cover for Exam 1
... If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cell divisions. When during meiosis do homologous chromosomes cross over? Ch. 10 “Foundation ...
... If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cell divisions. When during meiosis do homologous chromosomes cross over? Ch. 10 “Foundation ...
DNA, genes and chromosomes
... activities of the genes. A strand 150 to 200 nucleotides long is wrapped twice around a core of eight histone proteins to form a structure called a nucleosome. The histone octamer at the centre of the nucleosome is formed from two units each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. The chains of histones a ...
... activities of the genes. A strand 150 to 200 nucleotides long is wrapped twice around a core of eight histone proteins to form a structure called a nucleosome. The histone octamer at the centre of the nucleosome is formed from two units each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. The chains of histones a ...
Answers to Exam Practice Questions 1. Mitosis produces two
... enzyme to produce pigment can control the color of a flower. Another gene could control the production of red blood cells. 18. Most mutations have little to no effect on the individual, however mutations that cause drastic changes in the protein structure or the gene activity can result in genetic d ...
... enzyme to produce pigment can control the color of a flower. Another gene could control the production of red blood cells. 18. Most mutations have little to no effect on the individual, however mutations that cause drastic changes in the protein structure or the gene activity can result in genetic d ...
Genetics Unit Test
... 32. In RNA the base thymine is replaced with what base? a. Protein c. Cytosine b. Uracil d. Adenine 33. Each set of three bases is a code for a. a specific cell. c. a specific ribosome. b. a specific chromosome. d. a specific amino acid. 34. The first step in making a protein is a. RNA copying DNA. ...
... 32. In RNA the base thymine is replaced with what base? a. Protein c. Cytosine b. Uracil d. Adenine 33. Each set of three bases is a code for a. a specific cell. c. a specific ribosome. b. a specific chromosome. d. a specific amino acid. 34. The first step in making a protein is a. RNA copying DNA. ...
Old exam 2 from 2002
... was responsible for inheritance, used radiolabeled sulfur and phosphorus that tagged either protein or nucleic acid in separate experiments. They used a virus of E. coli called a: ...
... was responsible for inheritance, used radiolabeled sulfur and phosphorus that tagged either protein or nucleic acid in separate experiments. They used a virus of E. coli called a: ...
Chapter_3ol2
... parts of genes, called exons, are actually transcribed into mRNA (most of the nucleotide sequences in genes are not expressed during protein synthesis. Some noncoding sequences, called introns, are initially transcribed into mRNA and then clipped out. ...
... parts of genes, called exons, are actually transcribed into mRNA (most of the nucleotide sequences in genes are not expressed during protein synthesis. Some noncoding sequences, called introns, are initially transcribed into mRNA and then clipped out. ...
File
... • 2. Frameshift mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA – This would cause every codon to be wrong from that point on in protein coding – Example: • THE CAT ATE THE FAT RAT • THE ATA TET HEF ATR ATT ...
... • 2. Frameshift mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA – This would cause every codon to be wrong from that point on in protein coding – Example: • THE CAT ATE THE FAT RAT • THE ATA TET HEF ATR ATT ...
genetics heredity test ANSWERS
... Unit of heredity that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and codes for the inherited trait ...
... Unit of heredity that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and codes for the inherited trait ...
Hypertrichosis Sex Linked
... family have varying degrees of the disease? • Female humans inherit two X chromosomes; only one is active in each cell. • The other X chromosome becomes inactivated during embryogenesis via the process of X inactivation – Also call lyonization. • The inactivated X is called a Barr Body. • Selection ...
... family have varying degrees of the disease? • Female humans inherit two X chromosomes; only one is active in each cell. • The other X chromosome becomes inactivated during embryogenesis via the process of X inactivation – Also call lyonization. • The inactivated X is called a Barr Body. • Selection ...
Hypertrichosis
... family have varying degrees of the disease? • Female humans inherit two X chromosomes; only one is active in each cell. • The other X chromosome becomes inactivated during embryogenesis via the process of X inactivation – Also call lyonization. • The inactivated X is called a Barr Body. • Selection ...
... family have varying degrees of the disease? • Female humans inherit two X chromosomes; only one is active in each cell. • The other X chromosome becomes inactivated during embryogenesis via the process of X inactivation – Also call lyonization. • The inactivated X is called a Barr Body. • Selection ...
Airgas template
... While each chromosome contains the same genetic material, the same genes are not activated in every cell. For example, if a gene responsible for a digestive enzyme were to be induced in the lung, the result would be digestion of lung tissue, which would result in ...
... While each chromosome contains the same genetic material, the same genes are not activated in every cell. For example, if a gene responsible for a digestive enzyme were to be induced in the lung, the result would be digestion of lung tissue, which would result in ...
Key Terms Cell Reproduction
... 2. What structure in a cell’s nucleus holds the hereditary information? 3. term for the joining of an egg and sperm 4. the sections of DNA that contain instructions for producing specific proteins 5. What are male sex cells called? 7. the term for any permanent change in a gene or chromosome 8. the ...
... 2. What structure in a cell’s nucleus holds the hereditary information? 3. term for the joining of an egg and sperm 4. the sections of DNA that contain instructions for producing specific proteins 5. What are male sex cells called? 7. the term for any permanent change in a gene or chromosome 8. the ...
Assignment #1
... pairs of chromosomes(4) separate and segregate(5) randomly during cell division to produce gametes(6) containing one chromosome of each type. b. Only certain cells in a multicellular(7) organism undergo meiosis. c. Random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele(8) wi ...
... pairs of chromosomes(4) separate and segregate(5) randomly during cell division to produce gametes(6) containing one chromosome of each type. b. Only certain cells in a multicellular(7) organism undergo meiosis. c. Random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele(8) wi ...
File
... • Males - XY Females - XX • Comment - The X and Y chromosomes are a homologous pair, but only for a ...
... • Males - XY Females - XX • Comment - The X and Y chromosomes are a homologous pair, but only for a ...
Name - Piscataway High School
... Recessive – the allele that is only expressed when two copies are present Answer the following questions in complete sentences. How are the terms genes, locus and allele related? All have something to do with a particular segment of DNA, or nucleotides. A gene is a region of DNA, a series of nucleo ...
... Recessive – the allele that is only expressed when two copies are present Answer the following questions in complete sentences. How are the terms genes, locus and allele related? All have something to do with a particular segment of DNA, or nucleotides. A gene is a region of DNA, a series of nucleo ...
Glossary of Medical Terms
... abnormal accumulation of substances within the body and can lead to severe health problems in affected dogs. Melanin A natural substance that gives color (pigment) to hair, skin, and the iris of the eye Metabolic Acidosis Occurs when the body produces too much acid, or when the kidneys are not ...
... abnormal accumulation of substances within the body and can lead to severe health problems in affected dogs. Melanin A natural substance that gives color (pigment) to hair, skin, and the iris of the eye Metabolic Acidosis Occurs when the body produces too much acid, or when the kidneys are not ...
BIOLOGY - San Marcos Unified School District
... • Gametes are Haploid (N) which means they half the number of chromosomes as our somatic (regular body) cells which are diploid (2N) ...
... • Gametes are Haploid (N) which means they half the number of chromosomes as our somatic (regular body) cells which are diploid (2N) ...
Meiosis Review - Northern Highlands
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
OCR Biology B - Centre of the Cell
... (b) gene mutations. To include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anaemia. ...
... (b) gene mutations. To include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anaemia. ...
The DNA connection - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism’s cells. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits of an organism. Genes and DNA: recall; chromosomes are mostly DNA. DNA has four different nitrogen basis (A adenine, T thymine, ...
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism’s cells. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits of an organism. Genes and DNA: recall; chromosomes are mostly DNA. DNA has four different nitrogen basis (A adenine, T thymine, ...
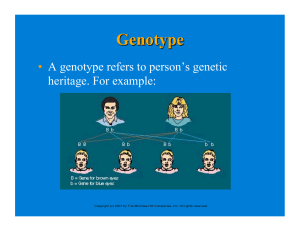
• A genotype refers to person`s genetic heritage. For example:
... • Recessive genes exert influence only if two genes of a pair are recessive. ...
... • Recessive genes exert influence only if two genes of a pair are recessive. ...
Document
... grain stainability, using the Belling agent, revealed only a slight reduction in vitality of the tetraploid lines (87.9%-94.6%) as compared with the initial diploid line (98.4%). Therefore we may have to look to megas por ogenes i s or to abnormalities in the zygotic phase or the e mhryo forming sta ...
... grain stainability, using the Belling agent, revealed only a slight reduction in vitality of the tetraploid lines (87.9%-94.6%) as compared with the initial diploid line (98.4%). Therefore we may have to look to megas por ogenes i s or to abnormalities in the zygotic phase or the e mhryo forming sta ...
Genetics Unit Test
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13. X and Y chromosomes determine gender. For example, XX is female. XY is male. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14. ...
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13. X and Y chromosomes determine gender. For example, XX is female. XY is male. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14. ...
Genetics Unit Test
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13. X and Y chromosomes determine gender. For example, XX is female. XY is male. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14. ...
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13. X and Y chromosomes determine gender. For example, XX is female. XY is male. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14. ...
Slide 1
... of reproductive cells (meiosis I) so that each cell gets one of the factors. Dominance: Sometimes one factor dominates the other factor. A dominant trait masks/suppresses the alternative (recessive) trait for a particular feature. Conversely, a recessive trait is masked or suppressed by the dominant ...
... of reproductive cells (meiosis I) so that each cell gets one of the factors. Dominance: Sometimes one factor dominates the other factor. A dominant trait masks/suppresses the alternative (recessive) trait for a particular feature. Conversely, a recessive trait is masked or suppressed by the dominant ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.