Energy Conversion Quiz Answer Key
... 3. How does the law in question 2 apply to energy conversion? When energy changes from one form to another, the total amount of energy remains the same because energy cannot be created or destroyed. ...
... 3. How does the law in question 2 apply to energy conversion? When energy changes from one form to another, the total amount of energy remains the same because energy cannot be created or destroyed. ...
Energy Worksheet
... 5. The scientific rule that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed is called the Law of ________. 6. The movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves is ________ 7. The energy of position – such as a rock on a hill is __________ energy. 8. The movement of objects and substa ...
... 5. The scientific rule that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed is called the Law of ________. 6. The movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves is ________ 7. The energy of position – such as a rock on a hill is __________ energy. 8. The movement of objects and substa ...
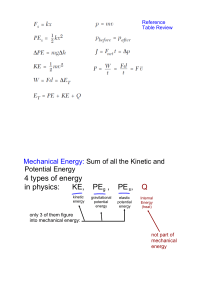
4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PEs, Q
... What is its kinetic energy just as it reaches the ground? ...
... What is its kinetic energy just as it reaches the ground? ...
Energy Transformations
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
ENERGY
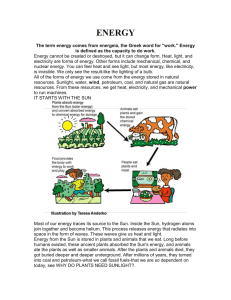
... ENERGY The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can ...
... ENERGY The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can ...
Energy Notes
... Convection - Transfer of heat in a fluid through currents. Conductor - A substance that conducts energy well. Insulator - Does not conduct energy well. Temperature - The measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. Specific Heat - The amount of heat necessary to raise the t ...
... Convection - Transfer of heat in a fluid through currents. Conductor - A substance that conducts energy well. Insulator - Does not conduct energy well. Temperature - The measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. Specific Heat - The amount of heat necessary to raise the t ...
Unit 9 Test Review – Work and Energy
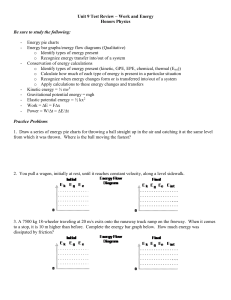
... c. How does the acceleration of B compare to that of A? 5. A 50.0 kg diver steps off a diving board and drops straight down into the water. The water provides an average net force of resistance of 1500 N to the diver’s fall. If the diver comes to rest 5.0 m below the water’s surface, what is the tot ...
... c. How does the acceleration of B compare to that of A? 5. A 50.0 kg diver steps off a diving board and drops straight down into the water. The water provides an average net force of resistance of 1500 N to the diver’s fall. If the diver comes to rest 5.0 m below the water’s surface, what is the tot ...
2nd 6 Weeks - Forms of Energy, Circuits and Force
... Energy – what is needed to do work or cause change ...
... Energy – what is needed to do work or cause change ...
Physical Science Final Exam Study Guide Part 2
... 49. Energy that travels through space in the form of waves 50. Energy stored in chemical bonds 51. The ability to do work 52. Energy associated with motion and position 53. Energy associated with electrical charge 54. Energy that depends on an object’s height (Ch 16) 55. Heat flows spontaneously fro ...
... 49. Energy that travels through space in the form of waves 50. Energy stored in chemical bonds 51. The ability to do work 52. Energy associated with motion and position 53. Energy associated with electrical charge 54. Energy that depends on an object’s height (Ch 16) 55. Heat flows spontaneously fro ...
File
... (that is, heat other things up or burn things) from the wood. The wood is the source of the energy. Plants make their food by photosynthesis. The energy they need comes from the Sun. ...
... (that is, heat other things up or burn things) from the wood. The wood is the source of the energy. Plants make their food by photosynthesis. The energy they need comes from the Sun. ...
Energy - Wsfcs
... energy is moving electric charges that produce electricity or electrical energy. This is found in batteries, or power lines used to run such devices as computers , radios or lights. ...
... energy is moving electric charges that produce electricity or electrical energy. This is found in batteries, or power lines used to run such devices as computers , radios or lights. ...
Weekly Overview - School District 27J
... Briefly describe the Law of Conservation of Mass (you are more than welcome to use your notes and textbook to help you). Based on your description, explain what you believe the Law of Conservation of Energy is. Support your answer with a real world example. ...
... Briefly describe the Law of Conservation of Mass (you are more than welcome to use your notes and textbook to help you). Based on your description, explain what you believe the Law of Conservation of Energy is. Support your answer with a real world example. ...
Vocabulary for Energy Unit
... Chemical energy – energy stored in between smaller particles holding them together to make larger ones, i.e. “food” energy Conduction - a way to transfer energy directly from one object to another because the particles bump into each other, particles do not change location they vibrate in place tran ...
... Chemical energy – energy stored in between smaller particles holding them together to make larger ones, i.e. “food” energy Conduction - a way to transfer energy directly from one object to another because the particles bump into each other, particles do not change location they vibrate in place tran ...
Week 3 CCA Review
... to be pulled into wire), and good conductors of heat and electricity. 2. Nonmetals are located primarily to the right of the stair step line on the Periodic Table. Nonmetals are usually dull, brittle, not malleable or ductile, and poor conductors. 3. Metalloids are elements that have some properties ...
... to be pulled into wire), and good conductors of heat and electricity. 2. Nonmetals are located primarily to the right of the stair step line on the Periodic Table. Nonmetals are usually dull, brittle, not malleable or ductile, and poor conductors. 3. Metalloids are elements that have some properties ...
Law of the Conservation of Energy
... batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned into kinetic energy when you start running around or into potential energy when you climb up to the top of the slide and wait before sliding down. Energy cannot be created or d ...
... batteries and gasoline. All of these types of energy interact with one another. The chemical energy from food can be turned into kinetic energy when you start running around or into potential energy when you climb up to the top of the slide and wait before sliding down. Energy cannot be created or d ...
ENERGY and Energy Transformations
... Identify the Energy Transformations Involved in the Human Body Input: • Food (Chemical) • Light (Radiant) • Sound (Sound) ...
... Identify the Energy Transformations Involved in the Human Body Input: • Food (Chemical) • Light (Radiant) • Sound (Sound) ...
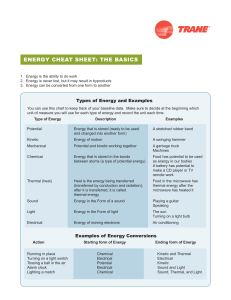
energy CheAt Sheet: the bASiCS
... Types of Energy and Examples You can use this chart to keep track of your baseline data. Make sure to decide at the beginning which unit of measure you will use for each type of energy and record the unit each time. ...
... Types of Energy and Examples You can use this chart to keep track of your baseline data. Make sure to decide at the beginning which unit of measure you will use for each type of energy and record the unit each time. ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... 4. Lots of implications for stopping distances and other aspects of car safety ...
... 4. Lots of implications for stopping distances and other aspects of car safety ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... 4. Lots of implications for stopping distances and other aspects of car safety ...
... 4. Lots of implications for stopping distances and other aspects of car safety ...
L29_AS2_2008_09_KE_GPE_Efficiency
... Kinetic energy : the energy of an object due to movement. No movement no energy! •Which would hurt the most, dropping a feather on your toe or a 1kg lump of iron? •Which would hurt the most, being hit by a slow or fast moving car? Conceptually we can see that K.E. Is related to both mass and speed ...
... Kinetic energy : the energy of an object due to movement. No movement no energy! •Which would hurt the most, dropping a feather on your toe or a 1kg lump of iron? •Which would hurt the most, being hit by a slow or fast moving car? Conceptually we can see that K.E. Is related to both mass and speed ...
Cochise College
... An elevator and cable of mass 2600 kg contains a group of people of mass 500kg. An electric motor of 30% efficiency operates the elevator. (70% of the incoming electrical energy is lost in friction and heat.) If electrical energy costs the hotel 11 cents per kilowatthour, how much electrical energy ...
... An elevator and cable of mass 2600 kg contains a group of people of mass 500kg. An electric motor of 30% efficiency operates the elevator. (70% of the incoming electrical energy is lost in friction and heat.) If electrical energy costs the hotel 11 cents per kilowatthour, how much electrical energy ...