Energy and Forces
... energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or destroyed E2D Describe how matter and energy change from one form to another in living things and in the physical environment. …and take a stab at these new N ...
... energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or destroyed E2D Describe how matter and energy change from one form to another in living things and in the physical environment. …and take a stab at these new N ...
Transparancies for Energy & Momentum Section
... • e.g. raise a 10kg weight 2m • F=mg=10*9.8 N, • W=Fx=98*2=196 Nm=196J ...
... • e.g. raise a 10kg weight 2m • F=mg=10*9.8 N, • W=Fx=98*2=196 Nm=196J ...
Mr. Kelley`s 8th Grade Science – February
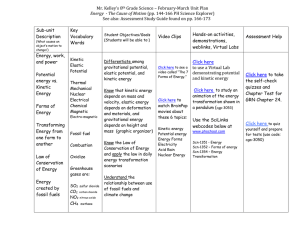
... Mr. Kelley’s 8th Grade Science – February-March Unit Plan Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
... Mr. Kelley’s 8th Grade Science – February-March Unit Plan Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
Ideas about Work and Energy
... this is the dot product) Work can be positive or negative. Positive work increases the energy of an object. Negative work decreases the energy of an object (think of friction on a sliding object) ...
... this is the dot product) Work can be positive or negative. Positive work increases the energy of an object. Negative work decreases the energy of an object (think of friction on a sliding object) ...
How is Work and Power Related? Chapter 5 Work and Power
... energy, power and use the concept of conservation of energy ...
... energy, power and use the concept of conservation of energy ...
Technology Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology
... Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology—Terms and Definitions Biofuels: organic material that can be burned or converted into methane. Biogas: A mixture of methane and carbon dioxide produced by the bacterial decomposition of organic wastes and used as a fuel. Biomass: a type of resource ha ...
... Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology—Terms and Definitions Biofuels: organic material that can be burned or converted into methane. Biogas: A mixture of methane and carbon dioxide produced by the bacterial decomposition of organic wastes and used as a fuel. Biomass: a type of resource ha ...
Work and Energy PPT - Aurora City Schools
... This is the energy that an object possesses due to its position of being stretched or deformed FOR A SPRING (or similar)… EPE= ½ k x2 x = amount of stretch k = the spring constant (a characteristic of the object being stretched) ...
... This is the energy that an object possesses due to its position of being stretched or deformed FOR A SPRING (or similar)… EPE= ½ k x2 x = amount of stretch k = the spring constant (a characteristic of the object being stretched) ...
The Down-Low On Energy
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Problems
... book that is placed on a shelf that is 2.5 meters high? 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcase. The height of each shelf is 1.0 meters, 1.5 meters, and 2.0 meters. 4) If you had a book that had a mass of 2.7 kg and it is sitti ...
... book that is placed on a shelf that is 2.5 meters high? 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcase. The height of each shelf is 1.0 meters, 1.5 meters, and 2.0 meters. 4) If you had a book that had a mass of 2.7 kg and it is sitti ...
Forms of energy
... Fill in the blanks with the words at the bottom of the page. You can use words more than once. 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within ...
... Fill in the blanks with the words at the bottom of the page. You can use words more than once. 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within ...
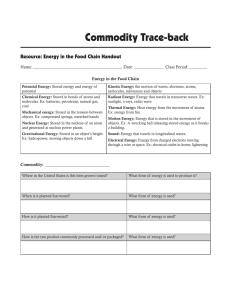
Energy in the Food Chain Handout
... objects. Ex: compressed springs, stretched bands Nuclear Energy: Stored in the nucleus of an atom and generated at nuclear power plants. Gravitational Energy: Stored in an object’s height. Ex: hydropower, moving objects down a hill ...
... objects. Ex: compressed springs, stretched bands Nuclear Energy: Stored in the nucleus of an atom and generated at nuclear power plants. Gravitational Energy: Stored in an object’s height. Ex: hydropower, moving objects down a hill ...
Energy - Griffin School District
... Burning candle: chemical energy is converted into heat and light ...
... Burning candle: chemical energy is converted into heat and light ...
File
... 5. An object’s gravitational potential energy is directly related to… 6. Give three examples of objects with elastic potential energy. 7. A 3-kilogram cat is resting on top of a bookshelf that is 2meters high. What is the cat’s gravitational potential energy relative to the floor? 8. The energy stor ...
... 5. An object’s gravitational potential energy is directly related to… 6. Give three examples of objects with elastic potential energy. 7. A 3-kilogram cat is resting on top of a bookshelf that is 2meters high. What is the cat’s gravitational potential energy relative to the floor? 8. The energy stor ...
Chapter 13 Section 2 pg. 447-451
... stored in the chemical bonds that hold chemical compounds together. ...
... stored in the chemical bonds that hold chemical compounds together. ...
Energy and energy resources
... Other types of energy Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually b ...
... Other types of energy Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually b ...
Additional Energy Terms
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
Advanced Version
... S8P2. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the law of conservation of energy to develop arguments that energy can transform from one form to another within a system. ...
... S8P2. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the law of conservation of energy to develop arguments that energy can transform from one form to another within a system. ...
Energy Transformation Demos
... • Burning coal – chemical to thermal and EM • Phosphorescence (firefly) – chemical to EM • Playing a violin – mechanical to Sound • Turning on a lamp – electrical to thermal and EM • Sun emitting energy- nuclear to EM ...
... • Burning coal – chemical to thermal and EM • Phosphorescence (firefly) – chemical to EM • Playing a violin – mechanical to Sound • Turning on a lamp – electrical to thermal and EM • Sun emitting energy- nuclear to EM ...
Energy - Hudson Falls Central School District
... compared to horses. James Watt expressed the power of his steam engines in horsepower, or the rate at which horses could do work. ...
... compared to horses. James Watt expressed the power of his steam engines in horsepower, or the rate at which horses could do work. ...
Energy - Office Mix
... Energy: Ability to do work Different Types of Energy The Ninja, a roller coaster at Six Flags over Georgia, has a height of 122 ft and a speed of 52 mi/h. The potential energy due to its height changes into kinetic energy of motion. ...
... Energy: Ability to do work Different Types of Energy The Ninja, a roller coaster at Six Flags over Georgia, has a height of 122 ft and a speed of 52 mi/h. The potential energy due to its height changes into kinetic energy of motion. ...
Law of Conservation of Energy
... the law of conservation of energy? A. An object always has the same amount of energy. B. Energy can change between many different forms, such as potential, kinetic, and thermal, but it is ultimately destroyed. C. The total quantity of energy in the universe never changes, it just changes forms. D. T ...
... the law of conservation of energy? A. An object always has the same amount of energy. B. Energy can change between many different forms, such as potential, kinetic, and thermal, but it is ultimately destroyed. C. The total quantity of energy in the universe never changes, it just changes forms. D. T ...
Chemical Energy
... least kinetic energy? When would it have the greatest and the least potential energy? If the potential energy at Y was 30,000 j and the Kinetic energy was 40,000 j, what is the mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your ...
... least kinetic energy? When would it have the greatest and the least potential energy? If the potential energy at Y was 30,000 j and the Kinetic energy was 40,000 j, what is the mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your ...