TOPIC: Energy AIM: What is energy?
... be used for electricity generation. Compressed biogas can also be used as an alternative vehicle fuel. It is a colorless, odorless, inflammable gas. It comprises of methane and carbon dioxide. Biogas is produced when organic matter is broken down by anaerobic bacteria. Bio energy is a major player i ...
... be used for electricity generation. Compressed biogas can also be used as an alternative vehicle fuel. It is a colorless, odorless, inflammable gas. It comprises of methane and carbon dioxide. Biogas is produced when organic matter is broken down by anaerobic bacteria. Bio energy is a major player i ...
Physics Unit 2 Energy Fact Sheet
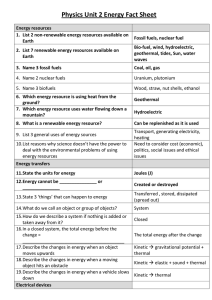
... 8. What is a renewable energy resource? 9. List 3 general uses of energy sources 10.List reasons why science doesn’t have the power to deal with the environmental problems of using energy resources ...
... 8. What is a renewable energy resource? 9. List 3 general uses of energy sources 10.List reasons why science doesn’t have the power to deal with the environmental problems of using energy resources ...
Work and Energy Study Guide - Ms. Gamm
... (2) Relate the work done by a force to the area under a graph of force as a function of position, and calculate this work in the case where the force is a linear function of position. (4) Use the scalar product operation to calculate the work performed by a specified constant force F on an object th ...
... (2) Relate the work done by a force to the area under a graph of force as a function of position, and calculate this work in the case where the force is a linear function of position. (4) Use the scalar product operation to calculate the work performed by a specified constant force F on an object th ...
Ecosystem_concepts_UG_II_SM1
... Ecosystem: Defined area in which a community lives with interactions taking place among the organisms between the community and its nonliving physical environment. ...
... Ecosystem: Defined area in which a community lives with interactions taking place among the organisms between the community and its nonliving physical environment. ...
Energy and Electrical Definitions
... Water Energy Water must be Moving •Hydroelectric Power- dams & rivers •Tidal – vertical movement of tides •Wave – using the up/down motion of waves •Thermal-using the temperature difference of oceans ...
... Water Energy Water must be Moving •Hydroelectric Power- dams & rivers •Tidal – vertical movement of tides •Wave – using the up/down motion of waves •Thermal-using the temperature difference of oceans ...
Chapter 3 - Bakersfield College
... continue spinning about a fixed axis; conservation of angular momentum is the description of the tendency of spinning objects to remain spinning. 1. The greater the mass of an object and the more rapidly it rotates, the greater its angular momentum. 2. The angular momentum of a spinning object also ...
... continue spinning about a fixed axis; conservation of angular momentum is the description of the tendency of spinning objects to remain spinning. 1. The greater the mass of an object and the more rapidly it rotates, the greater its angular momentum. 2. The angular momentum of a spinning object also ...
Potential Energy
... Sound (movement of sound waves) Light (movement of light waves) Magnetic (energy that pulls opposite charges together) Heat (thermal energy) An energy transfer occurs when the energy in one object causes a change in another object (e.g. the energy in a bowling ball will be transferred to the ...
... Sound (movement of sound waves) Light (movement of light waves) Magnetic (energy that pulls opposite charges together) Heat (thermal energy) An energy transfer occurs when the energy in one object causes a change in another object (e.g. the energy in a bowling ball will be transferred to the ...
Study Vocabulary for Objects in Motion
... Note- Work can only be done to a system by an external force +More work that is done by an object, the more energy it exerts. +Since energy is equal to work, the unit for both is the same, the Joule (J). 1 Joule = 1 Newton-mete The amount of work done is the change in the amount of energy that the s ...
... Note- Work can only be done to a system by an external force +More work that is done by an object, the more energy it exerts. +Since energy is equal to work, the unit for both is the same, the Joule (J). 1 Joule = 1 Newton-mete The amount of work done is the change in the amount of energy that the s ...
Chapter 9-Energy Review Sheet Answer Key Section 1 Notes What
... 12. What does the Law of Conservation of Energy state? a. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. 13. Define a closed system and give an example. a. A closed system is a group of objects that transfer energy only to each other. Example-A sun giving light energy to seed to make it grow and converts th ...
... 12. What does the Law of Conservation of Energy state? a. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. 13. Define a closed system and give an example. a. A closed system is a group of objects that transfer energy only to each other. Example-A sun giving light energy to seed to make it grow and converts th ...
Title: Changes in Velocity due to Potential and Kinetic Energy
... energy. Have students determine the kinetic and potential energy of the car. Student Questions for Inquiry: 1. Why is the first hill the highest? (The first hill is the highest to give the car maximum potential energy for conversion to kinetic energy so that the car can have enough energy to complet ...
... energy. Have students determine the kinetic and potential energy of the car. Student Questions for Inquiry: 1. Why is the first hill the highest? (The first hill is the highest to give the car maximum potential energy for conversion to kinetic energy so that the car can have enough energy to complet ...
Study Guide
... Radiant Energy: Energy carried by electromagnetic waves, like light, microwaves, radio waves. Sound Energy: Energy produced by sound vibrations (waves of pressure) Chemical Energy: Energy stored in the chemical bonds of molecules and released during a chemical reaction. Food, batteries, fuel. ...
... Radiant Energy: Energy carried by electromagnetic waves, like light, microwaves, radio waves. Sound Energy: Energy produced by sound vibrations (waves of pressure) Chemical Energy: Energy stored in the chemical bonds of molecules and released during a chemical reaction. Food, batteries, fuel. ...
District Exam for Science Study Guide
... Explain four differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. o Shape (plant = rectangular while animal = circular). o Chloroplasts in plants not animals. o Plants have cell wall but animals do not. o Plants have 1 large central vacuole but animals have many small ones. Explain and describe the ...
... Explain four differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. o Shape (plant = rectangular while animal = circular). o Chloroplasts in plants not animals. o Plants have cell wall but animals do not. o Plants have 1 large central vacuole but animals have many small ones. Explain and describe the ...
Energy Notes - Northside Middle School
... The Law of Conservation of Energy Energy can be neither created nor destroyed by ordinary means. It can only be changed from one form to another. If energy seems to disappear, then consider that energy might have been changed to sound, heat or light All forms of energy can be converted into othe ...
... The Law of Conservation of Energy Energy can be neither created nor destroyed by ordinary means. It can only be changed from one form to another. If energy seems to disappear, then consider that energy might have been changed to sound, heat or light All forms of energy can be converted into othe ...
January 2014: Mid-Year Proficiency Study Guide Chapter 1
... Example: When you are driving in a car and the car comes to a stop your body wants to continue to move forward (inertia), but the seatbelt (unbalanced force) stops you b. Newton’s 2nd Law – law that states that the acceleration of an object is equal to the net force exerted on the object divided b ...
... Example: When you are driving in a car and the car comes to a stop your body wants to continue to move forward (inertia), but the seatbelt (unbalanced force) stops you b. Newton’s 2nd Law – law that states that the acceleration of an object is equal to the net force exerted on the object divided b ...
Section 3.1 - CPO Science
... against each other. • Some of this energy is converted to heat. Name two surfaces creating friction in each picture. ...
... against each other. • Some of this energy is converted to heat. Name two surfaces creating friction in each picture. ...
Types of Energy
... • Chemical energy is energy stored within the chemical bonds in matter. • Chemical energy can be released, for example in batteries or sugar/food, when these substances react to form new substances. Electrical energy • Electrical energy is the energy flowing in an electric circuit. • Sources of elec ...
... • Chemical energy is energy stored within the chemical bonds in matter. • Chemical energy can be released, for example in batteries or sugar/food, when these substances react to form new substances. Electrical energy • Electrical energy is the energy flowing in an electric circuit. • Sources of elec ...
3rd Nine Weeks Study Guide
... What two things do you need to increase to increase the kinetic energy of an object? What is the energy associated with the motion and position of an object? What is an energy transformation? When an object falls what is the energy transformation that is taking place? (What type of energy is being t ...
... What two things do you need to increase to increase the kinetic energy of an object? What is the energy associated with the motion and position of an object? What is an energy transformation? When an object falls what is the energy transformation that is taking place? (What type of energy is being t ...
ENERGY
... Law of Conservation of Energy. b.Explain the relationship between potential and kinetic energy. c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat, light, electricity, mechanical motion, sound) and their characteristics. ...
... Law of Conservation of Energy. b.Explain the relationship between potential and kinetic energy. c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat, light, electricity, mechanical motion, sound) and their characteristics. ...
Introduction to Matter/Describing Matter: States of Matter
... Current is the rate at which a charge passes a given point. (I) The unit is Amps. Static electricity Static electricity is the buildup of electric charges on an object. It’s when objects rub against each other and become a charge. Electromagnetism Electromagnetism is the interaction between electric ...
... Current is the rate at which a charge passes a given point. (I) The unit is Amps. Static electricity Static electricity is the buildup of electric charges on an object. It’s when objects rub against each other and become a charge. Electromagnetism Electromagnetism is the interaction between electric ...
Work and Energy notes
... Accident investigators are aware that a car going 100km/h has 4x the KE it would have at 50km/h. Therefore, it will skid 4x as far when its brakes are locked. Speed limits/braking distances are determined by accounting for this, along with driver’s reaction times. When the brakes of a motorcycle ...
... Accident investigators are aware that a car going 100km/h has 4x the KE it would have at 50km/h. Therefore, it will skid 4x as far when its brakes are locked. Speed limits/braking distances are determined by accounting for this, along with driver’s reaction times. When the brakes of a motorcycle ...
heat-and-temperature-are-not-same-thing
... The particles in liquids and gases can move from place to place. Convection happens when particles with a lot of thermal energy in a liquid or gas move, and take the place of particles with less thermal energy. Thermal energy is transferred from hot places to cold places by convection. ...
... The particles in liquids and gases can move from place to place. Convection happens when particles with a lot of thermal energy in a liquid or gas move, and take the place of particles with less thermal energy. Thermal energy is transferred from hot places to cold places by convection. ...
Energy - Denton ISD
... Energy can be neither created nor destroyed by ordinary means. It can only be converted from one form to another. If energy seems to disappear, then scientists look for it – leading to many important discoveries. ...
... Energy can be neither created nor destroyed by ordinary means. It can only be converted from one form to another. If energy seems to disappear, then scientists look for it – leading to many important discoveries. ...
Negawatt power

Negawatt power is a theoretical unit of power representing an amount of energy (measured in watts) saved. The energy saved is a direct result of energy conservation or increased energy efficiency. The term was coined by the chief scientist of the Rocky Mountain Institute and environmentalist Amory Lovins in 1989, arguing that utility customers don’t want kilowatt-hours of electricity; they want energy services such as hot showers, cold beer, lit rooms, and spinning shafts, which can come more cheaply if electricity is used more efficiently. Lovins felt an international behavioral change was necessary in order to decrease countries' dependence on excessive amounts of energy. The concept of a negawatt could influence a behavioral change in consumers by encouraging them to think about the energy that they spend.A negawatt market can be thought of as a secondary market, in which electricity is allocated from one consumer to another consumer within the energy market. In this market, negawatts could be treated as a commodity. Commodities have the ability to be traded across time and space, which would allow negawatts to be incorporated in the international trading system. Roughly 10% of all U.S. electrical generating capacity is in place to meet the last 1% of demand and there is where the immediate efficiency opportunity exists.On March 15, 2011, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), the agency that regulates the U.S. electrical grid, approved a rule establishing the approach to compensation for demand response resources intended to benefit customers and help improve the operation and competitiveness of organized wholesale energy markets. This means that negawatts produced by reducing electrical use can demand the same market prices as real megawatts of generated electricity.The incentives for a negawatt market include receiving money, reduction of national energy dependency, and the local electricity deregulation within certain nations or states. As for the cost incentive, those who produce negawatts or simply conserve energy can earn money by selling the saved energy. The negawatt market could help nations or states obtain a deregulated electricity system by creating another market to purchase electricity from. The negawatt market also has two main drawbacks. Currently, there is no way to precisely measure the amount of energy saved in negawatts, and electricity providers may not want customers to use less energy due to the loss of profit.