* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ENERGY
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
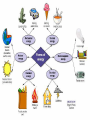
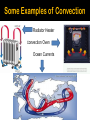
ENERGY S8P2. Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of energy. a.Explain energy transformation in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy. b.Explain the relationship between potential and kinetic energy. c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat, light, electricity, mechanical motion, sound) and their characteristics. What is Energy? In science, energy is the ability to do work. Work is done when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force. The Law of Conservation of Energy Energy CANNOT be created or destroyed, but it CAN change forms. Types of Energy There are 2 main types of energy: Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy **************************************** All forms of energy fall into one of these two categories. There Are Seven Major Forms of Energy Mechanical Energy Mechanical energy is the potential energy and the kinetic energy added together. Sound Energy Sound energy is caused by an object’s vibrations. When an object vibrates, its vibrations transmit through the air so that we can hear it from another location. Chemical Energy Chemical energy is the energy of a compound that changes as its atoms are rearranged. Electrical Energy Electrical energy is the energy of moving electrons. Light Energy Light energy is produced by the vibrations of electrically charged particles. Like sound vibrations, light vibrations cause energy to be transmitted. Thermal Energy Thermal energy is all of the kinetic energy due to random motion of the particles that make up an object. Heat is thermal energy. Nuclear Energy Nuclear energy, the energy that comes from changes in the nucleus of an atom. Fission is when the nucleus of an atom is split apart. Fusion is when the nucleus of two atoms are joined or “fused” together. Also known as light energy. ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS S8P2. Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of energy. d. Describe how heat can be transferred through matter by the collisions of atoms (conduction) or through space (radiation). In a liquid or gas, currents will facilitate the transfer of heat (convection). Thermal Energy or Heat Heat is energy that moves from an object at a higher temperature to an object at a lower temperature. REMEMBER…the less molecules (mass) in a given space (or volume) the less dense it will be. Density=mass/volume Conduction Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy from one substance to another through direct contact. Convection Convection is the transfer of thermal energy by the movement of a liquid or a gas. Some Examples of Convection Radiator Heater Convection Oven Ocean Currents Heat Rises! Convection Currents The vertical movement of air or liquid currents due to temperature variations. Example of Convection in Nature Tempest in a Teapot: How Convection Brews a Storm - YouTube Radiation Radiation is the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves, such as visible light and infrared waves. The Electromagnetic Spectrum