Facial Bones
... Facial Bones Nasal Small Paired bones that fuse to form the bridge of the nose. Lacrimal Paired bones, each about the size of a fingernail. They are the smallest bones in the face. Posterior and lateral to the Nasal bones. Mandible Lower jaw bone. It is the largest and strongest of the facial bones ...
... Facial Bones Nasal Small Paired bones that fuse to form the bridge of the nose. Lacrimal Paired bones, each about the size of a fingernail. They are the smallest bones in the face. Posterior and lateral to the Nasal bones. Mandible Lower jaw bone. It is the largest and strongest of the facial bones ...
The Pelvic Girdle
... Marks of the Ischium: the rough Ischial tuberosity receives the weight of the body when we sit, and the Ischial spine above the lesser sciatic notch is an important anatomical landmark. ...
... Marks of the Ischium: the rough Ischial tuberosity receives the weight of the body when we sit, and the Ischial spine above the lesser sciatic notch is an important anatomical landmark. ...
Table Summarizing Key Features of Cranial and Facial Bones
... These joints hold the bones of the meanings in both anatomy and surgery. skull together. In the context of anatomy, a 'suture' is a type of immovable joint found only between skull bones and consisting of a small amount of connective tissue between the bones. There are several of these joints in the ...
... These joints hold the bones of the meanings in both anatomy and surgery. skull together. In the context of anatomy, a 'suture' is a type of immovable joint found only between skull bones and consisting of a small amount of connective tissue between the bones. There are several of these joints in the ...
Skull
... 1. The 13 immovable facial bones & the moveable mandible bone of the lower jaw form the face; they provide attachments for muscles of mastication & expression (total number of facial bones ...
... 1. The 13 immovable facial bones & the moveable mandible bone of the lower jaw form the face; they provide attachments for muscles of mastication & expression (total number of facial bones ...
Musculoskeletal System Anatomy
... Phalanges = finger and toe bones. Pelvic bone = hip bone, three bones fused. Ischium = lower rear portion, you sit on. Ilium = upper, wing shaped on each side. Pubis = anterior portion of the pelvic bone. Acetabulum = socket in pelvic bone for the head of the femur. Tibia and fibula = lower leg bone ...
... Phalanges = finger and toe bones. Pelvic bone = hip bone, three bones fused. Ischium = lower rear portion, you sit on. Ilium = upper, wing shaped on each side. Pubis = anterior portion of the pelvic bone. Acetabulum = socket in pelvic bone for the head of the femur. Tibia and fibula = lower leg bone ...
Pathology Codes - Museum of London
... The bilateral, symmetrical nature of the new bone plaques observed in the lower legs suggests some kind of systemic infection. It’s possible the changes in the feet may be related to this possible infection. The compact new bone to the anterior vertebrae is suspicious; given the marked retro-auricul ...
... The bilateral, symmetrical nature of the new bone plaques observed in the lower legs suggests some kind of systemic infection. It’s possible the changes in the feet may be related to this possible infection. The compact new bone to the anterior vertebrae is suspicious; given the marked retro-auricul ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR EXAM 1 - Part 1 Students should know terms as
... 24. What are the four main tissue types in the human body? 25. Describe/draw the 9 epithelial tissues. How do their structures relate to their functions? Familiarize yourself with the photomicrographs of each. Where would you find them? 26. What are the 6 types of connective tissue proper and their ...
... 24. What are the four main tissue types in the human body? 25. Describe/draw the 9 epithelial tissues. How do their structures relate to their functions? Familiarize yourself with the photomicrographs of each. Where would you find them? 26. What are the 6 types of connective tissue proper and their ...
Skull notes
... – Joins parietal bone (squamosal suture) – Form parts of sides and base of cranium – External auditory meatus (???) – Mandibular fossae – depressions in the temporal bone that articulate with condyles (???) of the mandible ...
... – Joins parietal bone (squamosal suture) – Form parts of sides and base of cranium – External auditory meatus (???) – Mandibular fossae – depressions in the temporal bone that articulate with condyles (???) of the mandible ...
Anatomical Terms Worksheet
... axis of your body these bones include your ribs sternum skull and spinal column the appendicular skeleton contains the bones of your limbs and the bones which connect your limbs to the axial skeleton 14 Types of bones – Word Match Match the correct terms with their meanings. Place the correct letter ...
... axis of your body these bones include your ribs sternum skull and spinal column the appendicular skeleton contains the bones of your limbs and the bones which connect your limbs to the axial skeleton 14 Types of bones – Word Match Match the correct terms with their meanings. Place the correct letter ...
LT 6 Anatomical Terms
... skull and spinal column the appendicular skeleton contains the bones of your limbs and the bones which connect your limbs to the axial skeleton 14 Types of bones – Word Match Match the correct terms with their meanings. Place the correct letter in the empty column Type of bone ...
... skull and spinal column the appendicular skeleton contains the bones of your limbs and the bones which connect your limbs to the axial skeleton 14 Types of bones – Word Match Match the correct terms with their meanings. Place the correct letter in the empty column Type of bone ...
Skull Bones - Obsessed With Skulls
... • Contains cartilage filled spaces called fontanels that allow for brain growth & compression during birth • Face is smaller in comparison to cranium • Adult’s cranium 1/8 of total body length • Infant’s cranium ¼ of total body length • Frontal bones split • Temporal bone is a ring of bone • Conical ...
... • Contains cartilage filled spaces called fontanels that allow for brain growth & compression during birth • Face is smaller in comparison to cranium • Adult’s cranium 1/8 of total body length • Infant’s cranium ¼ of total body length • Frontal bones split • Temporal bone is a ring of bone • Conical ...
Skull - Dr. Steve W. Altstiel
... • The skull has 22 bones (some doubled), so 14 different named bones. 1. Cranium – part that holds and protects the brain… composed of 8 bones held together by sutures. a. Sutures ...
... • The skull has 22 bones (some doubled), so 14 different named bones. 1. Cranium – part that holds and protects the brain… composed of 8 bones held together by sutures. a. Sutures ...
Common Bone Features: Holes and Depressed Areas
... • Ventral to the parietal bone • Contain middle and inner ear structures which are within the External acoustic meatus. • Form the ______________________ joints with the mandible and zygomatic __________ with the zygomatic bone. ...
... • Ventral to the parietal bone • Contain middle and inner ear structures which are within the External acoustic meatus. • Form the ______________________ joints with the mandible and zygomatic __________ with the zygomatic bone. ...
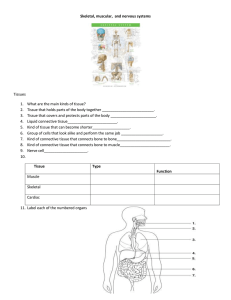
Skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems
... 38. A good source of calcium is (cereals / dairy products). 39. New blood cells are made in the (red / yellow) bone marrow. 40. Yellow marrow is located in (long / short) bones. 41. Bone marrow fills the spaces in the (compact / spongy) bone. 42. Bone gets its food and oxygen from the (periosteum / ...
... 38. A good source of calcium is (cereals / dairy products). 39. New blood cells are made in the (red / yellow) bone marrow. 40. Yellow marrow is located in (long / short) bones. 41. Bone marrow fills the spaces in the (compact / spongy) bone. 42. Bone gets its food and oxygen from the (periosteum / ...
Anatomical Definitions
... As a result, bone is added where needed and removed where it is not In the first year of life, almost 100% of the skeleton is replaced. In adults, remodeling proceeds at about 10% per year An imbalance in the regulation of bone remodeling's two sub‐processes, bone resorption and bone formation, ...
... As a result, bone is added where needed and removed where it is not In the first year of life, almost 100% of the skeleton is replaced. In adults, remodeling proceeds at about 10% per year An imbalance in the regulation of bone remodeling's two sub‐processes, bone resorption and bone formation, ...
Moghadame
... Expanded ends of long bones Exterior is compact bone, and the interior is spongy bone Joint surface is covered with articular (hyaline) cartilage Epiphyseal line separates the diaphysis from the epiphyses ...
... Expanded ends of long bones Exterior is compact bone, and the interior is spongy bone Joint surface is covered with articular (hyaline) cartilage Epiphyseal line separates the diaphysis from the epiphyses ...
Stiffness
... • Scaphoid - most commonly fractured • Carpal tunnel - space between carpal bones and ...
... • Scaphoid - most commonly fractured • Carpal tunnel - space between carpal bones and ...
Skeletal System
... tissues (bone, cartilage, dense connective, blood, nerve) Bone Structure Epiphyses – expanded ends of bones that form joints Hyaline cartilage cover the epiphyses Diaphysis – the shaft of the bone Periosteum (tough layer of connective tissue) covers the bone Compact bone (tightly packed ti ...
... tissues (bone, cartilage, dense connective, blood, nerve) Bone Structure Epiphyses – expanded ends of bones that form joints Hyaline cartilage cover the epiphyses Diaphysis – the shaft of the bone Periosteum (tough layer of connective tissue) covers the bone Compact bone (tightly packed ti ...
Reem A Axial Skeleton
... The bones of the skeleton form an internal framework to support soft tissues, protect vital organs, bear the body’s weight, and help us move. Typically, there are 206 bones in an adult skeleton, although this number varies in some individuals. A larger number of bones are present at birth, but the t ...
... The bones of the skeleton form an internal framework to support soft tissues, protect vital organs, bear the body’s weight, and help us move. Typically, there are 206 bones in an adult skeleton, although this number varies in some individuals. A larger number of bones are present at birth, but the t ...
I. The human skeleton contains 206 named bones which perform a
... c. They are the levers that are pulled upon by skeletal muscles to create movement. d. They store minerals such as calcium (Ca2+) and phosphate (PO42-). e. They are the site of blood cell formation (hematopoiesis). f. They provide storage for triglycerides. II. Bones have an exterior composed of com ...
... c. They are the levers that are pulled upon by skeletal muscles to create movement. d. They store minerals such as calcium (Ca2+) and phosphate (PO42-). e. They are the site of blood cell formation (hematopoiesis). f. They provide storage for triglycerides. II. Bones have an exterior composed of com ...
The Skeletal System
... Bones have their own nerves and blood vessels . The skeletal system’s cell matrix acts as our calcium bank by storing and releasing calcium ions into the blood as needed. Proper levels of calcium ions in the blood are essential to the proper function of the nervous and muscular systems, and bones he ...
... Bones have their own nerves and blood vessels . The skeletal system’s cell matrix acts as our calcium bank by storing and releasing calcium ions into the blood as needed. Proper levels of calcium ions in the blood are essential to the proper function of the nervous and muscular systems, and bones he ...
Bone

A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the vertebral skeleton. Bones support and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals and also enable mobility. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have a complex internal and external structure. They are lightweight yet strong and hard, and serve multiple functions. Mineralized osseous tissue or bone tissue, is of two types – cortical and cancellous and gives it rigidity and a coral-like three-dimensional internal structure. Other types of tissue found in bones include marrow, endosteum, periosteum, nerves, blood vessels and cartilage.Bone is an active tissue composed of different cells. Osteoblasts are involved in the creation and mineralisation of bone; osteocytes and osteoclasts are involved in the reabsorption of bone tissue. The mineralised matrix of bone tissue has an organic component mainly of collagen and an inorganic component of bone mineral made up of various salts.In the human body at birth, there are over 270 bones, but many of these fuse together during development, leaving a total of 206 separate bones in the adult, not counting numerous small sesamoid bones. The largest bone in the body is the thigh-bone (femur) and the smallest is the stapes in the middle ear.