∫
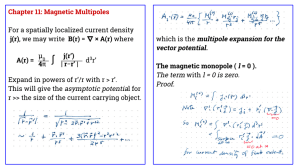
... Chapter 11: Magnetic Multipoles For a spatially localized current density j(r), we may write B(r) = ∇ × A(r) where A(r) = ...
... Chapter 11: Magnetic Multipoles For a spatially localized current density j(r), we may write B(r) = ∇ × A(r) where A(r) = ...
8Jsumm
... A reed switch has two thin pieces of iron inside it. If a magnet is held near the switch, the pieces of iron are magnetised and touch each other. A reed switch can also be switched on using an electromagnet. Any switch that is worked by electricity is called a relay. Relays are used to make things s ...
... A reed switch has two thin pieces of iron inside it. If a magnet is held near the switch, the pieces of iron are magnetised and touch each other. A reed switch can also be switched on using an electromagnet. Any switch that is worked by electricity is called a relay. Relays are used to make things s ...
Unit 6 Magnetism
... • An electromagnet is a temporary magnet made by placing iron inside a current carrying coil of wire • The more the wire is coiled around the iron, it causes a stronger magnetic field • When current flows through the electromagnet it moves toward or away from another magnet, converting electric ener ...
... • An electromagnet is a temporary magnet made by placing iron inside a current carrying coil of wire • The more the wire is coiled around the iron, it causes a stronger magnetic field • When current flows through the electromagnet it moves toward or away from another magnet, converting electric ener ...
Midterm Exam No. 02 (Spring 2015) PHYS 520B: Electromagnetic Theory
... 1. (20 points.) The vector potential for a point magnetic moment m is given by A= ...
... 1. (20 points.) The vector potential for a point magnetic moment m is given by A= ...
Unit 3_electricity and magnetism_97
... that affect current I can describe advantages and disadvantages of series and parallel circuits I can identify what makes an object magnetic I can describe and create an electromagnet ...
... that affect current I can describe advantages and disadvantages of series and parallel circuits I can identify what makes an object magnetic I can describe and create an electromagnet ...
Name: Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday`s Law 1. When
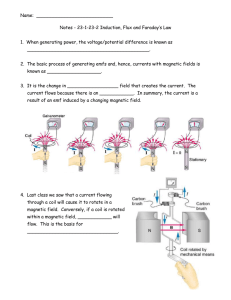
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
... Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday’s Law 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the chan ...
Interactions between Electricity and Magnetism
... Mag/Elec Interactions Electro-magnets If you coil a wire into a helical form (like wrapping a wire around a cylinder) and run a current through it, each circular coil creates a small mag field. The mag field from each coil “adds up” to create what looks like a magnet with a North and South po ...
... Mag/Elec Interactions Electro-magnets If you coil a wire into a helical form (like wrapping a wire around a cylinder) and run a current through it, each circular coil creates a small mag field. The mag field from each coil “adds up” to create what looks like a magnet with a North and South po ...
College Physical Science Chapter 9 Assignment MAGNETIC
... 6. Why is the magnetic field strength inside a current carrying loop of wire greater than the field strength about a straight section of wire? MOTORS- read pg. 215-220 7. What relative direction between a magnetic field & a current-carrying wire results in the greatest force on the wire? In the smal ...
... 6. Why is the magnetic field strength inside a current carrying loop of wire greater than the field strength about a straight section of wire? MOTORS- read pg. 215-220 7. What relative direction between a magnetic field & a current-carrying wire results in the greatest force on the wire? In the smal ...
Magnets exert forces Magnets have two poles
... First magnetic rocks discovered 2000 years ago in “Magnesia” 12th century Chinese used them to make compasses and navigate Today many uses: electric motors and generators ...
... First magnetic rocks discovered 2000 years ago in “Magnesia” 12th century Chinese used them to make compasses and navigate Today many uses: electric motors and generators ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.