Forces on Moving Charges in Magnetic Fields Standards
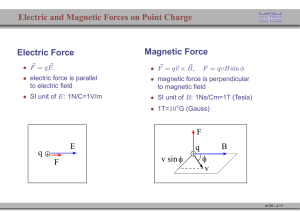
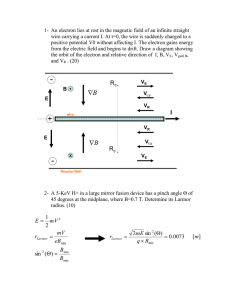
... Students should understand the force experienced by a charged particle in a magnetic field, so they can: 1) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force in terms of q, v, and B and explain why the magnetic force can perform no work. 2) Deduce the direction of a magnetic field from information ...
... Students should understand the force experienced by a charged particle in a magnetic field, so they can: 1) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force in terms of q, v, and B and explain why the magnetic force can perform no work. 2) Deduce the direction of a magnetic field from information ...
Electromagnetism
... The more turns in the coil, the stronger the field The more current flowing through the wire, the stronger the field ...
... The more turns in the coil, the stronger the field The more current flowing through the wire, the stronger the field ...
Magnetism from Electricity
... Magnetism from electricity • In 1820, Danish scientist Han Christian Oersted discovered accidently that when electricity passed through a wire…a magnetic field was created ...
... Magnetism from electricity • In 1820, Danish scientist Han Christian Oersted discovered accidently that when electricity passed through a wire…a magnetic field was created ...
magnetic field - DiMaggio
... Destroying (demagnetizing) a Magnet: hammering it dropping it heating it What would happen if a magnet was cut in half? o You would create 2 smaller magnets with new smaller poles! Electromagnets: electromagnetism: the interaction between electricity and magnetism When electric current f ...
... Destroying (demagnetizing) a Magnet: hammering it dropping it heating it What would happen if a magnet was cut in half? o You would create 2 smaller magnets with new smaller poles! Electromagnets: electromagnetism: the interaction between electricity and magnetism When electric current f ...
Chapter 18
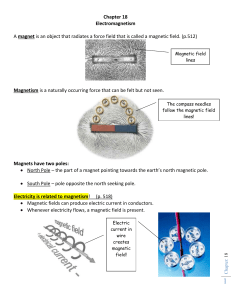
... Magnetism is a naturally occurring force that can be felt but not seen. The compass needles follow the magnetic field lines! ...
... Magnetism is a naturally occurring force that can be felt but not seen. The compass needles follow the magnetic field lines! ...
e-magnet lab day
... solenoid with the iron core can be more than 1,000 times greater than the field inside the solenoid without the iron core. ...
... solenoid with the iron core can be more than 1,000 times greater than the field inside the solenoid without the iron core. ...
EM_INDUCTION
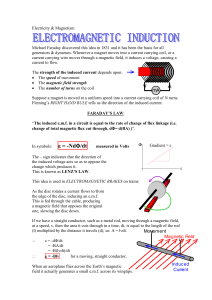
... This is fed through the cable, producing a magnetic field that opposes the original one, slowing the disc down. If we have a straight conductor, such as a metal rod, moving through a magnetic field, at a speed, v, then the area it cuts through in a time, dt, is equal to the length of the rod (l) mul ...
... This is fed through the cable, producing a magnetic field that opposes the original one, slowing the disc down. If we have a straight conductor, such as a metal rod, moving through a magnetic field, at a speed, v, then the area it cuts through in a time, dt, is equal to the length of the rod (l) mul ...
SA1 REVISION WORKSHEET 2
... point directly above it? 9. Draw the patterns of magnetic field lines through and around a current carrying solenoid. What does the magnetic field pattern inside the solenoid indicate? (A)How can this principle be utilized to make an electromagnet? (B) State two ways by which strength of this electr ...
... point directly above it? 9. Draw the patterns of magnetic field lines through and around a current carrying solenoid. What does the magnetic field pattern inside the solenoid indicate? (A)How can this principle be utilized to make an electromagnet? (B) State two ways by which strength of this electr ...
Guided Reading Chapter 22 Section 2 Also do: 539 #1
... 7. What other property (destructive) is increased when you increase the current of an electromagnet? ...
... 7. What other property (destructive) is increased when you increase the current of an electromagnet? ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.