
Sample Final File
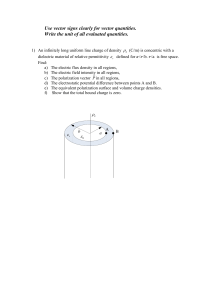
... Write the unit of all evaluated quantities. 1) An infinitely long uniform line charge of density L (C/m) is concentric with a dielectric material of relative permittivity r defined for a
... Write the unit of all evaluated quantities. 1) An infinitely long uniform line charge of density L (C/m) is concentric with a dielectric material of relative permittivity r defined for a
Electromagnet notes
... Magnetism and Electricity When electric current flows through a wire, a ___________________ forms around the wire. ...
... Magnetism and Electricity When electric current flows through a wire, a ___________________ forms around the wire. ...
PHY-ZS-004 Electromagnetic Induction
... • Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion of a magnetic material due to the arrangement of its atoms, particularly its electrons. ...
... • Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion of a magnetic material due to the arrangement of its atoms, particularly its electrons. ...
NAME: Quiz #5: Phys142 1. [4pts] Find the resulting current through
... 1. [4pts] Find the resulting current through R1 in the following circuit: ...
... 1. [4pts] Find the resulting current through R1 in the following circuit: ...
Magnetism and Induction Review
... Magnetism and Induction Review 1. How will a magnet that is free to rotate, like a compass, align itself with earth’s magnetic field? 2. How do opposite poles affect each other? What about like poles? 3. What do you get when you break a magnet in half? 4. Can you ever make it small enough to get jus ...
... Magnetism and Induction Review 1. How will a magnet that is free to rotate, like a compass, align itself with earth’s magnetic field? 2. How do opposite poles affect each other? What about like poles? 3. What do you get when you break a magnet in half? 4. Can you ever make it small enough to get jus ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.













![NAME: Quiz #5: Phys142 1. [4pts] Find the resulting current through](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006404813_1-90fcf53f79a7b619eafe061618bfacc1-300x300.png)








