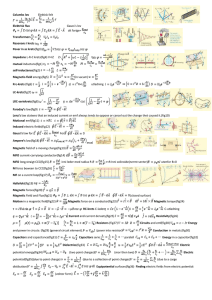
Potential energy of a magnetic dipole in a magnetic field. When a
... When θ = 180! , U has its maximum value ...
... When θ = 180! , U has its maximum value ...
Columbs lov Elektrisk flux Transformers Resonans i krets
... LC-krets(fig(7) LRC-seriekrets(fig8) Faraday’s law(fig9) Lenz’s law statwes that an induced current or emf always tends to oppose or cancel out the change thet caused it.(fig10) Motional emf(fig11) Induced electric fields(fig12) Gauss’s law for ...
... LC-krets(fig(7) LRC-seriekrets(fig8) Faraday’s law(fig9) Lenz’s law statwes that an induced current or emf always tends to oppose or cancel out the change thet caused it.(fig10) Motional emf(fig11) Induced electric fields(fig12) Gauss’s law for ...
Script: How is electricity produced
... What are the most common methods of generating electricity? ...
... What are the most common methods of generating electricity? ...
File - Lagan Physics
... b) The ammeter needle would move first in one direction, then back to zero and then in the opposite direction and back to zero again. It would continue like this as long as the wire was moving in and out of the magnetic field. c) i) The ammeter would still move from one side to the other, but would ...
... b) The ammeter needle would move first in one direction, then back to zero and then in the opposite direction and back to zero again. It would continue like this as long as the wire was moving in and out of the magnetic field. c) i) The ammeter would still move from one side to the other, but would ...
01 - Cobb Learning
... A solenoid is a coil of wire that carries electric current. An electromagnet is a solenoid that has an iron coil. An electromagnet has a stronger magnetic field than the solenoid has. ...
... A solenoid is a coil of wire that carries electric current. An electromagnet is a solenoid that has an iron coil. An electromagnet has a stronger magnetic field than the solenoid has. ...
File - Science with Ms. C
... Know that magnetism is the force of ________________ _____ __________________of magnetic materials. Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that____________ ______ ____________ , a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field af ...
... Know that magnetism is the force of ________________ _____ __________________of magnetic materials. Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that____________ ______ ____________ , a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field af ...
Drill
... An electromagnet is a magnet that consists of a solenoid wrapped around an iron core. A solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying an electric current. ...
... An electromagnet is a magnet that consists of a solenoid wrapped around an iron core. A solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying an electric current. ...
Lecture 16
... A magnetic field is a collection of measurements across a region of space that indicates the relative strength of the magnetic force and the direction of the force on a north pole of a magnet placed there. The symbol for the magnetic field is B. The unit is the Tesla or Gauss. ...
... A magnetic field is a collection of measurements across a region of space that indicates the relative strength of the magnetic force and the direction of the force on a north pole of a magnet placed there. The symbol for the magnetic field is B. The unit is the Tesla or Gauss. ...
Worksheet 8.2 - Magnetic Forces on Wires and Charges
... 1. A particle carrying a charge of 0.50 μC enters a magnetic field of strength 0.045 T, with a velocity of 350 m/s. The velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field. What is the magnetic force acting on the charged particle? 2. A segment of conducting wire 5.0 cm long carrying 5.0 A of current is ...
... 1. A particle carrying a charge of 0.50 μC enters a magnetic field of strength 0.045 T, with a velocity of 350 m/s. The velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field. What is the magnetic force acting on the charged particle? 2. A segment of conducting wire 5.0 cm long carrying 5.0 A of current is ...
EM worksheet
... Both magnets and electromagnets have their attractive features. Electromagnets can be made stronger by adding coils or turns of wire or by adding more electricity. Permanent magnets can actually lose some of their magnetism overtime as a result of being dropped repeatedly. Similar to regular magnets ...
... Both magnets and electromagnets have their attractive features. Electromagnets can be made stronger by adding coils or turns of wire or by adding more electricity. Permanent magnets can actually lose some of their magnetism overtime as a result of being dropped repeatedly. Similar to regular magnets ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.