Proteins
... 20 different amino acids are found as part of proteins (8 amino acids are essential because they cannot be made by people) The 20 amino acids can be linked together in any sequence whatsoever, and in chains of varying lengths. This explains why there are so many proteins. A chain of amino acids is c ...
... 20 different amino acids are found as part of proteins (8 amino acids are essential because they cannot be made by people) The 20 amino acids can be linked together in any sequence whatsoever, and in chains of varying lengths. This explains why there are so many proteins. A chain of amino acids is c ...
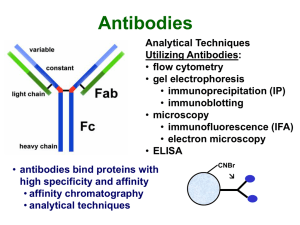
Typical IP Protocol
... 3. Add protein G-agarose, etc 4. Extensively wash 5. Elute with sample buffer 6. SDS-PAGE 7. Detection • protein stain • radioactivity ...
... 3. Add protein G-agarose, etc 4. Extensively wash 5. Elute with sample buffer 6. SDS-PAGE 7. Detection • protein stain • radioactivity ...
Proteins - Downtown Magnets High School
... interpreted from data regarding the concentrations of product or substrate as a function of time. These representations demonstrate the relationship between an enzyme’s activity, the disappearance of substrate, and/ or presence of a competitive ...
... interpreted from data regarding the concentrations of product or substrate as a function of time. These representations demonstrate the relationship between an enzyme’s activity, the disappearance of substrate, and/ or presence of a competitive ...
Name: Practice – 22.5-22.6 Circular Motion in a Magnetic Field
... 105 m/s in a 0.250-T field. What is the separation between their paths when they hit a target after traversing a semicircle? ...
... 105 m/s in a 0.250-T field. What is the separation between their paths when they hit a target after traversing a semicircle? ...
Microscopy Lecture
... • RI of a material a measure of the speed of light in material • RI is the ratio of the velocity of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the specified material • Incident angle (θ1) is related to the refraction angle (θ2) by Snell’s Law • n1sin(θ1)=n2sin(θ2) • Used in calculating focusing powe ...
... • RI of a material a measure of the speed of light in material • RI is the ratio of the velocity of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the specified material • Incident angle (θ1) is related to the refraction angle (θ2) by Snell’s Law • n1sin(θ1)=n2sin(θ2) • Used in calculating focusing powe ...
Student Misconceptions
... molecules are accurate. However, organic molecules are less static than students imagine. Conveniently drawn as linear, monosaccharides usually form rings in aqueous solutions. There may be considerable rotation around single bonds within organic molecules, unless their structure is stabilized by in ...
... molecules are accurate. However, organic molecules are less static than students imagine. Conveniently drawn as linear, monosaccharides usually form rings in aqueous solutions. There may be considerable rotation around single bonds within organic molecules, unless their structure is stabilized by in ...
Lecture #6 - Suraj @ LUMS
... hydrogen are not very reactive. Functional groups: One or more H atoms of the carbon skeleton may be replaced by a functional group. Groups of atoms that have unique chemical and physical properties. Usually a part of molecule that is chemically active. Similar activity from one molecule to another. ...
... hydrogen are not very reactive. Functional groups: One or more H atoms of the carbon skeleton may be replaced by a functional group. Groups of atoms that have unique chemical and physical properties. Usually a part of molecule that is chemically active. Similar activity from one molecule to another. ...
New study illuminates ability of hot
... genetic information contained in the cell's DNA. This information is transferred via molecules known as messenger RNA, in a process called translation. The team was able to identify the exact part of the messenger RNA helix that the RbfA protein acts on during protein construction - it acts to ensur ...
... genetic information contained in the cell's DNA. This information is transferred via molecules known as messenger RNA, in a process called translation. The team was able to identify the exact part of the messenger RNA helix that the RbfA protein acts on during protein construction - it acts to ensur ...
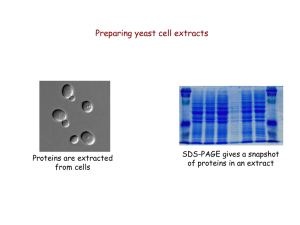
Isolation of proteins
... phenylalanine (PHE), tryptophan (TRY), and proline (PRO) (aromatic amino acid residues). As the Coomassie preferentially binds to select amino acids and changes from a cationic (+) state to an anionic (-) one ...
... phenylalanine (PHE), tryptophan (TRY), and proline (PRO) (aromatic amino acid residues). As the Coomassie preferentially binds to select amino acids and changes from a cationic (+) state to an anionic (-) one ...
Determination of Proteins
... those which contain a non amino acid component in addition to the amino acids. e.g. lipoprotein , phosphoproteins etc. ...
... those which contain a non amino acid component in addition to the amino acids. e.g. lipoprotein , phosphoproteins etc. ...
UNIT:
... Know what colors correspond to visible wavelengths. Identify the regions of the electromagnetic spectrum occupied by gamma, x-rays, UV, visible, IR, and microwaves indicating relative wavelength, frequency, and energy. Know basic principles of how instruments determine results. List and compare the ...
... Know what colors correspond to visible wavelengths. Identify the regions of the electromagnetic spectrum occupied by gamma, x-rays, UV, visible, IR, and microwaves indicating relative wavelength, frequency, and energy. Know basic principles of how instruments determine results. List and compare the ...
Nutrient Notes
... nutrients once considered “bad” such as fats and carbohydrates perform vital functions in the body and if one consumes too many “good” nutrients such as vitamins or minerals there can be harmful results, as well. ...
... nutrients once considered “bad” such as fats and carbohydrates perform vital functions in the body and if one consumes too many “good” nutrients such as vitamins or minerals there can be harmful results, as well. ...
Biochemistry Review Game
... • Each of the following slides will list a characteristic of one (or more) of the biomolecules. • You will need to be the first group to hold up the correct white board in order to get points! ...
... • Each of the following slides will list a characteristic of one (or more) of the biomolecules. • You will need to be the first group to hold up the correct white board in order to get points! ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... 25. What makes up only a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum? 26. Visible light only represents a small band within the entire? What? 27. Which law states that a light beam’s angle of reflection is equal to its angle of incidence? 28. An interaction of light with matter that causes light t ...
... 25. What makes up only a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum? 26. Visible light only represents a small band within the entire? What? 27. Which law states that a light beam’s angle of reflection is equal to its angle of incidence? 28. An interaction of light with matter that causes light t ...
RCT Chapter 7
... α and β forms of the hemiacetal, the bonds at this position are sometimes depicted with wavy lines, as shown here, to indicate that the structure may be either α or β. ...
... α and β forms of the hemiacetal, the bonds at this position are sometimes depicted with wavy lines, as shown here, to indicate that the structure may be either α or β. ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.