Lecture 7 Proteins 1. Which amino acids are considered as acidic
... such requirement is there, as protein are separated according to their molecular size. 5. Which salt is used for precipitation of proteins? Answer: Neutral salts are mainly used for the precipitation of protein as protein doesn’t get denatured and activity is recovered upon redissolving the pellet. ...
... such requirement is there, as protein are separated according to their molecular size. 5. Which salt is used for precipitation of proteins? Answer: Neutral salts are mainly used for the precipitation of protein as protein doesn’t get denatured and activity is recovered upon redissolving the pellet. ...
Amino acids, peptides and proteins
... • The α- carbon is optically active in all amino acids other than glycine. The two possible isomers are termed D and L. All naturally occurring amino acids found in proteins are of the L-configuration • Chirality is derived from the Greek word cheir for ‘hand’– the left and right hands are mirror im ...
... • The α- carbon is optically active in all amino acids other than glycine. The two possible isomers are termed D and L. All naturally occurring amino acids found in proteins are of the L-configuration • Chirality is derived from the Greek word cheir for ‘hand’– the left and right hands are mirror im ...
ppt format
... The next 2 slides show the above argument in graphical form. The 3rd slide shows that atoms other than Hydrogen (HI = neutral hydrogen) show a similar pattern of absorption line strength with temperature, but with each different atom having a different “just right” temperature where its absorption p ...
... The next 2 slides show the above argument in graphical form. The 3rd slide shows that atoms other than Hydrogen (HI = neutral hydrogen) show a similar pattern of absorption line strength with temperature, but with each different atom having a different “just right” temperature where its absorption p ...
Organisms are relatively similar at a molecular level
... in all organisms. Because of this, we should be able to compare the sequences of amino acids in their proteins to gain an understanding about their relationships. How much similarity in protein sequences would you expect between a whale and a fish? A whale and a dog? A dog and a shrimp? A shrimp and ...
... in all organisms. Because of this, we should be able to compare the sequences of amino acids in their proteins to gain an understanding about their relationships. How much similarity in protein sequences would you expect between a whale and a fish? A whale and a dog? A dog and a shrimp? A shrimp and ...
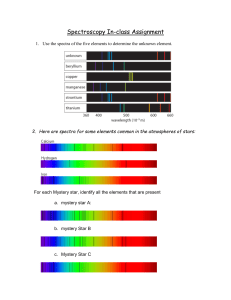
Spectra
... Thermal radiators emit light at all wavelengths Atomic emission occurs only at particular wavelengths ...
... Thermal radiators emit light at all wavelengths Atomic emission occurs only at particular wavelengths ...
AP BIOLOGY Unit 1 – Chemistry and Molecules of Life
... Describe what occurs during a dehydration synthesis reaction? Describe what occurs during a hydrolysis reaction? What are the two types of nucleic acids? What are the monomers of nucleic acids? What are the three components of a nucleic acid monomer? What are the functions of nucleic acids? How do w ...
... Describe what occurs during a dehydration synthesis reaction? Describe what occurs during a hydrolysis reaction? What are the two types of nucleic acids? What are the monomers of nucleic acids? What are the three components of a nucleic acid monomer? What are the functions of nucleic acids? How do w ...
Molecules of Life - Reading molecules of life
... Have you ever tried to put oil in water? They don’t mix. Oil is a type of lipid. Lipids are molecules such as fats, oils, and waxes. The most common lipids in your diet are probably fats and oils. Fats are solid at room temperature, whereas oils are fluid. Animals use fats for long-term energy stora ...
... Have you ever tried to put oil in water? They don’t mix. Oil is a type of lipid. Lipids are molecules such as fats, oils, and waxes. The most common lipids in your diet are probably fats and oils. Fats are solid at room temperature, whereas oils are fluid. Animals use fats for long-term energy stora ...
Biomolecules
... result of functional groups- a configuration of atoms attached to the carbon skeleton • Functional groups maintain chemical properties no matter where they occur • Polar molecules are hydrophilic • Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic • The degree to which organic molecules interact with water affects ...
... result of functional groups- a configuration of atoms attached to the carbon skeleton • Functional groups maintain chemical properties no matter where they occur • Polar molecules are hydrophilic • Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic • The degree to which organic molecules interact with water affects ...
Intro to EMR and Wave Equation
... •In a vacuum, all EMR travel at the speed of light regardless of frequency •19th century physics theory said all waves had to travel through something, the medium that EMR moved was called the ether (a transparent substance that filled all space) •Experiments were done to measure the speed of light ...
... •In a vacuum, all EMR travel at the speed of light regardless of frequency •19th century physics theory said all waves had to travel through something, the medium that EMR moved was called the ether (a transparent substance that filled all space) •Experiments were done to measure the speed of light ...
Proteins
... cholesterol, which help make the plasma membrane of the cell. Recall that there are two forms of cholesterol. HDL and LDL. Which ones are better for you? ...
... cholesterol, which help make the plasma membrane of the cell. Recall that there are two forms of cholesterol. HDL and LDL. Which ones are better for you? ...
topic 4 - biochemistry - part 1 - organic compounds
... **Generally: The order in which the amino acids are linked together, determines the characteristics of the protein molecule. **Based on this sequence, the protein chains twist, turn, & bend into specific 3-D shapes. -The shape of a protein molecule is its: _______________________________________ -T ...
... **Generally: The order in which the amino acids are linked together, determines the characteristics of the protein molecule. **Based on this sequence, the protein chains twist, turn, & bend into specific 3-D shapes. -The shape of a protein molecule is its: _______________________________________ -T ...
Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences
... Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are prone to aggregating and sticking together, preventing them from performing their functions, and even making them toxic. This phenomenon is present in many neurodegenerative diseases ...
... Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are prone to aggregating and sticking together, preventing them from performing their functions, and even making them toxic. This phenomenon is present in many neurodegenerative diseases ...
Substances required for living processes
... When many amino acids join together a long-chain polypeptide is produced. The linking of amino acids in this way takes place during protein synthesis. There are around 20 different amino acids. Organisms join amino acids in different linear sequences to form a variety of polypeptides, then build th ...
... When many amino acids join together a long-chain polypeptide is produced. The linking of amino acids in this way takes place during protein synthesis. There are around 20 different amino acids. Organisms join amino acids in different linear sequences to form a variety of polypeptides, then build th ...
Document
... intermolecular contacts via exposed hydrophobic groups of partially folded proteins • Also help re-fold proteins that have denatured after passing through a membrane’s P-lipid bilayer, e.g., during transport into a mitochondrion (organelle). ...
... intermolecular contacts via exposed hydrophobic groups of partially folded proteins • Also help re-fold proteins that have denatured after passing through a membrane’s P-lipid bilayer, e.g., during transport into a mitochondrion (organelle). ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.