Chapter 8
... We define the weight of something as the force it exerts against the supporting floor or the weighing scale. (Remember the elevator video.) ...
... We define the weight of something as the force it exerts against the supporting floor or the weighing scale. (Remember the elevator video.) ...
timeline
... 600-400 BCE - Pythagoras of Samos sets up a school which rivals the Ionians. Parmenides of Elea, a student, proposes a spherical Earth made from condensed air and divided into five zones. He also sets forth ideas for stars being made of compressed fire and a finite, motionless, and spherical univers ...
... 600-400 BCE - Pythagoras of Samos sets up a school which rivals the Ionians. Parmenides of Elea, a student, proposes a spherical Earth made from condensed air and divided into five zones. He also sets forth ideas for stars being made of compressed fire and a finite, motionless, and spherical univers ...
File
... notation. This is 4.22 light years (4.22 ly). A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. (equaling 9.46 x 1012 km). Book analogy: If the Sun is a pinhead, the next star is another pinhead 35 miles away. This shows that the universe is made mostly of empty space. ...
... notation. This is 4.22 light years (4.22 ly). A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. (equaling 9.46 x 1012 km). Book analogy: If the Sun is a pinhead, the next star is another pinhead 35 miles away. This shows that the universe is made mostly of empty space. ...
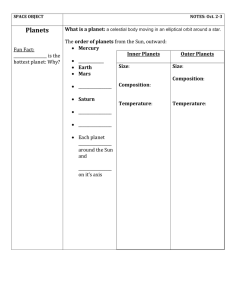
What is a planet
... How long does it takes our Moon to revolve: ______________ How long does it takes our Moon to rotate: _____________________ Planet with the MOST moons: ________________________(63) Planets with the LEAST moons: _____________________________ and ______________________________ (0 moons) ...
... How long does it takes our Moon to revolve: ______________ How long does it takes our Moon to rotate: _____________________ Planet with the MOST moons: ________________________(63) Planets with the LEAST moons: _____________________________ and ______________________________ (0 moons) ...
Motions of the Night Sky - d_smith.lhseducators.com
... From the different sizes of the full moon, ...
... From the different sizes of the full moon, ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... Calculate the maximum altitude of the Sun at any location and time of year using te 2-D Local Horizon Map. Predict where the Sun will be on the Whole Sky Map some number of months after its current position on the ecliptic. Unit 7: The Day Describe the location of sunrise and sunset along the ...
... Calculate the maximum altitude of the Sun at any location and time of year using te 2-D Local Horizon Map. Predict where the Sun will be on the Whole Sky Map some number of months after its current position on the ecliptic. Unit 7: The Day Describe the location of sunrise and sunset along the ...
NORTH SOUTH EAST WEST
... 15. In contrast, conjunction means that two objects appear in the same place in the sky as seen from Earth. Mercury is in conjunction with the Sun on June 21. Planets in conjunction with the sun are not visible. Planet Elongations, Mercury on May 17, Venus on June 3 – The interior planets Mercury an ...
... 15. In contrast, conjunction means that two objects appear in the same place in the sky as seen from Earth. Mercury is in conjunction with the Sun on June 21. Planets in conjunction with the sun are not visible. Planet Elongations, Mercury on May 17, Venus on June 3 – The interior planets Mercury an ...
Regents Review Questions.Unit 2.Astronomy
... 3 Most scientists believe Earth’s Early Archean atmosphere was formed primarily by gases released from (1) stream erosion (3) volcanic eruptions (2) chemical weathering (4) plant transpiration 4 During which month does the Sun appear to rise farthest north of due east for an observer in New York Sta ...
... 3 Most scientists believe Earth’s Early Archean atmosphere was formed primarily by gases released from (1) stream erosion (3) volcanic eruptions (2) chemical weathering (4) plant transpiration 4 During which month does the Sun appear to rise farthest north of due east for an observer in New York Sta ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... – Using a ruler marked in mm, we round to the nearest marking – at most off by half a division, or 0.5 mm – Cite a measurement of 15 mm as 15 0.5 mm to indicate that the real value of the length is likely to be anywhere between ...
... – Using a ruler marked in mm, we round to the nearest marking – at most off by half a division, or 0.5 mm – Cite a measurement of 15 mm as 15 0.5 mm to indicate that the real value of the length is likely to be anywhere between ...
Homework #5 Solutions Astronomy 10, Section 2 due: Wednesday
... 1) Why can the object pictured be bolted in place and used 24 hours a day without adjustment? The satellite dish is used to communicate with a satellite. It can be bolted down if the satellite is always in the same position in the sky. This can be achieved by putting the satellite at an altitude wh ...
... 1) Why can the object pictured be bolted in place and used 24 hours a day without adjustment? The satellite dish is used to communicate with a satellite. It can be bolted down if the satellite is always in the same position in the sky. This can be achieved by putting the satellite at an altitude wh ...
As two continental plates move toward each other, what landforms
... correct because 2 continental masses will push into each other and “crumple” the edges to form mountains ...
... correct because 2 continental masses will push into each other and “crumple” the edges to form mountains ...
Quiz # 2 - Oglethorpe University
... B. the changing distance from the Earth to the Sun. C. the tilt of the Earth’s equatorial plane with respect to its orbit. D. changing temperatures of the Sun. E. retrograde motion of the Sun. 2.) At the time of Copernicus, the fact that parallactic shifts of the brighter stars could NOT be detected ...
... B. the changing distance from the Earth to the Sun. C. the tilt of the Earth’s equatorial plane with respect to its orbit. D. changing temperatures of the Sun. E. retrograde motion of the Sun. 2.) At the time of Copernicus, the fact that parallactic shifts of the brighter stars could NOT be detected ...
Quiz 2 Key - Oglethorpe University
... B. the changing distance from the Earth to the Sun. C. the tilt of the Earth’s equatorial plane with respect to its orbit. D. changing temperatures of the Sun. E. retrograde motion of the Sun. 2.) At the time of Copernicus, the fact that parallactic shifts of the brighter stars could NOT be detected ...
... B. the changing distance from the Earth to the Sun. C. the tilt of the Earth’s equatorial plane with respect to its orbit. D. changing temperatures of the Sun. E. retrograde motion of the Sun. 2.) At the time of Copernicus, the fact that parallactic shifts of the brighter stars could NOT be detected ...
The Earth in Space
... 1. Year - is the time it takes for the earth to make one complete orbit around the Sun. 2. Month - is the time it takes for the Moon to go through one full period of phases. ...
... 1. Year - is the time it takes for the earth to make one complete orbit around the Sun. 2. Month - is the time it takes for the Moon to go through one full period of phases. ...
TOPIC 14 – MOTIONS OF EARTH, MOON, SUN
... 38. What are some examples of matter deflected with respect to Earth’s surface? __________________________________________________ Evidence of Earth’s Revolution Around the Sun 39. How long does it take the Earth to revolve around the sun? _________ 40. Earth’s orbit is a slightly eccentric ellipse. ...
... 38. What are some examples of matter deflected with respect to Earth’s surface? __________________________________________________ Evidence of Earth’s Revolution Around the Sun 39. How long does it take the Earth to revolve around the sun? _________ 40. Earth’s orbit is a slightly eccentric ellipse. ...
Space Unit Test - grade 6 science
... c) Planets and moons are all held in place by gravity ______ d) The moon is the Earth’s closest star ______ e) If it is daytime in Europe (north), the south side of Earth will have night ______ f) The tilt of the Earth’s axis changes as the Earth revolves around the sun ______ g) Everywhere on Earth ...
... c) Planets and moons are all held in place by gravity ______ d) The moon is the Earth’s closest star ______ e) If it is daytime in Europe (north), the south side of Earth will have night ______ f) The tilt of the Earth’s axis changes as the Earth revolves around the sun ______ g) Everywhere on Earth ...
Space
... Size and Distance in Space • In groups create a ‘to scale’ model of the distances between Sun and planets on the ...
... Size and Distance in Space • In groups create a ‘to scale’ model of the distances between Sun and planets on the ...
BABYLON and SUMERIA 3000BC
... recorded their observations about the daily, monthly and yearly position of the stars and planets. They advised the king about how their observations affected the calendar. And they advised the king about how omens seen on earth or in the skies might effect future events. ...
... recorded their observations about the daily, monthly and yearly position of the stars and planets. They advised the king about how their observations affected the calendar. And they advised the king about how omens seen on earth or in the skies might effect future events. ...
AST1001.ch2
... The Greeks knew that the lack of observable parallax could mean one of two things: 1. Stars are so far away that stellar parallax is too small to notice with the naked eye. 2. Earth does not orbit Sun; it is the center of the universe. With rare exceptions, such as Aristarchus, the Greeks rejected ...
... The Greeks knew that the lack of observable parallax could mean one of two things: 1. Stars are so far away that stellar parallax is too small to notice with the naked eye. 2. Earth does not orbit Sun; it is the center of the universe. With rare exceptions, such as Aristarchus, the Greeks rejected ...
Solar Eclipse Box - Hooked on Science
... STEP 5: Tape the 8 ½” x 11” piece of white copy paper on the inside of the other end of the box. Close and tape the box. STEP 6: Cut a hole, big enough for your head, in the bottom of the box. STEP 7: Stand with your back to the sun. Place the box over your head, with the aluminum foil towards the s ...
... STEP 5: Tape the 8 ½” x 11” piece of white copy paper on the inside of the other end of the box. Close and tape the box. STEP 6: Cut a hole, big enough for your head, in the bottom of the box. STEP 7: Stand with your back to the sun. Place the box over your head, with the aluminum foil towards the s ...
Notes on Sun-Earth-Moon (pg. 119)
... Near the equator, sunlight hits earth’s surface directly. Near the poles, however, sunlight hits Earth’s surface at an angle. ...
... Near the equator, sunlight hits earth’s surface directly. Near the poles, however, sunlight hits Earth’s surface at an angle. ...