Everything from Velocity, Seasons, Tides
... Orbital velocity is the speed at which a planetary body moves in its orbit around another body. If orbits were circular, this velocity would be constant. However, from discussion of Kepler’s Laws, we know that planetary bodies orbit the sun (or their planet) in elliptical paths. Therefore, whe ...
... Orbital velocity is the speed at which a planetary body moves in its orbit around another body. If orbits were circular, this velocity would be constant. However, from discussion of Kepler’s Laws, we know that planetary bodies orbit the sun (or their planet) in elliptical paths. Therefore, whe ...
Mon Mar 6, 2017 LEO`S RETURN March, they say, comes in like a
... Taurus the Bull, the Big and Little Dogs, Auriga the Charioteer, and the Gemini, all marked by bright stars. Now look toward the east. Not much there. But toward the eastern horizon, you'll find another star called Regulus, and it represents the heart of the constellation Leo the Lion. There are sev ...
... Taurus the Bull, the Big and Little Dogs, Auriga the Charioteer, and the Gemini, all marked by bright stars. Now look toward the east. Not much there. But toward the eastern horizon, you'll find another star called Regulus, and it represents the heart of the constellation Leo the Lion. There are sev ...
The Solar System and the Universe
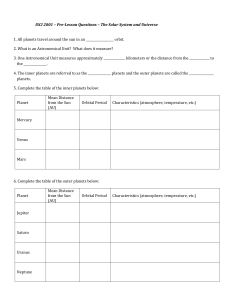
... 8. Energy is released in the core of the Sun through a process called _____________________. When this process is accompanied by high temperature within the sun it is referred to as ___________________________. 9. During thermonuclear fusion, four ________________ nuclei fuse together to form one __ ...
... 8. Energy is released in the core of the Sun through a process called _____________________. When this process is accompanied by high temperature within the sun it is referred to as ___________________________. 9. During thermonuclear fusion, four ________________ nuclei fuse together to form one __ ...
Document
... • The earth was too big to rotate once a day. It would fly apart. • Stars did not show parallaxes during the year, which they must if the earth goes around the sun. This argument was conclusive for most people. The only way out: the stars must be very far away! ...
... • The earth was too big to rotate once a day. It would fly apart. • Stars did not show parallaxes during the year, which they must if the earth goes around the sun. This argument was conclusive for most people. The only way out: the stars must be very far away! ...
March 2011 - Sunderland Astronomical Society
... elongated toward each other. They also interact tidally, keeping just one face toward the other, as the Moon does toward Earth. Such a close binary is “a built-in time bomb,” Drake declares. The continuous loss of mass from the two stars via solar wind carries away some of the double-star system’s a ...
... elongated toward each other. They also interact tidally, keeping just one face toward the other, as the Moon does toward Earth. Such a close binary is “a built-in time bomb,” Drake declares. The continuous loss of mass from the two stars via solar wind carries away some of the double-star system’s a ...
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (c.276-c.196 BC)
... Aristarchus of Samos (c.310-c.230 BC) A Greek mathematician and astronomer who was the first to propose a heliocentric theory, with Earth revolving around the Sun. To explain the lack of observed stellar parallax, he argued that the stars must lie very far away. However, his new scheme for the Solar ...
... Aristarchus of Samos (c.310-c.230 BC) A Greek mathematician and astronomer who was the first to propose a heliocentric theory, with Earth revolving around the Sun. To explain the lack of observed stellar parallax, he argued that the stars must lie very far away. However, his new scheme for the Solar ...
Test #1
... 27) A shift in the direction of an object caused by a change in the position of an observer is called a) parallax, b) precession, c) the Coriolis effect, d) epicycle motion 28) The angular distance of an object from the horizon is its a) latitude, b) declination, c) altitude, d) right ascension 29) ...
... 27) A shift in the direction of an object caused by a change in the position of an observer is called a) parallax, b) precession, c) the Coriolis effect, d) epicycle motion 28) The angular distance of an object from the horizon is its a) latitude, b) declination, c) altitude, d) right ascension 29) ...
key
... universe – everything that exists telescope – a device that collects light to make distant objects appear closer and larger astronomer – someone who observes or studies the universe refraction – the bending of waves as they go from one substance to another reflection – the bouncing of waves off a su ...
... universe – everything that exists telescope – a device that collects light to make distant objects appear closer and larger astronomer – someone who observes or studies the universe refraction – the bending of waves as they go from one substance to another reflection – the bouncing of waves off a su ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 14. Compare the effects of geocentric parallax and refraction. 15. Write notes on calenders. 16. Discuss the different phases of moon using a formula. 17. Explain how a lunar eclipse is caused. 18. Write notes on comet. SECTION – C Answer any TWO questions: 2 x 20 = 40 19. a) Discuss the horizontal ...
... 14. Compare the effects of geocentric parallax and refraction. 15. Write notes on calenders. 16. Discuss the different phases of moon using a formula. 17. Explain how a lunar eclipse is caused. 18. Write notes on comet. SECTION – C Answer any TWO questions: 2 x 20 = 40 19. a) Discuss the horizontal ...
Early Astronomy and Gravity
... 1. Planetary orbits are ellipses (and NOT circles), with the Sun at one focus (nothing at the other focus) 2. A line between the Sun and a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times 3. The square of a planet’s orbital period is proportional to the cube of its semimajor axis P2 ∝ R3 or ...
... 1. Planetary orbits are ellipses (and NOT circles), with the Sun at one focus (nothing at the other focus) 2. A line between the Sun and a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times 3. The square of a planet’s orbital period is proportional to the cube of its semimajor axis P2 ∝ R3 or ...
Grade 5 Science Pacing Guide 2015-2016 Quarter 2
... 5.2.2 Observe and use pictures to record how the sun appears to move across the sky in the same general way every day but rises and sets in different places as the seasons change. Big Idea: Shadows form when sunshine is blocked by a solid object and shadows change depending on the position of the su ...
... 5.2.2 Observe and use pictures to record how the sun appears to move across the sky in the same general way every day but rises and sets in different places as the seasons change. Big Idea: Shadows form when sunshine is blocked by a solid object and shadows change depending on the position of the su ...
The Solar System
... The Sun is a yellow star around which all the planets in our solar system orbit. Our Sun is not unique. It is one of billions of stars with orbiting planets throughout the universe. It is composed mostly of hydrogen gas and helium. The Sun provides heat and light for Earth and the other planets in o ...
... The Sun is a yellow star around which all the planets in our solar system orbit. Our Sun is not unique. It is one of billions of stars with orbiting planets throughout the universe. It is composed mostly of hydrogen gas and helium. The Sun provides heat and light for Earth and the other planets in o ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... a. North Celestial Pole. b. South Celestial Pole. c. Celestial Equator. d. Zodiac. 12. An imaginary sphere of infinite extent with Earth at its center on which the stars, planets, and other heavenly bodies appear to be located is known as the a. Zodiac. b. celestial sphere. c. atmosphere. d. lithosp ...
... a. North Celestial Pole. b. South Celestial Pole. c. Celestial Equator. d. Zodiac. 12. An imaginary sphere of infinite extent with Earth at its center on which the stars, planets, and other heavenly bodies appear to be located is known as the a. Zodiac. b. celestial sphere. c. atmosphere. d. lithosp ...
EarthSunMoon_QuestionSheet-LA
... The Moon is roughly ________________________ and is a lot smaller than the Earth. The Moon is about ________________________ km in diameter. How does long does it take for the Moon Earth to orbit around the Earth? The Moon is a natural satellite and travels around the Earth once every ______________ ...
... The Moon is roughly ________________________ and is a lot smaller than the Earth. The Moon is about ________________________ km in diameter. How does long does it take for the Moon Earth to orbit around the Earth? The Moon is a natural satellite and travels around the Earth once every ______________ ...
Earth in Space - 7-8WMS
... Earth revolves around the sun in a near-circular path, explaining cyclical phenomena such as seasons and changes in visible star patterns (constellations.) ...
... Earth revolves around the sun in a near-circular path, explaining cyclical phenomena such as seasons and changes in visible star patterns (constellations.) ...
Word Pro - Smvocab
... Angular Diameter - the apparent size of celestial objects measured by angle in degrees. Apogee - that point in the orbit of the moon or a planet which is most distant from the earth. Aristotle - one of the world's greatest thinkers and scientific investigators from ancient Greece. Astronomy - one of ...
... Angular Diameter - the apparent size of celestial objects measured by angle in degrees. Apogee - that point in the orbit of the moon or a planet which is most distant from the earth. Aristotle - one of the world's greatest thinkers and scientific investigators from ancient Greece. Astronomy - one of ...
Galileo`s telescopes Galileo (1564
... Two high tides per 24 hrs 50 mins Tidal component caused by the Sun, resulting in spring and neap tides according as the effect of the Sun adds to that of the Moon or not The Earth’s rotation period is slowing, giving the Moon more energy. The Moon is receding. Eventually, a day will be as lon ...
... Two high tides per 24 hrs 50 mins Tidal component caused by the Sun, resulting in spring and neap tides according as the effect of the Sun adds to that of the Moon or not The Earth’s rotation period is slowing, giving the Moon more energy. The Moon is receding. Eventually, a day will be as lon ...
Chapter-08
... If you double the distance between m1 and m2, the gravitational force on m2 1. Increases by 2 2. Increases by 4 3. Decreases by 1/2 4. Decreases by 1/4 5. Stays the same ...
... If you double the distance between m1 and m2, the gravitational force on m2 1. Increases by 2 2. Increases by 4 3. Decreases by 1/2 4. Decreases by 1/4 5. Stays the same ...
Solar System Teacher Notes
... The moon revolves around the Earth (not the sun). It takes about a month for the moon to complete one revolution. During this orbit around the Earth, the shape of the moon appears to change. We call that the phases of the moon. The moon is called a satellite. The half of the moon that faces the sun ...
... The moon revolves around the Earth (not the sun). It takes about a month for the moon to complete one revolution. During this orbit around the Earth, the shape of the moon appears to change. We call that the phases of the moon. The moon is called a satellite. The half of the moon that faces the sun ...
Celestial Sphere - Otterbein University
... • Stars that appear to be close are grouped together into constellations since antiquity • Officially 88 constellations (with strict boundaries for classification of objects) ...
... • Stars that appear to be close are grouped together into constellations since antiquity • Officially 88 constellations (with strict boundaries for classification of objects) ...
Astronomy Quiz 2
... b. Terrestrial planets d. Rocky planets 12. Due to solar winds, the tail of a comet usually faces a. away from the Earth. c. toward the Earth. b. toward the Sun. d. away from the Sun. 13. Which planetary body has the GREATEST gravitational pull? a. Jupiter c. The moon b. Neptune d. Earth 14. The Sun ...
... b. Terrestrial planets d. Rocky planets 12. Due to solar winds, the tail of a comet usually faces a. away from the Earth. c. toward the Earth. b. toward the Sun. d. away from the Sun. 13. Which planetary body has the GREATEST gravitational pull? a. Jupiter c. The moon b. Neptune d. Earth 14. The Sun ...
PHASES OF THE MOON
... The full Moon has the Earth between the Sun and the Moon. The full Moon rises at sunset, is highest in the sky at midnight, and sets at sunrise. During a full Moon, the maria (light areas) and the craters (the dark areas) are easy to see. The last quarter (3rd quarter), the position of the Sun, Moon ...
... The full Moon has the Earth between the Sun and the Moon. The full Moon rises at sunset, is highest in the sky at midnight, and sets at sunrise. During a full Moon, the maria (light areas) and the craters (the dark areas) are easy to see. The last quarter (3rd quarter), the position of the Sun, Moon ...