Astronomy Study Guide Review
... Equinox- latin for “equal nights” Vernal Equinox- Spring- March 20th Autumnal Equinox- Fall- Sept. 22nd Center of Sun is in the same plane as the Earth’s equator. ...
... Equinox- latin for “equal nights” Vernal Equinox- Spring- March 20th Autumnal Equinox- Fall- Sept. 22nd Center of Sun is in the same plane as the Earth’s equator. ...
Universal Gravitation
... If a falling object and the moon are acted on by the same force, the force gets weaker as the square of the distance. This is an inverse square law: a = C / r2. ...
... If a falling object and the moon are acted on by the same force, the force gets weaker as the square of the distance. This is an inverse square law: a = C / r2. ...
Stars and Moon Summative Review
... What is the difference between a blue shift and a red shift? ...
... What is the difference between a blue shift and a red shift? ...
Bad Astronomy
... attraction than the moon, the moon's relative nearness to the earth makes its gravitational pull more than twice as effective as the sun's. ...
... attraction than the moon, the moon's relative nearness to the earth makes its gravitational pull more than twice as effective as the sun's. ...
hw1
... Our solar system consists of the sun (a star), nine planets and various other heavenly bodies like satellites (e.g. moon), comets and asteroids. We are part of the Milky Way galaxy. It is a spiral galaxy, about 75,000 light years in diameter and consists of billions of stars along with gas and dust. ...
... Our solar system consists of the sun (a star), nine planets and various other heavenly bodies like satellites (e.g. moon), comets and asteroids. We are part of the Milky Way galaxy. It is a spiral galaxy, about 75,000 light years in diameter and consists of billions of stars along with gas and dust. ...
Space Vocabulary - Primary Grades Class Page
... A small, frozen mass of dust and gas revolving around the sun. ...
... A small, frozen mass of dust and gas revolving around the sun. ...
Motion of the Celestial Bodies
... the Sun, but it is also responsible for all other orbiting bodies (moon around planets, Comets-Sun, Galaxies turn) Orbit and the force of gravity There is a force of attraction between all objects with mass called the gravitational force. The greater the mass of an object the greater its gravitation ...
... the Sun, but it is also responsible for all other orbiting bodies (moon around planets, Comets-Sun, Galaxies turn) Orbit and the force of gravity There is a force of attraction between all objects with mass called the gravitational force. The greater the mass of an object the greater its gravitation ...
Name
... Describe the following astronomers’ theories: Pythagoras - ____________________________________________________________________________ Aristotle - ______________________________________________________________________________ Ptolemy - _______________________________________________________________ ...
... Describe the following astronomers’ theories: Pythagoras - ____________________________________________________________________________ Aristotle - ______________________________________________________________________________ Ptolemy - _______________________________________________________________ ...
Quarter 3 Benchmark Study Guide w/ Answer Key
... 10. Where do the lengths of daylight change the most over the year? At the poles 11. Why does a person on Earth always see the same side of the Moon? The Moon turns on its axis and orbits Earth in the same amount of time. 12. The lunar highlands have many round features called impact craters 13. The ...
... 10. Where do the lengths of daylight change the most over the year? At the poles 11. Why does a person on Earth always see the same side of the Moon? The Moon turns on its axis and orbits Earth in the same amount of time. 12. The lunar highlands have many round features called impact craters 13. The ...
introduction to astronomy phys 271
... The Sky – Celestial Sphere • North and South Celestial Poles • The Celestial Equator ...
... The Sky – Celestial Sphere • North and South Celestial Poles • The Celestial Equator ...
Study Guide for Earth/ Space Science Test 1. Rotation – The Earth
... 5. Seasons – opposite in hemispheres and caused by the tilt toward or away from the sun and the direct angle of sunlight hitting the area. Also caused by revolution. 6. Lunar – Moon – natural satellite – moon cycle is about 28 days long. Moon means month. Be able to identify phases of moon 7. Solar ...
... 5. Seasons – opposite in hemispheres and caused by the tilt toward or away from the sun and the direct angle of sunlight hitting the area. Also caused by revolution. 6. Lunar – Moon – natural satellite – moon cycle is about 28 days long. Moon means month. Be able to identify phases of moon 7. Solar ...
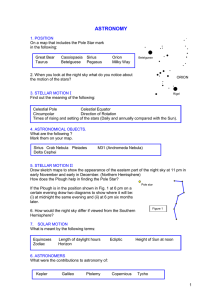
Astronomy work sheet
... If the Plough is in the position shown in Fig. 1 at 6 pm on a certain evening draw two diagrams to show where it will be: (i) at midnight the same evening and (ii) at 6 pm six months later. Figure 1 ...
... If the Plough is in the position shown in Fig. 1 at 6 pm on a certain evening draw two diagrams to show where it will be: (i) at midnight the same evening and (ii) at 6 pm six months later. Figure 1 ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... Calculate the travel time between two objects given their distance apart and the speed of travel, t=d/v, Using a proportion, calculate how big an object would be given the model size of another object. e.g. “If the Earth were the size of a softball (diameter = 8 cm, how big would the Milky Way g ...
... Calculate the travel time between two objects given their distance apart and the speed of travel, t=d/v, Using a proportion, calculate how big an object would be given the model size of another object. e.g. “If the Earth were the size of a softball (diameter = 8 cm, how big would the Milky Way g ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... – Argues that the earth is spherical based on the shape of its shadow on the moon during lunar eclipses ...
... – Argues that the earth is spherical based on the shape of its shadow on the moon during lunar eclipses ...
Name: Practice - 6.5 Newton`s Universal Law of Gravitation 1. Solar
... C. Something to Think About: If the force between the Sun and Earth is greater than the force between the Earth and the Moon, then why does the Moon have more influence on the ocean tides? ...
... C. Something to Think About: If the force between the Sun and Earth is greater than the force between the Earth and the Moon, then why does the Moon have more influence on the ocean tides? ...
Earth, Sun and Moon
... studied. From it we have learned a great deal about the physical processes which determine the structure and evolution of stars in general. ...
... studied. From it we have learned a great deal about the physical processes which determine the structure and evolution of stars in general. ...
Ancient Mathematics 450 B.C. 400 B.C. 350 B.C. 300 B.C. 250 B.C.
... Student of Plato who built philosophy based on observation, induction of general principles. Theory of causes determined motion and material of celestial objects. Aristarchus of Samos 310 B.C. – 230 B.C. Determined the distance from the earth to the moon and sun (correct method, incorrect results), ...
... Student of Plato who built philosophy based on observation, induction of general principles. Theory of causes determined motion and material of celestial objects. Aristarchus of Samos 310 B.C. – 230 B.C. Determined the distance from the earth to the moon and sun (correct method, incorrect results), ...
tire
... 8. A telescopes optical system that is continuously and automatically adjusted to compensate for the distortion caused by the Earth’s atmosphere. 9. A configuration of stars often named after an object, a person or an animal. 10. The blocking of all or part of the sunlight on the Moon by the Earth. ...
... 8. A telescopes optical system that is continuously and automatically adjusted to compensate for the distortion caused by the Earth’s atmosphere. 9. A configuration of stars often named after an object, a person or an animal. 10. The blocking of all or part of the sunlight on the Moon by the Earth. ...