Observing the Sky - University of Northern Iowa
... • The Moon does not rotate because we see only one side of it. • The dark side of the Moon always faces away from the Earth. • The Moon causes seasons. • The Moon is only visible at night. • Phases are caused by the Earth’s shadow. ...
... • The Moon does not rotate because we see only one side of it. • The dark side of the Moon always faces away from the Earth. • The Moon causes seasons. • The Moon is only visible at night. • Phases are caused by the Earth’s shadow. ...
ppt document - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... (1905 and following) predicted that different observers will measure different times, distances and masses based on the observers’ relative speeds. In particular, lifetimes and masses of particles differ if they are stationary compared to when they are moving. These effects are only noticeable as th ...
... (1905 and following) predicted that different observers will measure different times, distances and masses based on the observers’ relative speeds. In particular, lifetimes and masses of particles differ if they are stationary compared to when they are moving. These effects are only noticeable as th ...
Quiz # 1 - Oglethorpe University
... 10. If the Moon in its orbit around the Earth moves alternately between the Earth and the Sun and behind the Earth from the Sun, why do we not see solar and lunar eclipses every month? A) The Moon's motion in its orbit is so slow that it reaches eclipse position only once every six ...
... 10. If the Moon in its orbit around the Earth moves alternately between the Earth and the Sun and behind the Earth from the Sun, why do we not see solar and lunar eclipses every month? A) The Moon's motion in its orbit is so slow that it reaches eclipse position only once every six ...
Astronomical Beliefs - Communicating Astronomy With The Public
... the rain is washing and strengthening the moon. Dry spells are expected when the moon is strengthened –full moon. ...
... the rain is washing and strengthening the moon. Dry spells are expected when the moon is strengthened –full moon. ...
doc - UWM
... very hot gas where nuclear fusion can occur and which produces the light that make stars shine. A planet, on the other hand, gets its light reflected from its companion star. How can you tell the difference between a star and a planet in the sky? The stars in the sky appear to be in fixed positions ...
... very hot gas where nuclear fusion can occur and which produces the light that make stars shine. A planet, on the other hand, gets its light reflected from its companion star. How can you tell the difference between a star and a planet in the sky? The stars in the sky appear to be in fixed positions ...
Astronomy Objective 1 1. An asteroid is a small, rocky object that
... in a band between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. 2. An astronomical unit (AU) is the average distance between the Earth and the sun; approximately 150 million kilometers (93 million miles). 3. Astronomy is the scientific study of the universe. 4. The big bang theory is the theory that all matter an ...
... in a band between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. 2. An astronomical unit (AU) is the average distance between the Earth and the sun; approximately 150 million kilometers (93 million miles). 3. Astronomy is the scientific study of the universe. 4. The big bang theory is the theory that all matter an ...
1 astronomy: midterm review – part 2
... 4. Analog to the Earth’s North Pole projected on to the sky is known as ________________________ 5. Point directly overhead on the celestial sphere is called ____________________ 6. The angular unit of measure on the sky, equivalent to latitude on Earth is known as _________________ 7. The _________ ...
... 4. Analog to the Earth’s North Pole projected on to the sky is known as ________________________ 5. Point directly overhead on the celestial sphere is called ____________________ 6. The angular unit of measure on the sky, equivalent to latitude on Earth is known as _________________ 7. The _________ ...
Homework 1
... Assume you live on the moon near the center of the face that looks towards Earth. (a) Suppose you see a full earth in your sky. What phase of the Moon would people on Earth see? Explain. (b) Suppose people on Earth see a Full Moon. What phase would you see for Earth? (c) Suppose people on Earth see ...
... Assume you live on the moon near the center of the face that looks towards Earth. (a) Suppose you see a full earth in your sky. What phase of the Moon would people on Earth see? Explain. (b) Suppose people on Earth see a Full Moon. What phase would you see for Earth? (c) Suppose people on Earth see ...
Astronomy 212 EXAM 1 2000 September 29 Answer
... spins a bit faster on its axis. 17. According to Kepler’s third law, if planet A takes 10 years to orbit the Sun and planet B takes 20 years to orbit the Sun then planet B is twice as far from the Sun as planet A. 18. Newton’s second law states that the speed of an object is proportional to the forc ...
... spins a bit faster on its axis. 17. According to Kepler’s third law, if planet A takes 10 years to orbit the Sun and planet B takes 20 years to orbit the Sun then planet B is twice as far from the Sun as planet A. 18. Newton’s second law states that the speed of an object is proportional to the forc ...
Inverse Square Law - Hutto High School
... motion unless acted upon by an outside force • Also applied to objects traveling in a circular motion • So… His breakthrough was to explain how the same rules apply to little things like apples and big things like the moon. ...
... motion unless acted upon by an outside force • Also applied to objects traveling in a circular motion • So… His breakthrough was to explain how the same rules apply to little things like apples and big things like the moon. ...
Early Observers (The Beginnings of Astronomy)
... The ancient people had no history to learn from. Almost everything they knew about the universe came from what they could discover with their own eyes and minds. They thought that the universe was made up of the sun, moon, planets with all the stars somewhere towards the edge of the universe. ...
... The ancient people had no history to learn from. Almost everything they knew about the universe came from what they could discover with their own eyes and minds. They thought that the universe was made up of the sun, moon, planets with all the stars somewhere towards the edge of the universe. ...
Lecture 17 Newton on Gravity
... , by 2nd law of motion a1 F1 d2 = 12 , by Prop. 3. d2 We know one acceleration and both distances, so can calculate the other acceleration. (Continued on next slide.) ...
... , by 2nd law of motion a1 F1 d2 = 12 , by Prop. 3. d2 We know one acceleration and both distances, so can calculate the other acceleration. (Continued on next slide.) ...
Lecture 34 Newton on Gravity
... , by 2nd law of motion a1 F1 d2 = 12 , by Prop. 3. d2 We know one acceleration and both distances, so can calculate the other acceleration. (Continued on next slide.) ...
... , by 2nd law of motion a1 F1 d2 = 12 , by Prop. 3. d2 We know one acceleration and both distances, so can calculate the other acceleration. (Continued on next slide.) ...
Sun, Earth, Moon Foldable Sun Facts
... • We are going to modify it and add more info! • Take a legal size printer paper (8.5 x 14 in) – Cut off bottom 3 in – Fold in half “hot-dog” style, cut along crease – Give half to a friend, keep the other half – Cover bottom solar system half of foldable, tape it on, draw lines ...
... • We are going to modify it and add more info! • Take a legal size printer paper (8.5 x 14 in) – Cut off bottom 3 in – Fold in half “hot-dog” style, cut along crease – Give half to a friend, keep the other half – Cover bottom solar system half of foldable, tape it on, draw lines ...
BENCHMARK 4 STUDY GUIDE
... Tides are the result of the Moon’s gravitational attraction on the oceans on the Earth in addition to the gravitational pull on the Earth itself. Any location will experience two high tides and two low tides in a 24 hr period due to the Earth’s rotation on its axis and the positioning of the Moon. S ...
... Tides are the result of the Moon’s gravitational attraction on the oceans on the Earth in addition to the gravitational pull on the Earth itself. Any location will experience two high tides and two low tides in a 24 hr period due to the Earth’s rotation on its axis and the positioning of the Moon. S ...
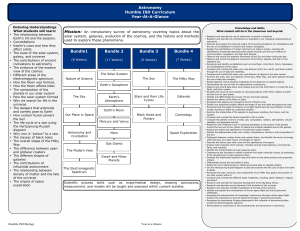
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... • Relate apparent versus absolute magnitude to the distances of celestial objects. • Demonstrate the use of units of measurement in astronomy. • Observe and record data about lunar phases and use that information to model the Sun, Earth, and Moon system. • Illustrate the cause of lunar phases by sho ...
... • Relate apparent versus absolute magnitude to the distances of celestial objects. • Demonstrate the use of units of measurement in astronomy. • Observe and record data about lunar phases and use that information to model the Sun, Earth, and Moon system. • Illustrate the cause of lunar phases by sho ...
Astronomy - Needham.K12.ma.us
... Tides are caused by gravity pulling on the Earth’s bodies of water and upon the Earth itself. There are 2 gravitational bodies that affect the tides: the sun and the moon. The moon is much closer to the Earth than the sun is, so it has a much greater influence upon the tides. Notice that wh ...
... Tides are caused by gravity pulling on the Earth’s bodies of water and upon the Earth itself. There are 2 gravitational bodies that affect the tides: the sun and the moon. The moon is much closer to the Earth than the sun is, so it has a much greater influence upon the tides. Notice that wh ...
Notes from Chapter 2
... Moon casts shadow on Earth: solar eclipse. Eclipses tutorial on masteringastronomy.com. ...
... Moon casts shadow on Earth: solar eclipse. Eclipses tutorial on masteringastronomy.com. ...
Earth Patterns, Cycles & Changes SOL 4.7
... Earth, Sun, & Moon Historical Contributions of this System a. ...
... Earth, Sun, & Moon Historical Contributions of this System a. ...
Diapositiva 1 - La Escuelona
... • There are eight large celestial bodies called planets. • Each planet rotates on its own invisible axis. • Each planet also orbits the Sun. • The planets can be classified into two ...
... • There are eight large celestial bodies called planets. • Each planet rotates on its own invisible axis. • Each planet also orbits the Sun. • The planets can be classified into two ...
Chapter 16: Our Solar System
... _____ 10. Which of the following planets is located one astronomical unit from the sun? a. Mercury b. Earth c. Mars d. Jupiter _____ 11. Which of the following terrestrial planets has retrograde rotation? a. Mercury b. Venus c. Earth d. Mars _____ 12. Which of the following planets in the outer sola ...
... _____ 10. Which of the following planets is located one astronomical unit from the sun? a. Mercury b. Earth c. Mars d. Jupiter _____ 11. Which of the following terrestrial planets has retrograde rotation? a. Mercury b. Venus c. Earth d. Mars _____ 12. Which of the following planets in the outer sola ...
Science Olympiad Invitational: Reach for the Stars
... 32. The planet with the greatest rotational speed is _______________________ 33. As the distance from the Sun increases, the orbital period of the planets _______________ 34. How many Earths would fit across the Jupiter’s equator? __________ 35. How many Earths would fit across the Sun’s equator? __ ...
... 32. The planet with the greatest rotational speed is _______________________ 33. As the distance from the Sun increases, the orbital period of the planets _______________ 34. How many Earths would fit across the Jupiter’s equator? __________ 35. How many Earths would fit across the Sun’s equator? __ ...
Terms - HULK SCIENCE
... A hunk of ice and gas that forms a long gassy tail as it orbits the sun Our sun, planets, moons asteroids, and comets A group of billions of stars held together by gravity The name our universe that we live in Everything The oval shape (like a flattened circle) of most orbits in space ...
... A hunk of ice and gas that forms a long gassy tail as it orbits the sun Our sun, planets, moons asteroids, and comets A group of billions of stars held together by gravity The name our universe that we live in Everything The oval shape (like a flattened circle) of most orbits in space ...
Lesson 4d Models of the Solar System
... Newton proposed that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that is proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects squared ...
... Newton proposed that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that is proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects squared ...