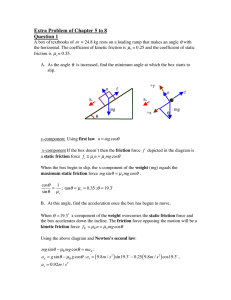
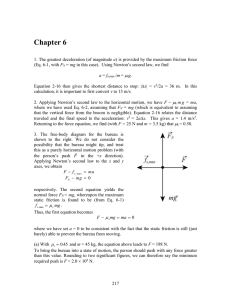
12.2 Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion 3. An automobile with a mass of 1200 kg accelerates at a rate of 3.0 m/s2 in the forward direction. What is the net force acting on the automobile? (Hint: Solve the acceleration formula for force.) Answer: a = F/m F = m/a = 1200 kg × 3.0 m/s2 = 3600 N ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion 3. An automobile with a mass of 1200 kg accelerates at a rate of 3.0 m/s2 in the forward direction. What is the net force acting on the automobile? (Hint: Solve the acceleration formula for force.) Answer: a = F/m F = m/a = 1200 kg × 3.0 m/s2 = 3600 N ...
Work/Energy Review KEY
... 21.A student performs the spring lab in class. She measures the distance from the floor to the bottom of the unloaded spring to be 60 cm. She hangs the 1 kg mass on the spring and allows it to come to a rest. The bottom of the spring is now 23.5 cm above the floor. (This is the time to determine th ...
... 21.A student performs the spring lab in class. She measures the distance from the floor to the bottom of the unloaded spring to be 60 cm. She hangs the 1 kg mass on the spring and allows it to come to a rest. The bottom of the spring is now 23.5 cm above the floor. (This is the time to determine th ...
Chapter 7: Conservation of Mechanical Energy in Spring Problems
... The previous example involved essentially just one particle, the car. The wall was fixed there as a device for exerting a constant force during the collision. A more complex example can be studied when two particles collide. We first make the approximation that the two particles are subjected to no ...
... The previous example involved essentially just one particle, the car. The wall was fixed there as a device for exerting a constant force during the collision. A more complex example can be studied when two particles collide. We first make the approximation that the two particles are subjected to no ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum
... Also applied to two (or more) masses blown apart by an explosion. ...
... Also applied to two (or more) masses blown apart by an explosion. ...
Chap8
... Center of Mass and Stability An object is said to be stable if an external force is required to tip it. The object is stable as long as the direction of the torque due to its weight, τw tends to keep it upright. This occurs as long as the object’s center of mass lies above its base. To tip the objec ...
... Center of Mass and Stability An object is said to be stable if an external force is required to tip it. The object is stable as long as the direction of the torque due to its weight, τw tends to keep it upright. This occurs as long as the object’s center of mass lies above its base. To tip the objec ...
Student Workbook
... 7. An electron has a mass of 9.11 x 10 -31kg. A certain elephant weighs 6600-Lbs. If this elephant walked with a speed of 2.1 m/s would it be possible for the electron to have the same kinetic energy? Support your answer. HINT: the speed of light is 6.706 x 108 mph and there are 1609 meters in a mil ...
... 7. An electron has a mass of 9.11 x 10 -31kg. A certain elephant weighs 6600-Lbs. If this elephant walked with a speed of 2.1 m/s would it be possible for the electron to have the same kinetic energy? Support your answer. HINT: the speed of light is 6.706 x 108 mph and there are 1609 meters in a mil ...
Chapter 8
... determined by the posi:on vector and the force – If the turning tendency of the force is counterclockwise, the torque will be posi:ve – If the turning tendency is clockwise, the torque will be nega:ve ...
... determined by the posi:on vector and the force – If the turning tendency of the force is counterclockwise, the torque will be posi:ve – If the turning tendency is clockwise, the torque will be nega:ve ...
Performance Benchmark E
... a force. And lastly, his Third Law describes what happens when objects interacting. Newton’s Third Law states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. This law is also known as the Law of Action-Reaction Pair. A force is a push or pull upon an object, which results ...
... a force. And lastly, his Third Law describes what happens when objects interacting. Newton’s Third Law states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. This law is also known as the Law of Action-Reaction Pair. A force is a push or pull upon an object, which results ...
physics revision cards
... F = ma means that there is also a Force acting towards the centre. This is centripetal force. ...
... F = ma means that there is also a Force acting towards the centre. This is centripetal force. ...
Lectures 17 and 18
... In many cases, one force acting on a particle will be much greater than any other force acting on the particle When using the Impulse Approximation, we will assume this is true The force will be called the impulse force pi and pf represent the momenta (momentums) immediately before and after the col ...
... In many cases, one force acting on a particle will be much greater than any other force acting on the particle When using the Impulse Approximation, we will assume this is true The force will be called the impulse force pi and pf represent the momenta (momentums) immediately before and after the col ...
Chapter 15 - KFUPM Faculty List
... displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is ...
... displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is ...